Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Discover the five key factors influencing food supply chain management, including demand forecasting, regulatory compliance, technological advancements, sustainability practices, and global trade dynamics. Understand how these elements shape efficiency and safety in food distribution.

In today’s fast-paced food industry, managing a food supply chain is far more complex than ever before. From the farm to the table, each step comes with its own set of challenges, making effective food supply chain management crucial to success. Have you ever wondered why some food companies face constant delays, while others seem to navigate disruptions smoothly?
A major issue is with 69% of businesses not having full visibility into their supply chains. Enhancing this visibility continues to be a key strategic focus.
Lack of visibility and control! Without real-time insights into what’s happening at each stage of the supply chain, companies risk delays, spoilage, and even non-compliance with regulations. The stakes are high, especially when safety, sustainability, and consumer trust are on the line. In this guide, we’ll dive into the five key factors that play a vital role in food supply chain management and explore how mastering them can give your business a competitive edge.
Key Takeaways
The Council of Logistics Management defines Supply Chain Management as, “the process of planning, implementing and controlling the efficient and cost-effective flow of materials, in-process inventory, finished goods and related information from point-of-order to point-of-consumption, for the purpose of conforming to customer requirements”.
Food supply chain management (FSCM) refers to, managing all activities in the food supply chain, extending from raw material sourcing to the product reaching the hands of the customer. Tracing the products from the origin and tracking every stage of the food supply chain guarantees the best quality of the product. Implementing food supply chain management can reduce food safety incidents, target food recalls, eliminate food fraud and establish trust among consumers.
57% of companies have poor visibility across their supply chains
Food Supply Chain Management (FSCM) is the intricate process that oversees the movement of food products from their origin (farm, fishery, or manufacturing plant) to the final consumer. It encompasses a broad spectrum of activities, including:
Identifying potential disruptions: By understanding the factors that can impact the supply chain, businesses can anticipate and prepare for challenges such as natural disasters, economic downturns, or regulatory changes.
Building resilience: Developing contingency plans and alternative sourcing options to minimize the impact of disruptions.
Informed business strategies: Understanding the interplay between different factors allows for the development of effective strategies to optimize the supply chain.
Resource allocation: Prioritizing investments in areas that have the greatest impact on supply chain performance.
Competitive advantage: Identifying opportunities to differentiate through supply chain practices.
Identifying bottlenecks: Pinpointing areas of the supply chain that are causing inefficiencies or delays.
Benchmarking: Comparing performance against industry standards and competitors.
Continuous improvement: Implementing strategies to enhance supply chain efficiency and effectiveness.
Adhering to regulations: Understanding the regulatory landscape and ensuring compliance with food safety, labor, and environmental standards.
Promoting sustainability: Identifying opportunities to incorporate sustainable practices into the supply chain.
Managing stakeholder expectations: Meeting the demands of consumers, suppliers, and other stakeholders.
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of these influencing factors, businesses can build more robust, efficient, and sustainable food supply chains.
Supply chain management is crucial in food and agri value chains because it ensures the efficient movement of goods from farm to fork, directly impacting food safety, quality, and availability. Effective management helps reduce waste, optimize inventory levels, and maintain product freshness. It also enhances transparency and traceability, which are essential for meeting regulatory requirements and consumer demands for sustainably sourced products.
Any happening which alters or forces to alter supply chain management is termed as an uncertainty. Environmental uncertainties are those unpredictable events outside the organization which have an impact on performance in the supply chain.
Environmental uncertainty can pose significant challenges for the food supply chain management on account of factors like weather extremities, natural disasters and climate change, all of which result impacts food production and results in food insecurity, biodiversity loss and low quality yields.
Organizations are addressing the sources of uncertainty by formulating management strategies on how to tackle environmental changes and improve the performance of the supply chain. Sourcing from multiple suppliers can reduce reliance on a single supplier and mitigate risks of environmental disruptions. Companies can develop contingency plans to face crop failures and transport disruptions.
With global markets in place, data is entered at each stage of the supply chain. Decision takers have an abundance of data at their disposal. It is necessary to optimally utilize such data to have proper inventory management.
Inventory management plays acritical role in food supply chain management as it ensures that right products are available at the right time in right quantities. Effective inventory management ensures that food is not wasted and helps to improve sustainability of supply chains. Tracking inventory levels in real-time improves supply chain visibility and inventory can be better managed across the supply chain, thereby ensuring better response to disruptions.
Electronic data capture aids in traceability in the food supply chain. The real-time data capture of the food product from source to consumption helps to identify issues that may arise due to food contamination and adulteration. It also helps in the event of food recalls with faster response times. The digital capture of data eliminates manual labour and saves time and costs and provides accuracy. Data driven insights help in making informed decisions thereby improving the supply chain efficiency and performance. Electronic data is easily shareable thereby helping collaboration between stakeholders in the supply chain.
