Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Explore the intricacies of traceability in South African agriculture, from farm to fork. Discover how technology and innovation are shaping the future of food safety and supply chain transparency in one of Africa's key agricultural hubs.

Traceability in South African agriculture isn’t just about tracking produce; it’s about ensuring safety, empowering consumers, and fostering sustainable practices. In a country like South Africa, with diverse agricultural sectors and export-oriented industries, robust traceability systems are instrumental in maintaining market competitiveness and meeting international standards.
According to FAO, South Africa has the second largest economy on the continent. There are approximately 2.5 million smallholder farming households in South Africa and 35,000 commercial farming units.
Traceability in agriculture refers to the ability to track the production, processing, and distribution of agricultural products throughout the supply chain. It involves documenting crucial information such as origin, handling practices, and transportation methods to ensure transparency and accountability.
But why does this matter?
Learn how to safeguard your brand and protect consumers.
Discover the essential guide to managing food recalls effectively.
The agricultural sector in South Africa plays a crucial role in the country’s economy, employing a significant portion of the population and contributing to both domestic food security and export revenues. Agriculture in South Africa is diverse, ranging from large-scale commercial farming to small-scale subsistence farming. The sector faces challenges such as climate variability, water scarcity, and land reform issues. However, it remains a vital part of the economy, providing employment opportunities and contributing to rural development.
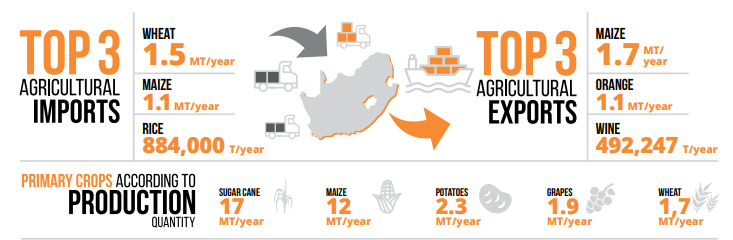
South Africa produces a wide variety of crops and livestock. Major crops include maize, wheat, sugarcane, citrus fruits, grapes, and various vegetables such as potatoes and tomatoes. Livestock production is also significant, with cattle, sheep, goats, and poultry being raised for meat, dairy, and other products. The country is known for its high-quality wine production, particularly in regions such as the Western Cape. Overall, South Africa’s agricultural sector is diverse and contributes significantly to the country’s food supply and economy.
In South African agriculture, several challenges persist, impacting the sector’s productivity and sustainability. These challenges include:
1. Water Scarcity: Limited access to water resources and periodic droughts affect crop cultivation and livestock farming.
2. Climate Variability: South Africa experiences unpredictable weather patterns, including droughts, floods, and heatwaves, which pose risks to agricultural production and livelihoods.
3. Land Reform Issues: Land ownership and distribution remain contentious issues, affecting agricultural development, investment, and rural livelihoods.
4. Labor Constraints: The agriculture sector faces challenges in attracting skilled labor, and labor disputes occasionally disrupt farming operations.
5. Market Access Barriers: Export restrictions, trade tariffs, and market volatility affect farmers’ ability to access international markets and secure fair prices for their produce.
6. Pest and Disease Outbreaks: Crop diseases, invasive species, and pest infestations pose threats to crop yields and livestock health, requiring effective pest management strategies.
Addressing these challenges requires collaborative efforts from government, farmers, industry stakeholders, and researchers to develop sustainable solutions and support the resilience of South Africa’s agricultural sector.
In South African agriculture, various traceability technologies are employed to ensure transparency and accountability throughout the supply chain. These include RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) tags, barcodes, GPS tracking, and blockchain technology. RFID tags are commonly used to track individual items or livestock, while barcodes provide quick identification of products. GPS tracking enables real-time monitoring of vehicles and assets, while blockchain technology ensures secure and immutable record-keeping of transactions and data.
In South Africa, farm management software has emerged as a transformative tool for agricultural operations, catering to the diverse needs of farmers across the country’s varied landscapes. From large commercial farms to smallholder operations, these software solutions offer a comprehensive suite of features designed to streamline farm management tasks. They enable farmers to efficiently plan and monitor crop production, manage inventory and inputs, track expenses, and analyze yield data. With the ability to integrate with IoT devices and satellite imagery, farm management software in South Africa empowers farmers to make data-driven decisions, optimize resource allocation, and enhance productivity while ensuring sustainable agricultural practices.
