Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Explore the transformative potential of blockchain technology in revolutionizing food supply chains. Discover how blockchain enhances transparency, traceability, and trustworthiness throughout the entire food production and distribution process

Embark on a journey of innovation as we delve into the transformative potential of blockchain technology in revolutionizing food supply chains. In an era marked by increasing demands for transparency, traceability, and sustainability, blockchain emerges as a powerful tool capable of reshaping the way we produce, distribute, and consume food.
According to Markets & Markets, the global blockchain in agriculture and food supply chain market is estimated at USD 133 million in 2020 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 48.1% to reach USD 948 million by 2025.
Join us as we explore the myriad applications of blockchain in enhancing food safety, optimizing logistics, and fostering trust between consumers and producers. Discover how this groundbreaking technology is poised to disrupt traditional supply chain practices and pave the way for a more resilient, efficient, and ethical food system.
Food supply chains play a crucial role in ensuring the efficient and timely delivery of food products from farm to table. These intricate networks encompass various stages, including production, processing, distribution, and retailing. From small-scale local farms to multinational corporations, each entity in the supply chain contributes to the overall flow of food products. With increasing consumer demands for transparency, sustainability, and food safety, supply chain management has become more complex than ever before. Technologies like blockchain are now being leveraged to enhance traceability, improve efficiency, and build trust among consumers. As the global population continues to grow and environmental challenges mount, the resilience and effectiveness of food supply chains are paramount in ensuring food security for all.
Blockchain technology operates by integrating sophisticated computational and cryptographic techniques within a decentralized data structure, facilitating the establishment of a digital trust system within an untrusted environment. At the core of blockchain lies the hash function, which generates unique identifiers using algorithmic methods for data authentication. To safeguard data integrity, the stored chain format incorporates inserted hash values, enabling verification for any modifications to the data. In transactions stored within the blockchain, data senders and receivers utilize digital signatures to validate their identities. Furthermore, the consensus mechanism involves all computer nodes, effectively mitigating the risks of data manipulation by minority attackers.

Blockchain technology offers transformative solutions to the challenges facing food supply chains, empowering stakeholders to create safer, more transparent, and sustainable food systems. By leveraging blockchain’s capabilities, the food industry can enhance efficiency, ensure quality, and build trust with consumers, ultimately improving the overall integrity of the global food supply chain.
Discover the Future of Food Supply Chains!
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing the way we track, trace, and ensure the safety of our food.
Blockchain enables real-time visibility into every stage of the food supply chain, from farm to fork. Each transaction, such as the movement of raw materials, processing, packaging, and distribution, is recorded in a secure and immutable digital ledger. This transparency allows all participants to track the journey of food products, ensuring accountability and reducing the risk of fraud or contamination.
With blockchain, the provenance of food products can be traced back to their source with unprecedented accuracy. Each item is assigned a unique identifier, such as a QR code or RFID tag, which is recorded on the blockchain along with relevant information such as origin, production methods, and handling procedures. In the event of a food safety issue or recall, stakeholders can quickly identify affected products and take targeted action to mitigate risks.
Unlock the Secrets of Effective Traceability!
Uncover the best practices for implementing traceability solutions in your business.
Blockchain facilitates the monitoring and verification of food quality and safety standards throughout the supply chain. Smart contracts embedded in the blockchain can automate compliance checks, ensuring that products meet regulatory requirements and industry standards. This proactive approach to quality assurance helps prevent the distribution of contaminated or counterfeit goods, safeguarding consumer health and brand reputation.
By streamlining record-keeping processes and reducing manual paperwork, blockchain enhances operational efficiency and reduces administrative costs in food supply chains. Smart contracts enable automated workflows, such as payment processing and contract fulfillment, leading to faster transactions and fewer errors. Additionally, the elimination of intermediaries and redundant data silos can result in significant cost savings for businesses.
Blockchain technology facilitates the monitoring and verification of sustainable sourcing practices throughout the food supply chain. By recording data such as origin, production methods, and environmental impact, blockchain enables stakeholders to ensure compliance with sustainability standards and certifications. This transparency promotes responsible sourcing practices, reduces environmental degradation, and supports the transition towards more sustainable agricultural practices.
Blockchain instills confidence and trust among consumers by providing transparent and verifiable information about the products they consume. By scanning a QR code or accessing a blockchain-enabled platform, consumers can access detailed data about the origin, production methods, and sustainability credentials of food products. This increased transparency builds trust and loyalty, driving demand for ethically sourced and responsibly produced food.