Collaboration among supply chain stakeholders is crucial for food supply chain management. They must work together to identify common goals and develop strategies to achieve them. A collaborative system will build transparency and cater to innovation and growth. It is said that the most important person in the supply chain is the supplier; through whom innovation and development take place. It is not only the relationships between the stakeholders but also managing people inside the organization that is important.
These partnerships would help in optimizing a supply chain, developing transparency and trust, better planning, forecasting, and replenishment of products. Effective food supply chain management requires a shared responsibility among all stakeholders and each one should take the responsibility for their role in the supply chain as well as their impact on
With continuous supply chain disruptions exposing the vulnerability of these supply chains, businesses need to rethink how to engage and collaborate with the other stakeholders. Sustainability and Technology will play a big role in building transparent and resilient supply chains. The data driven approach should foster better decision making across the value chains.
Sustainability requires collaboration with the involvement of all stakeholders right from production, manufacturing, distribution in ways that reduce carbon footprints, reduce waste and ensure social equity.
There have been a lot of technological advancements in the field of SCM ranging from the software which manages quality control to managing cash flow, inventory, security, and distribution.
It is sad that 63% of companies do not use technology to monitor their supply chain performance.
McKinsey emphasises the importance of digital transformation in food supply chain management. It suggests that companies should invest in building digital capabilities and partner with technology providers to enhance supply chain management practices.
As the volume and cross-border trades increase, Blockchain technology
has popularized its ability to smooth functioning along with providing traceability and security over the supply chain. Blockchain is a digital ledger that records data in a decentralized manner that is programmable, secure, unanimous, immutable and time stamped. It provides end-to-end transparency and builds a resilient supply chain.
All transactions are recorded and shared among the stakeholders in the supply chain. Since the transactions are time-stamped, and the data is immutable, a digital identity of the product is created. This gives credibility to the product. The farm to fork journey of the product can be viewed by the consumer through a QR code.
Given such visibility and disclosure, consumer trust and brand recognition materialize. There is a realization of a secure, safe and transparent supply chain.
Food safety is a top priority, with strict regulations to ensure products are safe for consumption. Contamination during production, improper storage, or packaging can jeopardize food safety. Ensuring that all suppliers and distributors comply with safety protocols can be difficult, especially when multiple parties are involved.
Implementing strict quality control measures, real-time monitoring systems, and blockchain for traceability can help ensure food safety across the supply chain.
Many food products are sourced globally, which introduces challenges like longer supply chains, international regulations, and cultural differences. Managing these logistics and ensuring compliance with various standards can be difficult.
Technology solutions like blockchain and satellite monitoring can provide visibility across borders, ensuring compliance with local regulations and maintaining quality.
Fluctuations in demand due to seasonal changes, consumer preferences, or unexpected events like pandemics and supply chain disruptions (e.g., natural disasters, strikes, etc.) can create delays or shortages.
Building resilience by diversifying suppliers, using AI for demand forecasting, and having contingency plans in place to adapt to sudden changes.
Striking the right balance in inventory management is crucial. Overstocking leads to waste due to perishability, while understocking can result in lost sales and stockouts.
Use data analytics and demand forecasting to predict demand accurately, optimize stock levels, and reduce food waste.
Consumers and regulators increasingly demand sustainable practices, including reducing the carbon footprint, waste, and environmental impact of food production and transportation.
Partnering with sustainable suppliers, using eco-friendly transportation, and adopting technologies that monitor and reduce environmental impact can help meet sustainability goals.
Traceability is the ability to track a food product through all stages of production, processing, and distribution. It has emerged as a cornerstone of modern food supply chain management, driven by increasing consumer demand for transparency, safety, and sustainability.
