Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Discover the key principles and practices of organic farming for sustainable agriculture in our insightful blog. Explore the benefits, techniques, and success stories that showcase how organic farming contributes to a healthier planet and a more sustainable food system. Join the movement towards a greener future.

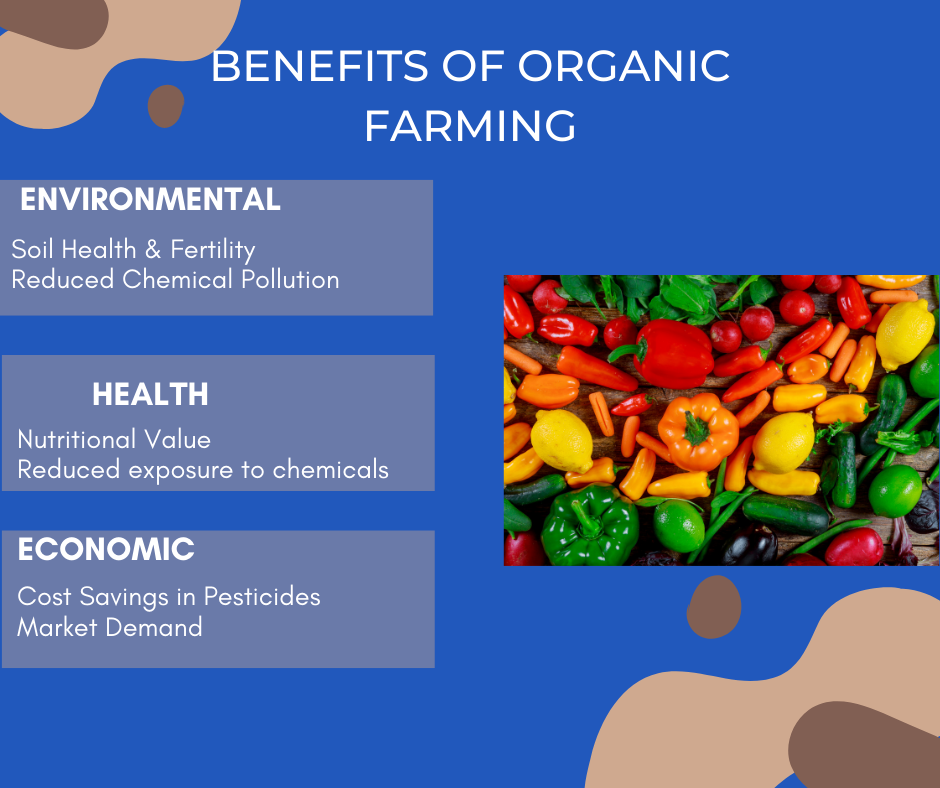
In an era where environmental concerns and the need for sustainable practices are at the forefront, organic farming emerges as a powerful solution for sustainable agriculture. Organic farming is an environmentally friendly approach to agriculture that emphasizes sustainability and natural processes. Without the use of synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, or genetically modified organisms (GMOs), it attempts to cultivate crops and raise cattle. This approach encourages biodiversity, soil health, and the overall health of ecosystems.
According to a report by Rodale Institute, organic farming can sequester 3500 pounds of CO2 per acre annually.
Organic farming minimizes soil erosion, maintains water quality, and decreases environmental pollution by eliminating toxic chemicals. Organic farming methods also improve food’s nutritional content, increase animal welfare, and boost the regional economy. Adopting organic farming is essential for a sustainable future since it ensures the planet’s long-term health and the welfare of future generations.
This blog delves into the principles, benefits and practices of organic farming, highlighting its role in building a more sustainable and resilient food system for the present and future generations.
An essential component of organic farming is soil management. Crop rotation, cover crops, and composting are among the techniques used by organic farmers to enhance the fertility and health of their soils. These methods improve sustainable agriculture and the long-term productivity of the land by improving soil structure, increasing nutrient content, retaining moisture, and fostering beneficial microbes.
Pest and disease management in organic farming is based on comprehensive and integrated strategies. Crop rotation, intercropping, and the use of resistant plant varieties are tactics used by organic farmers to control and prevent pests and diseases. In order to control pest populations, they also use physical barriers, biological controls like beneficial insects and microbial sprays, and other methods that minimize the need for synthetic pesticides while preserving ecological balance.
Organic farming places a strong emphasis on proactive and long-term weed control strategies. To reduce weed competition with crops, organic farmers use tactics like mulching, hand weeding, and cultivation. To control weeds, they also employ cover crops, smother crops, and appropriate crop spacing. Additionally, hoeing and flame weeding are frequently used to eradicate weeds without the use of synthetic herbicides, encouraging ecological harmony and soil health.