Relevant regulations and standards governing traceability in South Africa include the Agricultural Product Standards Act (1990), which sets out standards for agricultural products. Additionally, the National Agricultural Marketing Council (NAMC) oversees traceability in the agricultural sector. The South African Bureau of Standards (SABS) also provides guidelines for traceability systems, ensuring compliance with international standards.
Compliance requirements for farmers and food producers involve implementing traceability systems to track the movement of agricultural products from farm to fork. This includes maintaining accurate records of production processes, inputs used, and distribution channels. Farmers and food producers must also adhere to labeling requirements, ensuring that products are properly labeled with batch numbers, expiration dates, and origin information. Compliance with these regulations helps ensure food safety, quality, and consumer confidence in South Africa’s agricultural products.
South Africa’s agricultural landscape is as diverse as its people. From the lush vineyards of Stellenbosch to the sun-drenched citrus groves of Limpopo, the country produces an array of fruits, vegetables, and grains. Let’s explore how traceability weaves through this vibrant tapestry:

Existing traceability practices in South African agriculture involve the use of technology such as barcoding, RFID tags, and blockchain to track the movement of agricultural products from farm to fork. These systems allow farmers to monitor the entire production process, including planting, harvesting, and distribution, ensuring transparency and accountability. By implementing traceability, South African agriculture can improve food safety, quality control, and reduce waste and losses.
Examples of successful traceability initiatives in South African agriculture include the use of blockchain technology to track the origin and journey of produce from farm to table. This ensures transparency and accountability in the supply chain, as consumers can easily verify the authenticity and quality of products. Another example is the implementation of RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags on livestock, enabling farmers to monitor their animals’ health and movements throughout their lifecycle.
The impact of these traceability initiatives on stakeholders and the supply chain is significant. Farmers benefit from improved efficiency and productivity, as they can better manage their resources and respond to market demands. Consumers gain confidence in the safety and quality of agricultural products, leading to increased trust and loyalty. Additionally, traceability helps mitigate risks such as contamination or fraud, ultimately enhancing the sustainability and competitiveness of the agricultural sector.
From regenerative agriculture to water conservation strategies, learn how farmers are embracing sustainability to ensure a brighter, greener future for generations to come.
Discover the sustainable farming practices shaping the landscape of South African agriculture!
TraceX blockchain traceability solutions revolutionize supply chain transparency in South Africa’s agricultural landscape. By harnessing the power of blockchain technology, TraceX ensures an immutable record of every step in the journey from farm to fork. Farmers, distributors, and consumers alike benefit from this unprecedented level of transparency, which safeguards against fraud, ensures product authenticity, and fosters trust throughout the supply chain.
Explore how TraceX’s Krishi Mangal project revolutionizied farm-level digitization and optimized supply chains for farmers.
Dive into our customer success story now!
Emerging trends and opportunities in traceability include the adoption of advanced technologies such as blockchain, RFID, and IoT sensors to enhance the transparency and accuracy of tracking agricultural products from farm to fork. These technologies enable real-time monitoring of the entire supply chain, ensuring compliance with regulations, improving food safety, and enhancing consumer trust. Additionally, there is a growing focus on sustainability and ethical sourcing, with traceability systems providing valuable data to support environmentally friendly practices and fair trade initiatives.
Potential challenges and considerations for the future of traceability in agriculture include the need for standardized protocols and interoperable systems to ensure seamless data sharing across different stakeholders and geographical regions. Privacy concerns and data security issues also need to be addressed to protect sensitive information while maintaining transparency. Furthermore, the cost of implementing traceability technologies and the complexity of integrating them into existing supply chain networks may pose challenges for smaller farmers and producers. Collaborative efforts between governments, industry players, and technology providers will be crucial in overcoming these challenges and unlocking the full potential of traceability in agriculture.
The key points discussed include the essential role of traceability in agriculture for ensuring food safety, quality control, and regulatory compliance. Advanced technologies such as blockchain, RFID, and IoT sensors are emerging trends that enhance transparency and accuracy throughout the supply chain. Traceability also supports sustainability and ethical sourcing initiatives by providing data to support environmentally friendly practices and fair trade.
Continued investment in traceability is crucial for sustainable agriculture in South Africa. Traceability systems help to improve food safety, reduce waste and losses, and enhance consumer trust. By implementing advanced technologies and standardized protocols, South Africa can strengthen its agricultural sector, ensure compliance with regulations, and support environmentally friendly practices. Additionally, traceability enables better market access and improved competitiveness, ultimately contributing to the long-term sustainability of the agricultural industry in South Africa.
