Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Discover how the dairy industry is revolutionizing its supply chain by integrating traceability and sustainability. Explore the role of innovative technologies like blockchain and IoT in enhancing transparency, efficiency, and environmental stewardship. Learn how stakeholders are collaborating to build a more resilient and sustainable dairy sector for the future.

Dairy supply chain stands at the forefront of transformative change, driven by the dual imperatives of traceability and sustainability. As consumers increasingly seek transparency and accountability in their food choices, the dairy industry is adapting to meet these evolving demands. From grass to glass, stakeholders are embracing innovative approaches to enhance traceability and promote sustainability throughout the supply chain.
With an increasing focus on personal health and wellness, organic dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt are gaining traction in the market. Traceability has emerged as a pivotal topic in the food industry, driven by consumer demand for transparency regarding the quality and safety of their food choices.
The dairy industry is experiencing rapid growth worldwide and is forecasted to reach a value of $1,032 billion by 2024. India ranks third in cow milk production, following the EU and the United States. According to Nielsen’s report, approximately 73% of consumers worldwide prefer companies that provide clear information about the origin and production methods of their products.
Milk is a nutritious food which has a short shelf life and is a breeding ground for bacterial pathogens. Milk processes help in stretching the shelf life and thereby reduce foodborne illness. Production and processing are the two main stages in the dairy supply chain followed by storage and distribution. The dairy product supply chain is a long and complex one with its own challenges.
The journey begins on dairy farms where cows are raised and milked. Dairy farmers focus on animal care, nutrition, and health to ensure high-quality milk production. Cows graze on pasture or are fed a balanced diet to support their health and milk productivity.
An estimated 90% of milk is produced by small hold dairy farmers. The dairy animals are fed on fodder, residue of crops and grass. Dairy farming encompasses breeding, rearing and welfare of cattle for production of milk. The principles of breeding help in milk production. Pasture is the natural feed for cattle. Other feeds are also supplemented. Herd management and animal welfare is very important. Disease outbreaks are common and proper veterinary services are mandatory.
Once the cows are milked, the raw milk is collected and stored in refrigerated tanks on the farm or transported to a nearby dairy processing facility. Quality testing may be conducted to ensure the milk meets regulatory standards for safety and freshness.
The producers are usually dispersed in rural areas and the logistics of linking them to markets is important. Considering the perishable nature of milk, streamlined collection and transportation of milk is vital. Milk is usually transported in cans or tankers and collected at specified collection centers. Milk collectors transport milk to processing centers, local markets, shops or hotels.
At the dairy processing facility, the raw milk undergoes various processing steps to produce a range of dairy products such as milk, cheese, yogurt, and butter. Processing may involve pasteurization to eliminate harmful bacteria, homogenization to ensure uniform consistency, and separation to remove excess fat or cream.
Milk that arrives at processing units are stored in bulk chillers at a temperature below 40 F. The milk is then subjected to a series of quality checks to ensure that the milk has been cooled and is bacteria free. It is tested for milk fat, protein and tested for adulterants and residues. The milk is rejected if it does not satisfy the quality checks.
Pasteurization involves a heat treatment process that kills the pathogens in milk and increases its shelf life. Homogenization of milk is carried out to reduce the size of fat and give the milk the color and texture. Milk can be further processed to give the other byproducts like butter, cheese and yoghurt.
Processed dairy products are packaged into containers suitable for retail sale or distribution. Packaging materials may vary depending on the product and market preferences, but they typically include bottles, cartons, tubs, or pouches.
Packaged dairy products are distributed to retail outlets such as grocery stores, supermarkets, convenience stores, and specialty shops. Distribution channels may involve wholesalers, distributors, and logistics companies responsible for transporting products from processing facilities to retail locations.
The homogenized and pasteurized milk are packaged into cartons and distributed to supermarkets and the end consumers. The cold storage conditions need to be maintained. The byproducts like cheese and yoghurt are often packed in customized packages depending on extra flavors added.
Consumers purchase dairy products from retail outlets for consumption at home or on the go. Retailers play a crucial role in merchandising, stocking, and promoting dairy products to meet consumer demand and preferences.
Finally, consumers enjoy dairy products as part of their daily diet, whether it’s a glass of milk with breakfast, a slice of cheese on a sandwich, or a serving of yogurt as a snack. The consumption of dairy products provides essential nutrients such as calcium, protein, vitamins, and minerals that contribute to overall health and well-being.
Overall, the “grass to glass” story highlights the interconnectedness of various stakeholders in the dairy supply chain, from farmers and processors to distributors and consumers. Each stage plays a critical role in delivering safe, nutritious, and delicious dairy products to consumers worldwide.
The dairy industry is a vital component of the global food system, encompassing the production, processing, and distribution of milk and dairy products. It plays a significant role in providing essential nutrients to consumers worldwide, contributing to food security and economic development in many regions. From milk and cheese to yogurt and butter, dairy products are consumed by people of all ages and cultures, making the industry indispensable to the agricultural sector.
Traceability and sustainability have become increasingly critical aspects of the dairy supply chain due to growing consumer demand for transparency, ethical practices, and environmental responsibility. Traceability refers to the ability to track the journey of dairy products from farm to table, ensuring accountability and safety throughout the supply chain. It involves recording and monitoring various stages of production, processing, and distribution to identify potential issues and mitigate risks related to food safety, quality, and authenticity.
Sustainability, on the other hand, entails adopting practices that promote the long-term viability of dairy production while minimizing negative environmental and social impacts. This includes reducing greenhouse gas emissions, conserving natural resources, promoting animal welfare, and supporting local communities. As concerns about climate change, biodiversity loss, and ethical sourcing continue to rise, dairy companies are under increasing pressure to integrate sustainability into their operations.

