Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Discover how sustainable agriculture practices are transforming the landscape for both agribusinesses and NGOs. Explore innovative approaches, successful case studies, and collaborative efforts driving positive change in the agricultural sector.

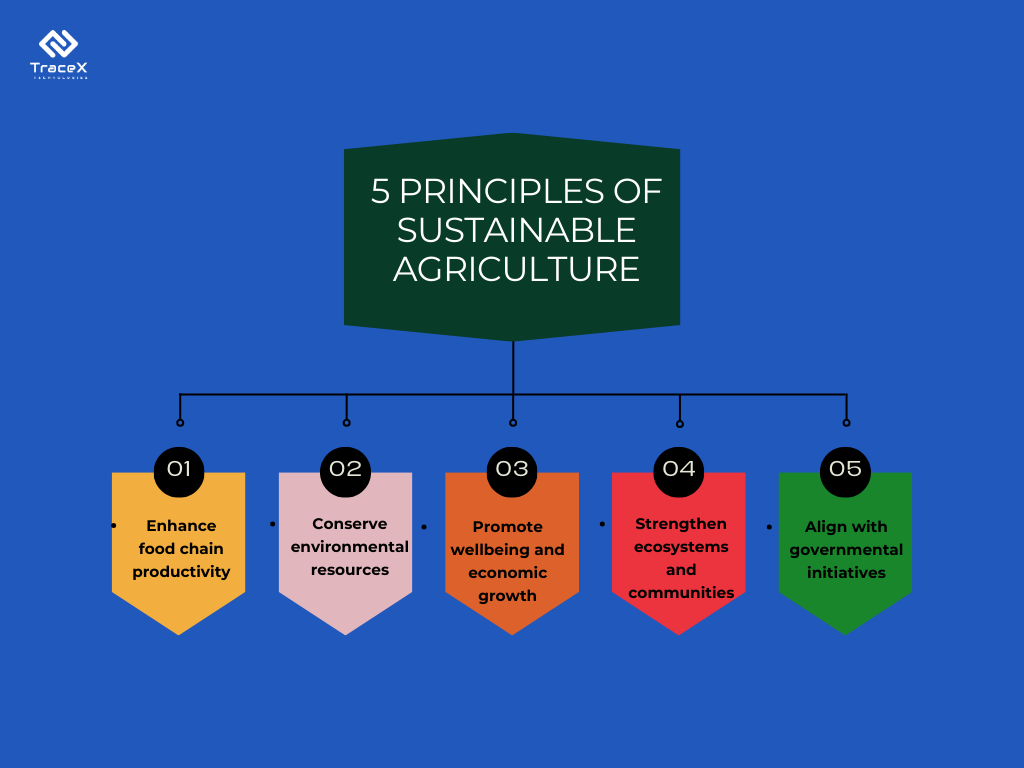
The global food system faces a critical crossroads. Our current agricultural practices are putting immense strain on the environment, contributing to climate change, biodiversity loss, and soil degradation. Consumers are also demanding more transparency and ethical sourcing, seeking food produced with a focus on sustainability. The importance of sustainable agriculture practices is imperative and agribusinesses and NGOs can play an important role in creating a more sustainable future for food production.
Agriculture stands as the largest global industry, engaging over one billion individuals and yielding a staggering $1.3 trillion in food annually. Covering roughly 50 percent of habitable land, both pasture and cropland serve as vital sources of sustenance and habitats for diverse species.
Through sustainable management, agricultural activities have the potential to conserve and rejuvenate crucial ecosystems, safeguard watersheds, and enhance the health of soil and water. Conversely, unsustainable practices pose significant threats to both the environment and human well-being.
Traditional agriculture methods often rely heavily on synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and monoculture farming – leading to environmental damage and resource depletion. The consequences are significant:
These factors not only threaten our environment but also endanger long-term food security.
Sustainable farming practices aim to minimize environmental impact while maximizing productivity and profitability. These practices encompass a range of approaches:
Regenerative Agriculture: This holistic approach focuses on improving soil health, biodiversity, and water management. Techniques include cover cropping, composting, and reduced tillage. Regenerative agriculture is a holistic approach that emphasizes restoring and enhancing ecosystem health while promoting sustainable food production. By focusing on principles such as soil health, biodiversity, and water management, regenerative agriculture aims to not only sustain but also improve the natural resources upon which agriculture depends.
Practices like cover cropping, crop rotation, and minimal tillage work synergistically to build soil organic matter, enhance soil structure, and increase water infiltration and retention. This leads to improved soil fertility, resilience to extreme weather events, and reduced reliance on external inputs like synthetic fertilizers and pesticides. Moreover, regenerative agriculture promotes biodiversity by creating habitats for beneficial insects, birds, and microorganisms, which contribute to natural pest control and pollination. Overall, by mimicking natural processes and prioritizing ecological health, regenerative agriculture fosters resilience, productivity, and long-term sustainability in agricultural systems.
Unlocking the Potential of Regenerative Agriculture: Embracing Sustainability in Farming
Explore how regenerative agriculture practices can revolutionize farming for a more sustainable future.
Organic Farming: This eliminates the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, promoting biodiversity and soil health. Through the use of natural fertilizers, crop rotation, and biological pest control, organic farming nurtures soil health and fertility while reducing reliance on external inputs. Moreover, by prioritizing organic methods, farmers contribute to the preservation of ecosystems, protect water quality, and promote the well-being of farmworkers and consumers alike.
