Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu

Picture a future where every item on the market has a proven track record of protecting our forests and preserving biodiversity. The European Union Deforestation-Free Regulation (EUDR) is not just another compliance requirement—it’s a bold step towards ensuring sustainable and ethical global supply chains. The EUDR mandates that businesses operating within the EU market must demonstrate that their supply chains are free from deforestation and land degradation. By targeting key commodities such as palm oil, soy, coffee, cocoa, rubber, and beef, the regulation aims to curb the destruction of the world’s vital ecosystems.
The EU Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) came into force on the 29th of June 2023 and on the 30th of December 2025 businesses will have to comply with all the requirements of the regulation.
For many businesses, adapting to these rigorous standards can seem overwhelming. Whether you’re a procurement head scrambling to ensure your supply chains meet new sourcing standards, a sustainability leader navigating complex compliance requirements, or a compliance officer facing the pressure of hefty fines, the EUDR presents a significant challenge.
That’s why we’ve created this comprehensive guide to help you navigate the EUDR landscape. From assessing your supply chain risks to implementing traceability technologies, this blog offers actionable insights and practical steps to ensure your business stays compliant and future-proof. Dive in and take the first step towards building a sustainable, deforestation-free supply chain!
Forests act as carbon sinks, absorbing and storing carbon dioxide, a major greenhouse gas. Their destruction contributes to global warming. Furthermore, forests are vital habitats for diverse species. Deforestation disrupts ecosystems, leading to species extinction. Protecting forests is integral to both climate action and the conservation of Earth’s biodiversity.
Deforestation contributes to around 10-15% of global greenhouse gas emissions, making it one of the largest sources of carbon emissions.
Deforestation refers to the deliberate and extensive removal of forests and trees from a specific area, often for agricultural, industrial, or urban development purposes. This practice has severe environmental consequences. It contributes to climate change by releasing stored carbon dioxide, disrupts ecosystems, causes habitat loss and fragmentation, endangers biodiversity, and can lead to soil erosion and altered water cycles. Deforestation is a major driver of global environmental degradation and poses significant threats to the planet’s health.
The EU’s new deforestation legislation is part of a broader initiative aimed at tackling the environmental and social consequences of global supply chains. Its primary objective is to prevent European companies from importing goods associated with unlawful deforestation and forest decline.
This regulation targets seven commodities: soy, beef, palm oil, wood, cocoa, coffee, and rubber. Several products made from these commodities are also targeted, including leather, chocolate, tires, and furniture.
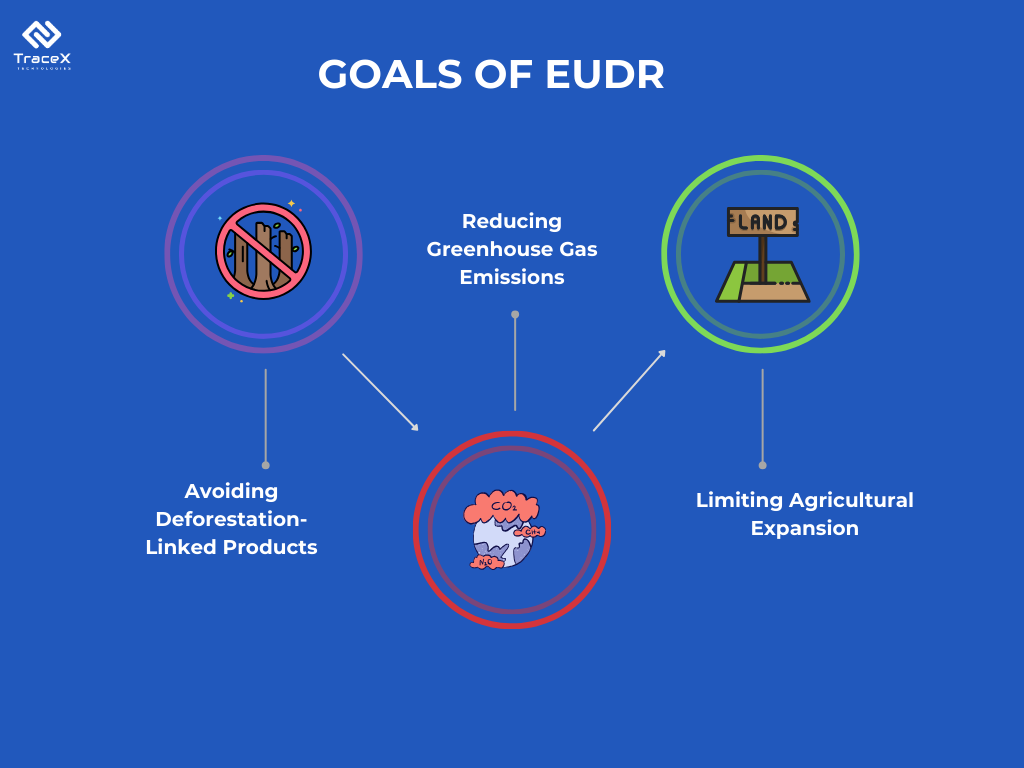
Under the law, companies are mandated to conduct thorough due diligence assessments on their supply chains, ensuring that imported products adhere to local laws and regulations. Furthermore, companies are expected to evaluate the environmental and social ramifications of their supply chains and take corrective measures to mitigate adverse effects. Additionally, the legislation prohibits the introduction of products into the EU market that are linked to illegal deforestation or forest degradation. Large companies have an 18-month grace period to ensure compliance once the regulation takes effect, after which penalties may be imposed.