The dairy supply chain faces several challenges that impact its efficiency, sustainability, and resilience.
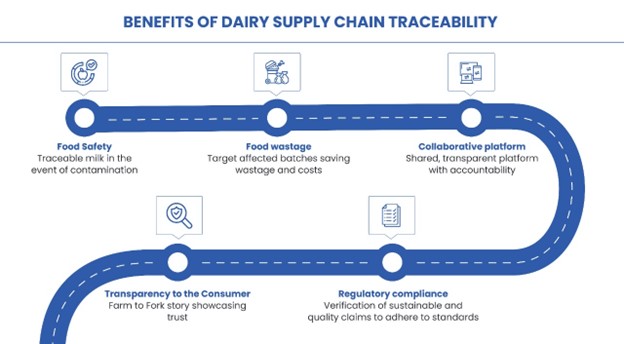
Traceability refers to the ability to track and trace the movement of products or ingredients throughout the supply chain. In the dairy industry, traceability is crucial for ensuring food safety, quality control, and regulatory compliance. It involves recording and documenting information about the origin, production, processing, and distribution of dairy products, allowing for transparency and accountability at every stage of the supply chain.

Each dairy farm identifies and records information about its milk production, including the health and treatment of dairy animals, feed sources, and milk collection practices.
Dairy processing facilities maintain records of milk intake, processing methods, and product formulation to ensure consistency and quality control.
Dairy products are labeled with unique codes or identifiers that enable traceability, including batch numbers, expiration dates, and product specifications.
Distributors and retailers track the movement of dairy products from processing facilities to retail outlets, maintaining records of storage conditions, transportation, and handling practices.
Dairy production plays a significant role in global food systems, but it also has environmental, social, and economic impacts that must be addressed. Sustainability in food supply chains involves balancing environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and economic viability to meet the needs of present and future generations. With growing concerns about climate change, resource depletion, and animal welfare, sustainability has become increasingly important for dairy producers, consumers, and stakeholders alike.
Methane emitted from enteric fermentation is the major hotspot contributing up to 75 per cent of the total GHG emissions of the dairy sector.
GHG emissions associated with milk production arise from all the activities that are involved in cradle to grave dairy supply chains. These activites include agriculture inputs like fertilizers, fossil fuel for production of feed for animals, processing of concentrates in cattle feed plants, enteric fermentation, manure management and post-harvest activities like processing of milk in cooperatives, conversion into dairy products and distribution through retail supply chains.