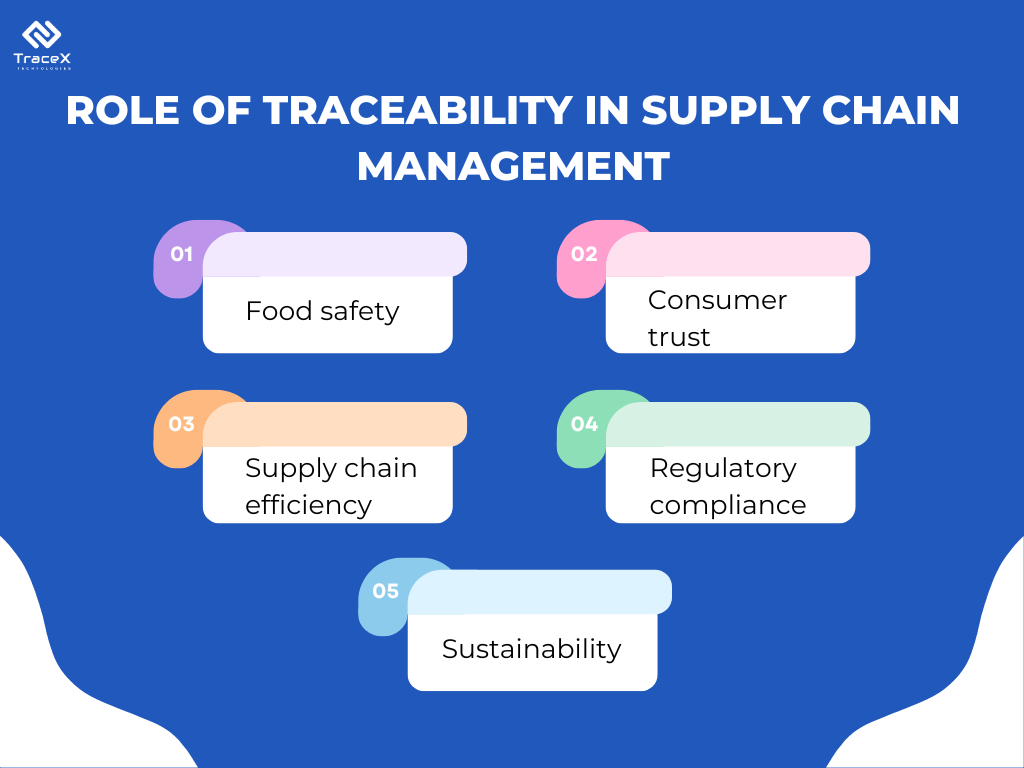
Advancements in technology, particularly blockchain, have revolutionized traceability: Blockchain offers a secure, transparent, and immutable record of product history. IoT enables real-time tracking of products through the supply chain. Data analytics provides insights into supply chain performance and identifies potential risks. By leveraging these technologies, businesses can create a robust traceability system that enhances consumer trust, mitigates risks, and supports sustainable practices.
The TraceX food traceability platform is a cutting-edge solution designed to help agribusinesses track their entire supply chain, from farm to fork, using blockchain technology. It provides end-to-end visibility, ensuring every step in the process is recorded on an immutable ledger, increasing transparency, authenticity, and accountability.
TraceX is empowering agribusinesses globally to transform their operations with reliable, transparent, and secure traceability solutions. By embracing this platform, companies not only improve their efficiency but also build a brand that resonates with today’s sustainability-focused consumers.
TraceX , in partnership with TechnoServe, is revolutionizing the coffee supply chain in the Araku Valley. By implementing end-to-end digital traceability, this initiative empowers 3500 farmers to enhance transparency, streamline data management, and uphold ethical and sustainable practices.
Traceability is pivotal in modern food supply chains, ensuring food safety, consumer trust, and operational efficiency. In the context of the Araku Valley coffee farmers, traceability. Enables rapid identification of contamination sources, safeguarding consumer health. It provides transparency about coffee origin, cultivation practices, and ethical standards. The platform streamlines supply chain processes, reduces waste, and improves efficiency. It allows to verify adherence to environmental and social standards, supporting sustainable practices. This enables compliance with regulations like EUDR and other relevant standards.
By leveraging technology and collaboration, TraceX and TechnoServe are demonstrating the transformative power of traceability in driving positive change for coffee farmers and consumers alike.
Food Supply chain management satisfies the consumer demands on food safety and sustainability. It has to also address the socio-economic and environmental benefits too. Along with the five factors charted, it is a compilation of various aspects that affect the supply chain and the decisions that bring about the rise or fall of an organization. Traceability is an integral part of the food supply chain systems. Technology disruptions with blockchain have empowered traceability systems to counter not only food safety issues but address the sustainability and authenticity of claims of a product.
The main factors include demand forecasting, regulatory compliance, technological advancements, sustainable agriculture practices, and global trade dynamics. Each of these elements plays a crucial role in shaping the efficiency, safety, and reliability of food distribution systems.
Technology enhances food supply chain management by improving transparency, traceability, and efficiency. Tools such as blockchain, IoT sensors, and AI for demand forecasting enable better decision-making, reduce waste, and ensure compliance with safety standards.
Sustainability is vital in food supply chains because consumers are increasingly concerned about environmental impacts. Implementing sustainable practices helps reduce carbon footprints, minimizes waste, and meets regulatory requirements, all of which are essential for long-term viability in the market.
