
Aftermath Of COVID-19 in Seafood Traceability
Disruption in fish production, new regulations, and increasing consumer demand for safe products has made the seafood supply chain traceability the new norm with blockchain solutions.

Have you ever stopped to wonder what’s really in your food? While we trust the labels and expect a safe, healthy product, the reality can be a bit murkier. Food adulteration, the deceptive addition of inferior or harmful substances to food products, is a widespread concern. Let us delve into the murky world of food adulteration, exploring its different forms, the health risks it poses, and what we can do as consumers to protect ourselves and fight for a transparent, safe food system.
Ever wondered if what you’re eating is truly what it seems? Unfortunately, food adulteration – the act of adding inferior or harmful substances to food products – is a global concern. This deceptive practice not only cheats consumers but can also pose serious health risks. Let’s delve deeper into the different types of adulteration and the common adulterants we should be aware of:
This occurs when the quality or composition of raw ingredients like fruits, vegetables, grains, or spices is compromised. Some common examples include:
Here, adulteration happens during the processing or manufacturing stage of food products. Examples include:
Here are some of the commonly used adulterants to be aware of:
By understanding these different types of adulteration and common adulterants, we can become more vigilant consumers. Look out for suspicious pricing, misleading labels, and unfamiliar ingredients. Choose reputable brands known for their commitment to quality and transparency. Let’s work together to ensure a safe and healthy food system for everyone.
Food adulteration, the deceptive practice of adding inferior or harmful substances to food, thrives in a complex ecosystem fueled by various factors. Understanding these underlying causes is crucial to combatting this issue and ensuring a safe and ethical food system.
Economic Factors:
Lack of Regulation and Enforcement:
Unethical Practices in the Food Industry:
Technological Advancements (Double-Edged Sword):
By acknowledging these various causes, we can work towards a multi-pronged approach to tackling food adulteration. Strengthening regulations, improving enforcement, promoting ethical practices within the industry, and leveraging technology for both detection and prevention are all crucial steps in ensuring a safer and more transparent food system for consumers worldwide.
Food adulteration, the deceptive act of adding inferior or harmful substances to food products, isn’t just a matter of misleading labels. It carries a series of far-reaching consequences that impact consumers, the economy, and the environment.
Food Safety:
The most immediate and concerning impact of food adulteration is on food safety. Common adulterants can lead to a range of health problems, including:
Economic Implications:
Food adulteration also has a significant economic impact on various stakeholders:
Loss of Consumer Trust in the Food Industry:
When consumers discover instances of food adulteration, it erodes their trust in the entire food system. This can lead to:
Environmental Impacts:
The environmental impact of food adulteration, while often overlooked, is also a concern:
Discover the Hidden Impact on Food Miles and Carbon Footprint to Learn How Your Food Choices Can Make a Difference!
The consequences of food adulteration are far-reaching and complex. By understanding these impacts, we can highlight the importance of robust food safety regulations, ethical practices within the industry, and consumer awareness.
Food adulteration, the deceptive practice of adding inferior or harmful substances to food, poses a significant threat to consumer health and trust in the food system. Thankfully, a range of methods exist to detect and prevent this issue. Let’s explore these detection tools and the role regulatory bodies play in ensuring food safety.
While not foolproof, these time-tested methods remain valuable tools for initial screening:
Modern science offers a more sophisticated arsenal for detecting adulteration:
Government agencies play a crucial role in establishing and enforcing food safety regulations. Here’s how they contribute to the fight against food adulteration:
These detection methods and regulatory actions work in tandem to safeguard the food chain. However, it’s an ongoing battle as new adulteration techniques emerge. Continuous improvement of testing methods, collaboration between regulatory bodies and scientific communities, and public awareness about food safety are all vital in creating a safer food system for the future.
Food adulteration, the deceptive act of adding inferior or harmful substances to food, thrives in the shadows of opaque supply chains. But a powerful weapon exists in the fight for a safer food system: traceability solutions.
Traditional food supply chains can be complex and lengthy, with ingredients traveling long distances and passing through multiple hands before reaching consumers. This lack of transparency creates opportunities for adulteration to occur at any point along the way.
Traceability solutions leverage technology to track the journey of food products from farm to fork. This can involve:
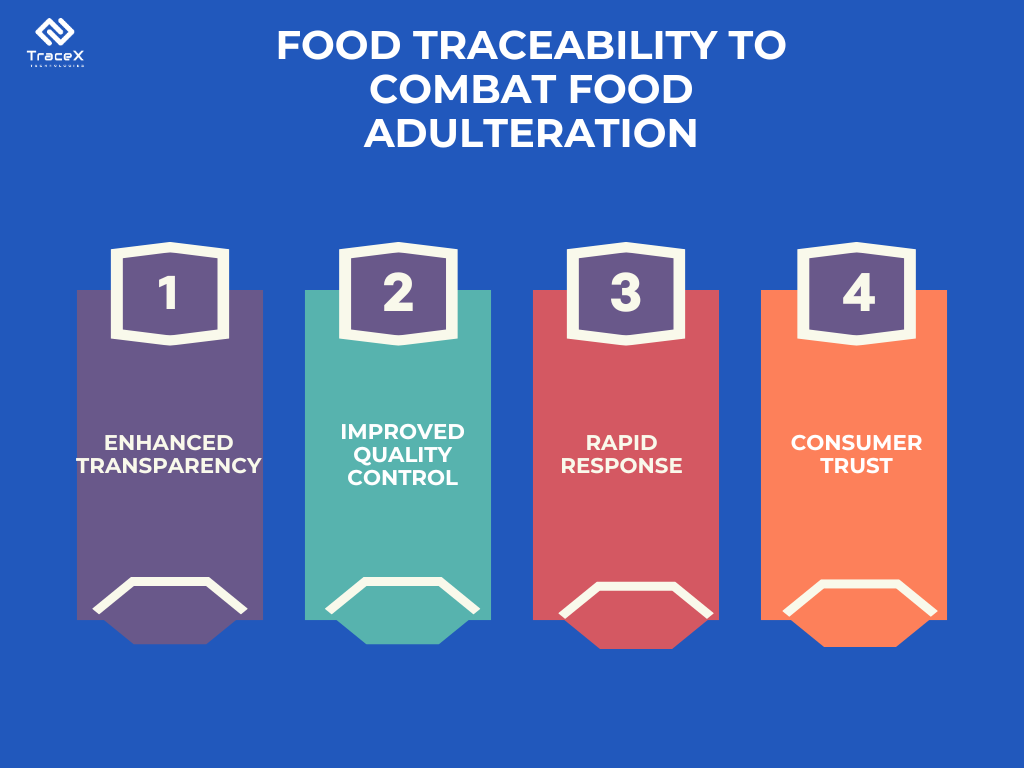
Traceability solutions offer several advantages in the fight against food adulteration:
Traceability solutions are not a silver bullet, but they are a powerful tool in the fight against food adulteration. By embracing traceability solutions and fostering a culture of transparency, we can work towards a safer, more ethical, and trustworthy food system for all.
