Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Discover how Non-Pesticidal Management (NPM) promotes sustainable agriculture by reducing chemical pesticide use, enhancing biodiversity, and ensuring safer food systems for a healthier future.

From battling pests that seem impervious to traditional methods to maintaining crop yields without synthetic aids, the road to sustainable farming isn’t always smooth. Yet, the rewards are worth the effort. By embracing non pesticidal management (NPM), we can nurture our crops while protecting our planet. Let’s explore how this innovative approach can transform the way we grow our food and ensure a healthier future for all.
Globally, pests inflict substantial agricultural burdens, causing billions of dollars in losses annually. According to FAO, annually, up to 40 percent of crops may be lost because of these threats.
Pests and diseases pose a significant risk to global food security, trade, and livelihoods. The FAO advocates for sustainable and ecological methods such as integrated pest management to mitigate the effects of pests and diseases. This includes ongoing monitoring, early warning systems, swift responses, and the implementation of innovative and eco-friendly prevention strategies to effectively manage pests and diseases sustainably.
Key Takeaways
Non-Pesticidal Management (NPM) is a set of practices designed to manage pests and diseases in crops without relying on synthetic chemicals. Instead of using traditional pesticides, NPM focuses on natural and sustainable methods to protect plants. It’s like switching from quick-fix solutions to long-term, eco-friendly strategies that work with nature rather than against it.
At its core, Non-Pesticidal Management is about creating a balanced ecosystem that naturally controls pest populations. Here are the main principles:
Conventional pest control often relies on synthetic pesticides to kill pests. These chemicals can be effective, but they come with drawbacks:
In contrast, Non-Pesticidal Management avoids these issues by using natural methods:
Sustainable agriculture is essential for maintaining the health of our planet and our food systems.
Environmental Impact of Synthetic Pesticides- Synthetic pesticides have been a go-to solution for farmers dealing with pests, but they come with significant environmental drawbacks:
Health Concerns Related to Pesticide Use- The health risks associated with pesticide use extend beyond the environment and directly impact people:
The Role of Sustainable Farm Management in Long-Term Food Security- Sustainable farming practices are key to addressing the problems caused by conventional methods and ensuring a stable food supply for the future:
In essence, sustainability in agriculture is about creating a balance that supports both the environment and our food systems. It’s a holistic approach that ensures we can produce food today without compromising the ability of future generations to do the same. By embracing sustainable practices, we’re not just protecting the planet—we’re securing our food supply and our health for the long term.
Non-Pesticidal Management (NPM) is all about finding clever, eco-friendly ways to manage pests without relying on synthetic chemicals.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a holistic approach to pest control that combines multiple strategies to manage pests in an effective and environmentally friendly way. Instead of just using one method, IPM integrates various techniques to keep pests under control. IPM aims to minimize the use of chemical pesticides by focusing on preventative and non-chemical methods first.
Biological control leverages nature’s own pest control mechanisms by using organisms that prey on or parasitize pests. For instance birds, ladybugs, and spiders are natural enemies of many pests. Introducing these predators to a farm can help keep pest populations in check. Certain insects lay their eggs on or in pest species. When the eggs hatch, the larvae consume the pests. For example, parasitic wasps can be used to control aphid populations.
Crop rotation involves changing the type of crops grown in a particular area each season. This practice disrupts the life cycles of pests and diseases that thrive on specific crops. Crop diversity—growing a mix of different plants—also helps by creating a less favorable environment for pests.
Healthy soil is crucial for healthy plants. Adding organic matter, such as compost or green manure, improves soil structure and nutrient content. This strengthens plants, making them more resistant to pests and diseases. Additionally, maintaining soil health supports beneficial soil organisms that can help control pests.
Mechanical and physical controls involve using tools and techniques to manage pests directly, Sticky traps or pheromone traps can capture pests before they cause significant damage. For example, using yellow sticky traps can catch flying insects like whiteflies. Physical barriers such as netting or row covers can prevent pests from reaching plants. This is especially useful for protecting crops from insects and birds. For smaller infestations, manually removing pests from plants can be effective. For instance, handpicking caterpillars from crops can reduce damage without chemicals.
Organic farming and Non-Pesticidal Management (NPM) share a common goal: reducing or eliminating the use of synthetic chemicals in agriculture to promote environmental sustainability and healthier food systems. Together, organic farming and NPM create a sustainable agricultural model that prioritizes ecosystem health, reduces reliance on chemicals, and produces safer, healthier food for consumers.
Farm management solutions make it easier for farmers to track and verify their Non-Pesticidal Management practices. From real-time monitoring to supply chain transparency and analytics, TraceX farm management platform provides the tools necessary to ensure NPM practices are effectively implemented, verified, and communicated, ultimately leading to more sustainable farming and better market opportunities for farmers.