The EU Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) represents a landmark step towards combating deforestation and promoting sustainable supply chains. This regulation casts a wide net, encompassing a range of commodities linked to deforestation, including soy, beef, palm oil, wood, cocoa, coffee, and rubber. Its primary objective is to prevent the sale of products associated with deforestation within the EU market.
By imposing stringent due diligence requirements on businesses, the EUDR aims to ensure that commodities are produced legally and sustainably. This includes traceability measures, risk assessments, and the development of deforestation-free supply chains. Compliance with the EUDR is mandatory for companies operating within the EU market, and non-compliance can result in significant penalties.
The EU Deforestation-Free Regulation (EUDR) targets not just raw commodities but also their derivatives, ensuring that products entering the EU market are free from deforestation and degradation. Here’s a breakdown of the key commodities covered by the EUDR, along with their derivatives:
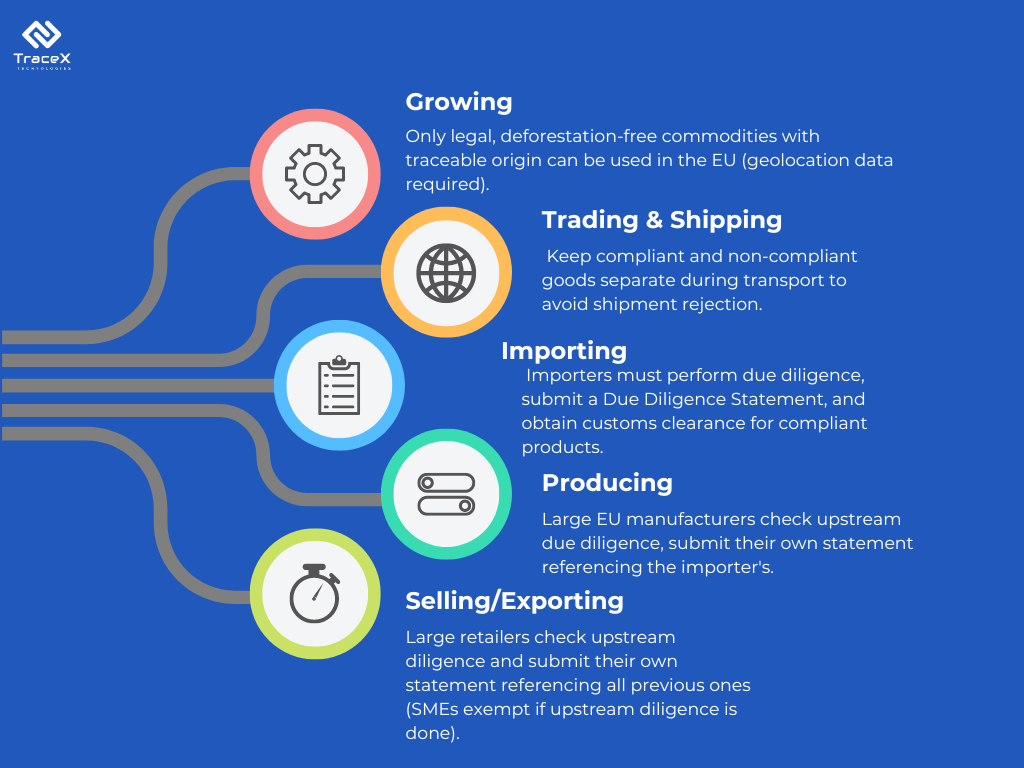
The EUDR applies regardless of whether the raw materials originate from within the EU or elsewhere. The EU Deforestation-Free Regulation (EUDR) has far-reaching implications for companies involved in the trade of certain key commodities. It sets out clear requirements for different stakeholders across the supply chain, from producers to importers and other intermediaries.