The major goal of nutrient management in organic farming is to keep crops supplied with a balanced and sustainable amount of nutrients. Compost, manure, and cover crops grown with green manure are examples of natural fertilizers that organic farmers employ to replenish the soil’s vital nutrients. Additionally, they use methods like crop rotation, which enhance nutrient availability and lessen nutritional imbalances.
Crop rotation and diversification are essential practices in organic farming. Crop rotation entails alternating various crops over time on the same plot of land. This enhances soil health, breaks disease and pest cycle cycles, and lessens the demand for synthetic inputs. In order to promote biodiversity, strengthen ecosystem resilience, and lower the chance of crop failure due to pests or environmental causes, diversification entails planting a range of crops in a specific area.
The distinction between organic and conventional farming lies in their underlying approaches to agriculture. Organic farming embraces a holistic and environmentally friendly ethos, eschewing synthetic chemicals and genetically modified organisms. Instead, it relies on natural methods such as crop rotation, composting, and biological pest control to maintain soil fertility and mitigate pests. Organic farming prioritizes biodiversity and promotes long-term sustainability.
On the other hand, conventional farming employs modern agricultural practices that often involve the use of synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and genetically modified seeds. While conventional methods may achieve higher yields in the short term, they sometimes raise concerns about environmental impact, soil health, and the potential residue of chemicals in food products.
Ultimately, the choice between organic and conventional farming reflects a balance between sustainable, nature-centric practices and high-efficiency, technology-driven approaches. Each has its merits and considerations, influencing the agricultural landscape and the broader discourse on sustainable food production.
Organic farming stands as a champion for pollinator health, providing a sanctuary where bees, butterflies, and other essential pollinators thrive. By abstaining from synthetic pesticides and prioritizing natural alternatives, organic practices create an environment conducive to biodiversity. Organic farms often feature diverse plant species, providing ample forage and habitat for pollinators. This commitment to ecological balance not only safeguards the delicate web of pollinator life but also contributes to the resilience of ecosystems, ensuring the continued pollination of crops for a sustainable and flourishing agricultural landscape.
By receiving an organic certification, businesses can demonstrate that their operations and goods comply with the fundamentals of organic farming. Accredited by regulatory bodies, certification bodies check that farmers adhere to specified organic criteria for inputs, pest control, animal welfare, and soil management. Although these requirements differ by location, they all work to increase transparency, morality, and consumer confidence in organic products. To keep their certification, organic farmers must submit to frequent inspections and keep thorough records.
Uncover the benefits, sustainability, and assurance that come with choosing certified organic products.
Discover the essential reasons behind Organic Certification in our latest blog
A framework for organic farming practices across many nations is provided by international organic standards and regulations. Guidelines for organic production, processing, and labeling are set by groups like the Codex Alimentarius Commission and the International Federation of Organic Agriculture Movements (IFOAM). These standards include a wide range of topics, such as labeling requirements, genetic engineering, pest control, and animal welfare. They help to facilitate international trade of organic goods, ensure consumer confidence, and harmonize organic practices around the globe.
Regenerative Organic Certification
Regenerative Organic Certification (ROC) is a pioneering standard that goes beyond traditional organic certification, aiming to elevate agricultural practices to new heights of sustainability. Embracing a holistic approach, ROC integrates three core pillars: soil health, animal welfare, and social fairness. Farms certified under ROC prioritize regenerative practices, emphasizing soil regeneration techniques, ethical treatment of animals, and fair labor practices.
TraceX’s traceability solutions empower organizations to effectively track and monitor organic crop production practices, ensuring compliance with organic standards, maintaining quality and fostering transparency throughout the supply chain. This enables companies to meet consumer demands for sustainable and organic products while maintaining operational efficiency and regulatory compliance.
Trace Gro, the pre-harvest farm management solution enables onboarding of farmers and their farms. Crops are configured along with their package of practices and input details. Tracking of these practices in real-time ensures timely recalls and adherence to organic standards. Recording and verifying each step in the organic supply chain ensures transparency and accountability. The digital immutable ledgers provide auditable data that facilitates compliance. Verified information like certifications, cultivation practices and sustainability initiatives helps companies to build trust and credibility with consumers.
Finally, organic farming is an essential method of agriculture that supports longevity, environmental protection, and the creation of wholesome food. Organic farmers support a more robust and balanced ecosystem by adhering to values including soil health, biodiversity preservation, and avoiding synthetic inputs. Reduced chemical exposure, improved soil quality, improved nutrition, and greater animal welfare are all advantages of organic farming. However, managing pests and diseases, nutrients, weeds, and market access are additional difficulties for organic farming. These difficulties can be overcome with creative approaches and assistance, allowing organic farming to flourish and play a vital part in creating a more resilient and sustainable food system for future generations.