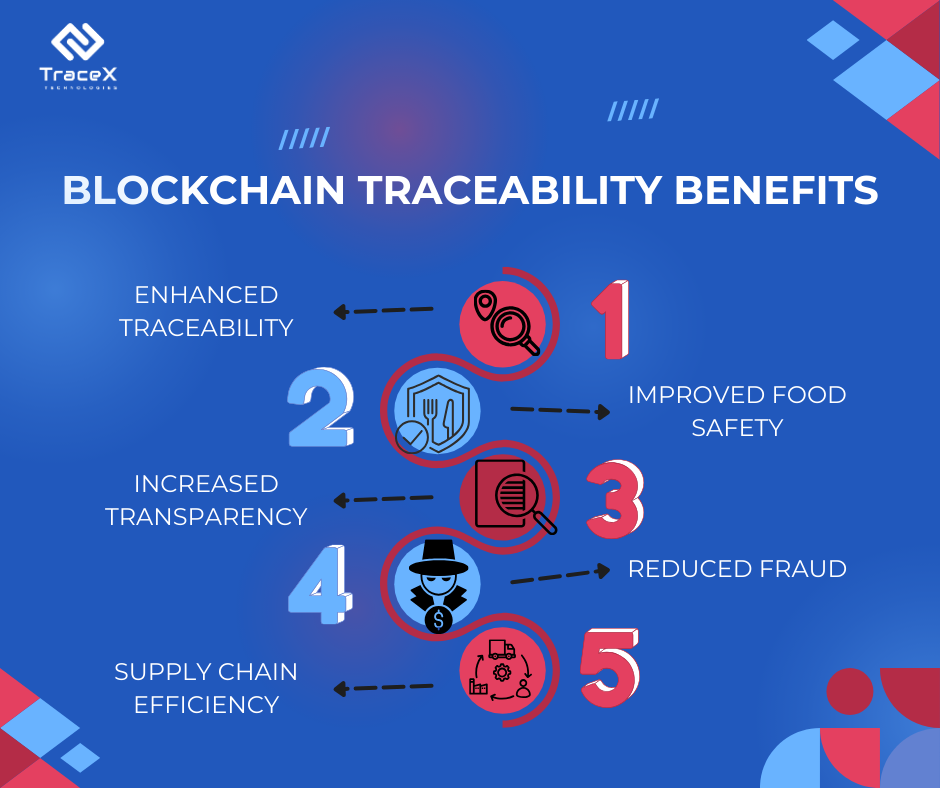
TraceX blockchain-powered traceability solutions empower stakeholders in the food and agriculture sector to create safer, more transparent, and sustainable food systems. By leveraging blockchain technology, TraceX addresses the challenges in the food supply chain, enhances transparency, traceability, and accountability, ultimately improving the integrity and sustainability of the global food supply chain.
TraceX leverages blockchain technology to provide real-time visibility and traceability throughout the food supply chain. By recording every transaction and movement on an immutable digital ledger, TraceX enables stakeholders to track the journey of food products from farm to fork. This transparency enhances accountability, reduces the risk of fraud or contamination, and improves overall supply chain integrity.
With TraceX, the provenance of food products can be accurately traced back to their source, enabling rapid identification of safety issues or recalls. By providing a transparent record of production methods, handling procedures, and quality assurance measures, TraceX enhances food safety standards and mitigates risks associated with contamination or adulteration.
TraceX facilitates the monitoring and verification of sustainable sourcing practices throughout the food supply chain. By recording data such as origin, production methods, and environmental impact, TraceX enables stakeholders to ensure compliance with sustainability standards and certifications. This transparency promotes responsible sourcing practices, reduces environmental degradation, and supports the transition towards more sustainable agricultural practices.
TraceX streamlines supply chain processes by automating record-keeping, reducing paperwork, and eliminating manual errors. Smart contracts embedded in the blockchain enable automated workflows for tasks such as payment processing, contract fulfillment, and compliance checks, leading to greater efficiency and cost savings for businesses.
TraceX instills confidence and trust among consumers by providing access to transparent and verifiable information about the products they consume. By scanning a QR code or accessing a blockchain-enabled platform, consumers can access detailed data about the origin, production methods, and sustainability credentials of food products. This increased transparency builds trust, enhances brand reputation, and drives demand for ethically sourced and sustainably produced food.
In conclusion, the integration of blockchain technology into food supply chains holds immense potential to revolutionize the way we produce, distribute, and consume food. By providing transparent and immutable records of transactions, blockchain ensures food safety, traceability, and authenticity. This not only enhances consumer trust but also promotes sustainability and ethical practices throughout the supply chain. As we continue to harness the power of blockchain technology, we pave the way for a future where food supply chains are more resilient, transparent, and equitable for all stakeholders involved.
If you are looking to improve the efficiency of your food supply chain, then check out how Blockchain traceability solution, TraceX, can help.