Essentially, if your business deals with these commodities in the EU market, you need to understand and comply with the EUDR.
The EU Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) outlines a series of requirements for companies placing agricultural commodities on the EU market. These requirements aim to promote transparency, traceability, and responsible sourcing practices throughout the supply chain.
This information lays the foundation for transparency and allows authorities to track commodities throughout the supply chain.
By understanding these risks, companies can take targeted action to mitigate them.
These mitigation efforts must be documented in a Due Diligence Statement (DDS) submitted to the EU.
By fulfilling these EUDR requirements, companies can ensure their products meet EU deforestation-free standards and contribute to a more sustainable future.
EUDR compliance involves a rigorous due diligence process for companies to ensure their products are sourced ethically and sustainably, particularly in terms of deforestation.
Country benchmarking for risk assessment under the EU Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) is a process where countries are classified based on their likelihood of contributing to deforestation. The European Commission (EC) assigns countries a risk rating—low, standard, or high risk—which determines the level of due diligence required from operators sourcing from these regions.
The EU takes enforcement of the Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) seriously. To deter violations, regular inspections are conducted. Companies found non-compliant face a range of penalties, varying in severity based on the specific infringement and decided by each EU member state
Remember, complying with the EUDR isn’t just about avoiding penalties; it’s about demonstrating your commitment to a sustainable future.
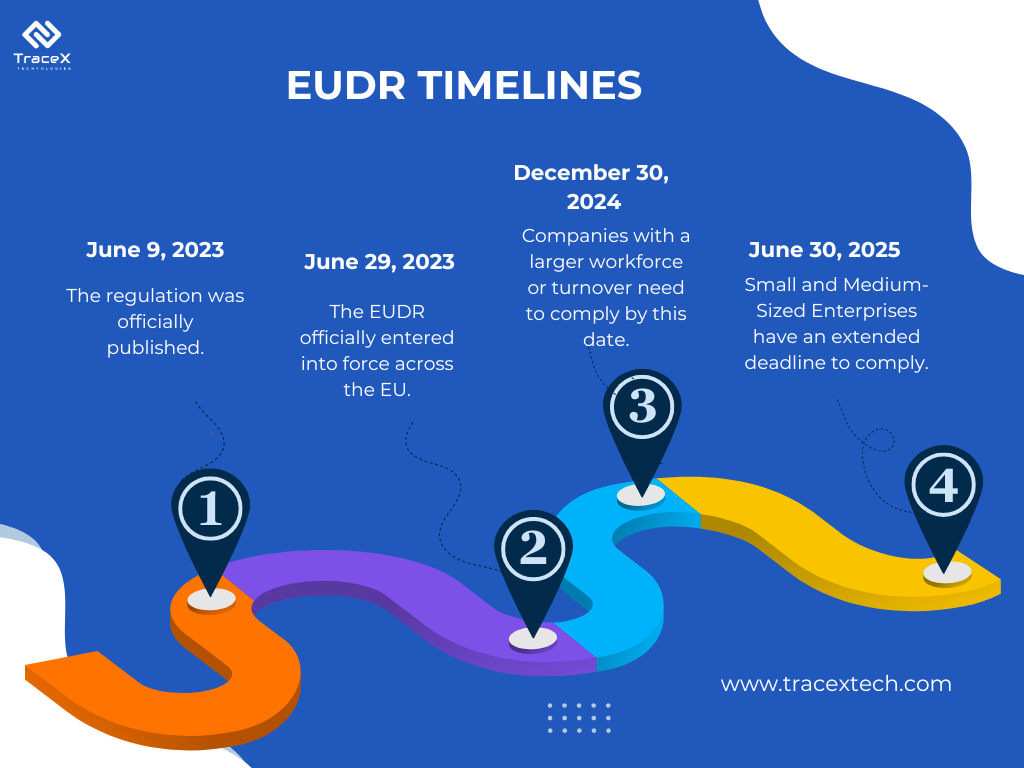
Achieving compliance with the EU Deforestation-Free Regulation (EUDR) involves multiple phases, each focused on ensuring your supply chain is fully transparent, traceable, and free from deforestation. This step-by-step roadmap will guide you through the process, from assessment to ongoing monitoring
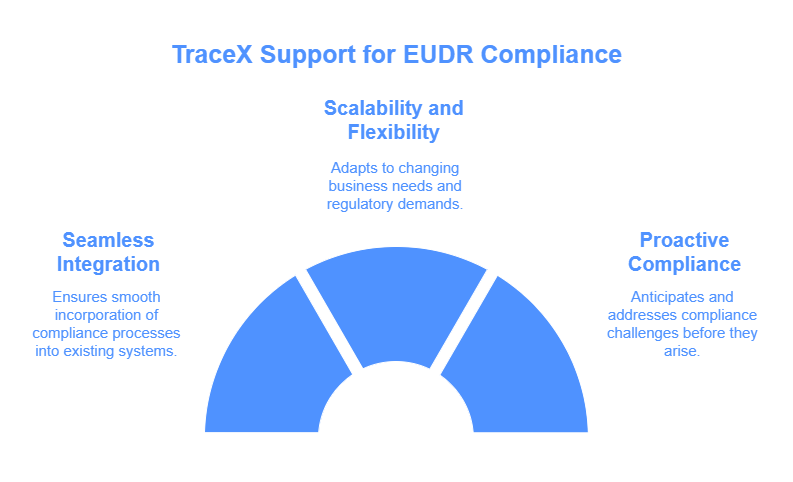
Achieving compliance with the EU Deforestation-Free Regulation (EUDR) can be complex, but several tools and technologies can help streamline the process. These technologies offer transparency, traceability, and real-time monitoring, ensuring that businesses can meet regulatory requirements efficiently.
Blockchain technology provides an immutable, transparent record of transactions that is particularly useful for traceability in supply chains. By using blockchain, businesses can track the entire journey of a commodity from its source to its final destination, ensuring that it’s sourced sustainably and in line with EUDR requirements.
Geolocation tools are key in mapping and verifying the origins of commodities. These tools utilize satellite data, GPS, and other location-based technologies to track the geographic coordinates of sourcing regions, ensuring that commodities are coming from deforestation-free areas.