Precision Agriculture: Utilizing technology to optimize resource use through data-driven decisions on irrigation, fertilization, and pest control. Data-driven decisions play a pivotal role in advancing sustainability within agriculture by offering insights that optimize resource management and minimize environmental impact. Through the collection and analysis of various data points such as soil moisture levels, weather patterns, crop yields, and pest populations, farmers can make informed choices regarding irrigation, fertilization, and pest control. By leveraging precision agriculture techniques, they can apply inputs more efficiently, reducing waste and minimizing the use of chemical inputs. Ultimately, this data-driven approach fosters sustainable practices that enhance productivity while conserving natural resources and protecting ecosystems for future generations.
Water Conservation Techniques: Implementing drip irrigation, rainwater harvesting, and mulching to conserve water resources. Water conservation practices play a crucial role in nurturing sustainability within agriculture by mitigating the strain on limited water resources and promoting ecosystem health. Techniques such as drip irrigation, rainwater harvesting, and mulching help optimize water usage, ensuring that crops receive adequate moisture while minimizing wastage. By adopting these practices, farmers can reduce reliance on groundwater and surface water sources, mitigating the risk of depletion and promoting long-term water security. Additionally, water conservation measures contribute to soil health and biodiversity preservation, fostering resilient agricultural systems capable of withstanding environmental challenges such as drought and climate variability. Overall, integrating water conservation practices into agricultural operations enhances sustainability by balancing the needs of agriculture with the preservation of vital water resources.
Explore the Future of Water Conservation: Dive into Sustainable Practices and Innovative Technologies
Fair Labor Practices: Ensuring fair wages, safe working conditions, and respect for workers’ rights throughout the supply chain. Fair labor practices are integral to promoting sustainability in agriculture as they ensure equitable treatment of workers and uphold social responsibility throughout the supply chain. By providing fair wages, safe working conditions, and respecting workers’ rights, agricultural operations foster a supportive and dignified work environment. This not only enhances the well-being and livelihoods of farmworkers but also contributes to social stability and community development. Moreover, fair labor practices help build trust and credibility with consumers, who increasingly prioritize ethical sourcing and social responsibility. By prioritizing fair labor practices, agricultural enterprises can strengthen their resilience, attract and retain skilled workers, and contribute to the long-term sustainability of the agricultural sector.
By embracing these practices, agribusinesses and NGOs can contribute to a more sustainable food system.
While the benefits of sustainable agriculture are clear, there are hurdles to overcome:
Witness the transformative power of sustainable practices combined with advanced technology as we explore the journey of land restoration. Experience firsthand how TraceX fosters ecological renewal and agricultural resilience, revitalizing barren lands and promoting sustainable farming practices.
Delve into how an agribusiness harnessed TraceX traceability and sustainability solutions to drive sustainable exports and usher in an era of data-driven agriculture. Witness how these solutions not only reduced environmental impact but also established new benchmarks for responsible practices in the industry.
By integrating TraceX solutions, the biopharmaceutical company witnessed notable enhancements in production monitoring, labor practices, and supply chain transparency. They prioritized equitable wages for migrant workers, thereby bolstering social responsibility and adhering to ethical standards. Utilizing data-driven insights, the company proactively addressed challenges and optimized operational efficiency. Consequently, their commitment to responsible practices in the supply chain not only fortified consumer trust but also elevated brand reputation, resulting in heightened demand for their ethically and sustainably sourced rose products.
Both agribusinesses and NGOs play crucial roles in driving the shift towards sustainable agriculture:
Agribusinesses are increasingly embracing sustainability initiatives to foster positive change in agricultural practices. One approach involves incentivizing farmers to adopt sustainable methods by offering premium prices or long-term contracts. Additionally, providing technical assistance and training equips farmers with the knowledge and resources needed to implement sustainable practices effectively. Agribusinesses also play a pivotal role in advancing research and development efforts aimed at enhancing sustainability in agriculture. Moreover, promoting transparency and traceability throughout the supply chain ensures consumers have access to clear information about the sustainability practices employed, fostering trust and accountability.
NGOs play a crucial role in advancing sustainable agriculture practices through advocacy, education, and collaboration. They raise awareness among consumers about the significance of sustainable agriculture, encouraging demand for eco-friendly products. Moreover, NGOs provide vital capacity-building support to farmers, particularly small-scale ones, through training programs and access to resources for implementing sustainable practices. Additionally, they foster collaboration among various stakeholders, including agribusinesses and government agencies, to develop policies and programs that promote and support sustainable agriculture initiatives.
Creating a sustainable future in agriculture hinges on collaboration among agribusinesses, NGOs, policymakers, and consumers. This collaboration can take various forms, including multi-stakeholder partnerships that pool expertise and resources to develop effective solutions and share best practices. Robust certification programs play a pivotal role in guiding consumer choices and incentivizing producers to adopt sustainable practices. Moreover, investing in innovation fosters the development of new technologies and approaches for sustainable agriculture. Consumer education is also vital, as it raises awareness about the benefits of sustainable agriculture and empowers individuals to make environmentally conscious choices. Through collaboration and the adoption of sustainable practices, we can build a future where agribusinesses thrive, NGOs fulfill their missions, and consumers enjoy responsibly sourced food, all while safeguarding our planet for future generations.
The shift towards sustainable agriculture is an ongoing journey. Agribusinesses and NGOs have a crucial role to play in leading and supporting this transformation. By embracing innovation, investing in collaboration, and prioritizing ethical sourcing and environmental responsibility, we can pave the way for a more sustainable and equitable food system for generations to come.