Explore the pivotal role of understanding carbon footprints in shaping a sustainable future
Uncover why measuring and reducing carbon footprints is crucial for businesses, the environment, and society.
Implementing sustainable livestock management practices ensures the well-being of animals, preserves natural resources, and promotes environmental conservation. By embracing sustainable approaches, we safeguard both the health of our livestock and the future of our planet.
Environmental Conservation: Adopting practices to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, minimize water usage, and promote biodiversity conservation on dairy farms.
Animal Welfare: Ensuring the health and well-being of dairy animals through proper nutrition, housing, and veterinary care, as well as implementing animal welfare standards and certifications.
Resource Utilization: Implementing strategies to optimize resource use, such as efficient feed management, waste reduction, and renewable energy adoption.
Sustainable Sourcing: Partnering with suppliers who adhere to sustainable agricultural practices and ethical sourcing standards for feed ingredients and other inputs.
Waste Management: Implementing recycling, composting, and waste-to-energy initiatives to minimize waste generation and environmental pollution in dairy processing.

Technology solutions for dairy traceability encompass a range of innovative tools and systems designed to track and monitor the journey of dairy products from farm to table. These solutions leverage advanced technologies such as blockchain, Internet of Things (IoT), and data analytics to enhance transparency, efficiency, and accountability throughout the supply chain.
Blockchain technology, for example, enables the creation of immutable, transparent, and secure digital ledgers that record every transaction and movement of dairy products. By storing information in a decentralized and tamper-proof manner, blockchain ensures that stakeholders can verify the authenticity and provenance of dairy products at any point in the supply chain.
IoT devices, such as sensors and smart tags, are used to collect real-time data on various parameters such as temperature, humidity, and location. These devices are attached to dairy products, containers, and equipment, allowing for continuous monitoring and tracking throughout the production, storage, and transportation process.
Data analytics tools analyze the vast amount of data generated by IoT devices and other sources to extract valuable insights into the dairy supply chain. By processing data related to production volumes, quality metrics, transportation routes, and consumer preferences, dairy producers can optimize their operations, improve decision-making, and identify opportunities for efficiency and sustainability improvements.
TraceX blockchain traceability solutions provide dairy supply chain stakeholders with the tools and insights needed to address traceability and sustainability challenges effectively. By leveraging blockchain technology, provenance verification, sustainability monitoring, and compliance assurance capabilities, TraceX empowers stakeholders to build transparent, resilient, and sustainable dairy supply chains.
TraceX utilizes blockchain technology to create a transparent and immutable ledger that records every step of the dairy supply chain journey. From farm to processing facilities to distribution and retail, every transaction and movement of dairy products is securely recorded, providing stakeholders with real-time visibility into the product’s journey. This level of traceability enables quick identification and mitigation of any issues such as contamination, spoilage, or fraud, thereby ensuring food safety and quality assurance.
With TraceX, dairy products can be traced back to their exact source, including the farm or dairy where they were produced. This provenance verification helps in ensuring the authenticity and quality of dairy products, mitigating the risk of counterfeit or adulterated products entering the supply chain. By providing consumers with assurance regarding the origin and production practices of dairy products, TraceX enhances trust and confidence in the dairy supply chain.
TraceX extends beyond traceability to include sustainability monitoring capabilities. By capturing data related to sustainability metrics such as carbon footprint, water usage, and energy consumption at various stages of the supply chain, TraceX enables stakeholders to track and assess the environmental impact of dairy production and distribution.
TraceX ensures compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards governing dairy production and distribution. By maintaining a tamper-proof record of all transactions and activities, TraceX enables stakeholders to demonstrate adherence to food safety regulations, ethical sourcing practices, and sustainability initiatives.
In conclusion, the dairy industry stands at a pivotal moment where the integration of traceability and sustainability practices is essential for its long-term viability. By embracing technologies like blockchain, IoT, and data analytics, dairy supply chain stakeholders can unlock new opportunities for transparency, efficiency, and environmental stewardship. Through enhanced traceability, provenance verification, and sustainability monitoring, stakeholders can build consumer trust, mitigate risks, and drive positive environmental and social impact. As we move forward, it’s imperative for dairy supply chain participants to collaborate, innovate, and commit to sustainable practices that not only ensure the integrity of dairy products but also contribute to a healthier planet and society. Together, we can transform the dairy supply chain into a model of transparency, resilience, and sustainability for the future.