Data analytics solutions play a critical role in evaluating supply chain risks and ensuring ongoing compliance with EUDR requirements. These tools analyze large volumes of data from various sources, such as geolocation, transaction records, and environmental factors, to assess potential risks and generate compliance reports.
The TraceX EUDR Compliance Platform is an advanced, blockchain-powered solution designed to help businesses meet the stringent requirements of the EU Deforestation-Free Regulation (EUDR). It offers an integrated approach to ensure supply chain traceability, deforestation-free sourcing, and compliance with EU regulations for commodities like soy, palm oil, cocoa, beef, rubber, coffee, and wood.
The platform uses blockchain technology to offer end-to-end traceability across your supply chain. This means businesses can track their products in real-time, ensuring that every commodity—from raw materials to finished products—can be traced back to its source. With the EUDR’s emphasis on transparency, having this level of traceability is crucial to demonstrate compliance.
To meet EUDR requirements, it is essential to track the geographical location of sourcing regions. TraceX integrates geolocation tools that allow businesses to map where their commodities are sourced and ensure that these areas are deforestation-free.
The risk assessment capabilities of the TraceX platform help businesses identify potential deforestation risks within their supply chains. By analyzing sourcing regions and environmental data, the platform provides actionable insights to mitigate risks and ensure continued compliance.
With TraceX, businesses can generate the required compliance reports for submission to the EU. The platform automates the generation of these reports, ensuring that all necessary documentation—such as geolocation data, commodity sourcing, and sustainability certifications—are included in the correct format and meet EU guidelines.
TraceX offers features that facilitate supplier collaboration. It allows businesses to engage their suppliers directly through the platform, ensuring they are aligned on the data collection process and EUDR compliance requirements.
Addressing deforestation and promoting sustainability are pivotal in the global effort to combat climate change and protect biodiversity. The EU’s Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) is a significant step toward these goals, offering a model for responsible supply chain management. Achieving a balance between environmental goals and economic interests is essential, and international cooperation is paramount. Both businesses and consumers have a role to play in fostering a more sustainable and eco-conscious world.
Non-compliance with the EU Deforestation-Free Regulation (EUDR) can result in significant penalties for businesses. The penalties typically include:
Small businesses can take several steps to prepare for EUDR compliance, even with limited resources:
The EU Deforestation-Free Regulation (EUDR) is comprehensive, but there are some exemptions and flexibility for specific cases:



WhatsApp us