N+3F leveraged TraceX’s farm management platform to achieve pesticide-free sustainable agriculture by utilizing its blockchain-powered traceability system. Through this platform, N+3F was able to implement end-to-end traceability, allowing them to monitor and manage every stage of the farming process digitally. This digitization streamlined their farm management activities, ensuring that crops were grown efficiently without the need for synthetic pesticides. Additionally, the platform enabled N+3F to perform real-time quality checks, particularly for Maximum Residue Limits (MRL), ensuring that their produce remained pesticide-free and safe for consumers. By fostering collaboration among stakeholders, the platform built trust across the supply chain, reinforcing N+3F’s commitment to promoting a safer and more sustainable food system.
Non-Pesticidal Management (NPM) offers a sustainable and viable alternative to conventional pesticide-based farming. By focusing on natural pest control methods, improving soil health, and fostering biodiversity, NPM helps protect the environment, safeguard human health, and ensure long-term agricultural productivity. As more farmers adopt these methods and integrate technologies like TraceX’s farm management solutions to track and improve their practices, we move closer to a future where food is grown sustainably, safely, and pesticide-free.
Non-Pesticidal Management (NPM) is a farming approach that minimizes or eliminates the use of synthetic chemical pesticides by relying on natural pest control methods. It involves techniques like crop rotation, biological control using natural predators, maintaining soil health, and using physical barriers to manage pests. NPM focuses on sustainable and environmentally-friendly practices to protect crops without harming the ecosystem.
NPM supports sustainability by reducing reliance on harmful chemicals, which can degrade soil health, pollute water sources, and negatively impact biodiversity. By encouraging natural pest control methods and promoting practices that improve soil fertility, NPM helps maintain long-term agricultural productivity, preserves the environment, and promotes safer food production, ensuring a more resilient farming system.
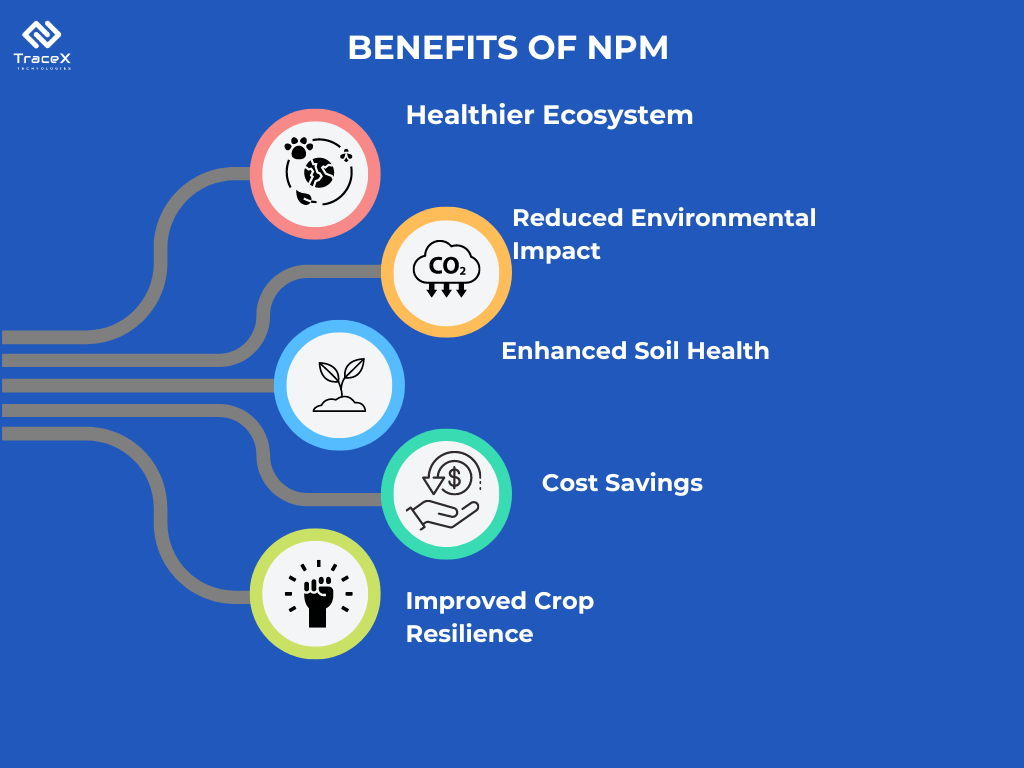
The benefits of NPM include improved soil health, reduced environmental impact, enhanced biodiversity, and lower production costs due to fewer chemical inputs. NPM also produces healthier crops free from synthetic pesticide residues, increasing consumer trust and marketability. Additionally, it promotes sustainable farming practices, ensuring the longevity of the agricultural ecosystem for future generations.