Adulteration poses a significant threat to the integrity of the milk supply chain, impacting both consumer health and the dairy industry’s reputation. Common adulterants such as water, urea, and detergent not only dilute the nutritional value of milk but also introduce harmful substances that can lead to serious health issues. To combat this challenge, TraceX blockchain solutions have emerged as a game-changer in ensuring transparency and accountability throughout the milk supply chain.
Adulteration poses a significant threat to the integrity of the seed supply chain, impacting agricultural productivity and farmer livelihoods. Adulterated seeds, often mixed with lower-quality or inert materials, result in reduced crop yields, poor plant health, and increased susceptibility to diseases and pests. This not only undermines farmers’ efforts to maximize their yields but also jeopardizes food security and agricultural sustainability. To address this challenge, TraceX blockchain solutions enables seamless tracking and tracing of seeds from production to distribution, providing stakeholders with real-time access to critical information about seed origin, quality, and handling practices.
Explore How Telangana Overcame the Spurious Seed Menace with TraceX’s Blockchain Solution! Learn More About Our Pioneering Pilot Project and Its Impact on Agricultural Sustainability.
Adulteration in the fruit and vegetable supply chain poses serious risks to consumer health, market integrity, and agricultural sustainability. In many instances, fruits and vegetables are adulterated with harmful chemicals, pesticides, or additives to enhance appearance, extend shelf life, or increase weight, compromising their safety and nutritional value. Such adulteration not only undermines consumer confidence but also erodes trust in the entire supply chain, leading to market inefficiencies and economic losses for farmers and traders. To combat this issue, TraceX enables seamless tracking and tracing of fruits and vegetables from farm to fork, allowing stakeholders to verify the authenticity and quality of produce at every stage of the supply chain.
Adulteration presents significant challenges in the spice supply chain, where spices are susceptible to contamination, dilution, and substitution with inferior or harmful substances. Common adulterants such as artificial colors, fillers, and undeclared ingredients compromise the quality, authenticity, and safety of spices, posing health risks to consumers and eroding trust in the supply chain. In response to these concerns, TraceX blockchain solutions have emerged as a crucial tool to combat adulteration in the spice industry.
Food adulteration is a global concern, impacting food safety and consumer trust. Fortunately, national and international efforts are underway to combat this issue. Let’s delve into recent regulatory developments and the crucial role of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States.
Global Efforts:
Food adulteration is a global concern, impacting food safety and consumer trust. Fortunately, national and international efforts are underway to combat this issue. Let’s delve into recent regulatory developments and the crucial role of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States.
The FDA is the primary federal agency responsible for ensuring the safety, wholesomeness, and proper labeling of food in the United States. Here’s how they play a critical role in combating food adulteration:
Food adulteration remains a significant worry throughout India, with occasional reports of individuals falling ill due to consuming contaminated foods. To address this issue, the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has introduced recent initiatives aimed at identifying and managing instances of food adulteration. As per an ANI report, the regulatory body is reaffirming its dedication to preserving the integrity of the food supply chain, thereby enhancing public health protection.
Combating food adulteration requires a multi-pronged approach. Continuous improvement of regulations, international collaboration, investment in advanced technologies, and public awareness are all key. In conclusion, food adulteration is a complex issue with far-reaching consequences. However, by understanding the different forms of adulteration, the factors that contribute to it, and the measures being taken to combat it, we can become more empowered consumers. TraceX blockchain technology offers a glimmer of hope in this fight. By providing transparent and immutable records of a food product’s journey, TraceX empowers consumers to make informed choices and hold businesses accountable. Let’s embrace innovation and transparency.

Disruption in fish production, new regulations, and increasing consumer demand for safe products has made the seafood supply chain traceability the new norm with blockchain solutions.
The problems faced by Seafood industry, one of the world’s first and largest commercial enterprises in the food industry are overfishing, illegal, unreported, unregulated (IUU) fishing, and bycatch. Emerging solutions in blockchain-based food traceability address these practices.

Learn about the critical role of traceability in ensuring food safety. Explore the significance of traceability systems like TraceX in tracking food products from farm to table, identifying hazards, and mitigating risks.
Leverage Blockchain enabled traceability platform for enhanced supply chain visibility
We use cookies on our website to give you the most relevant experience by remembering your preferences and repeat visits. By clicking “Accept All”, you consent to the use of ALL the cookies. However, you may visit "Cookie Settings" to provide a controlled consent.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
WhatsApp us