Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Unlocking the potential of ESG in agribusiness: Discover how Tracex's sustainability and carbon management solutions empower companies to adopt responsible practices, ensure environmental stewardship, and drive positive social impact. Learn how ESG integration revolutionizes the agribusiness sector, fostering sustainability, and transparency.

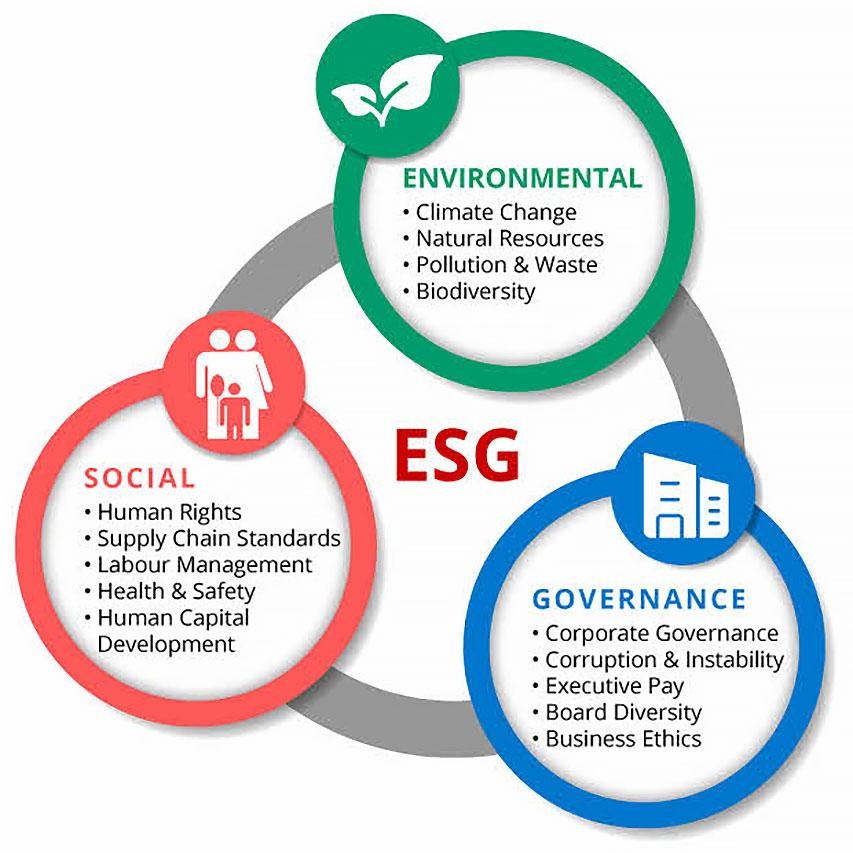
In the dynamic landscape of agribusiness, the importance of Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) factors has risen to the forefront. Embracing sustainability practices and responsible business conduct has become essential for companies in the agriculture industry. From mitigating environmental impacts to ensuring ethical supply chains and prioritizing stakeholder engagement, the integration of ESG principles is driving transformative change.
A survey by Accenture found that 72% of agribusiness executives believe that implementing ESG practices can create new business opportunities and drive innovation.
In this blog we delve into the significance of ESG in agribusiness and how it is reshaping the way companies operate, benefitting not only their bottom line but also the planet and society at large. Let us explore the powerful impact of ESG on the future of agriculture.
Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations are crucially important in the agricultural industry. They benefit local communities, encourage ethical labor practices, reduce negative environmental effects, and improve governance. The agricultural industry may support social progress, environmental protection, and long-term economic viability by incorporating ESG principles. ESG factors also help agribusinesses draw in ethical investors, fulfill changing customer demands for ethical and sustainable products, and reduce risks related to climate change and resource scarcity.
ESG integration encourages sustainability, fosters stakeholder trust, improves risk management, and satisfies consumer desires for morally and environmentally responsible products. Embracing sustainability and responsible practices not only helps mitigate environmental challenges but also fosters social inclusion, economic stability and supply chain resilience. By prioritizing ESG considerations, agriculture companies can contribute to a more sustainable and prosperous future for the industry, stakeholders and the planet as a whole.
Role of FMS in Sustainable Agriculture
In the age of digitization, technology stands out as a game-changer, presenting Farm Management Software (FMS) as a potent instrument to navigate the intricacies of contemporary agriculture. Sustainable farming necessitates more than just sowing seeds; it requires intelligent and effective farm management. From streamlining resource utilization to boosting productivity and environmental responsibility, FMS emerges as a key player. Crucially, farm management software contributes significantly to the progress of sustainable agriculture by elevating efficiency, optimizing resource deployment, and facilitating informed decision-making. It empowers farmers to maximize crop yields, monitor environmental impact, and champion responsible practices, thereby fostering long-term agricultural sustainability.
In the current business environment, considerations related to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) have become pivotal in driving sustainable practices and meeting stakeholder expectations. With the introduction of the Corporate Sustainability and Reporting Directive (CSRD) in the European Union and the associated reporting requirements outlined in the ESRS, there is an increased emphasis on companies enhancing their ESG reporting. This includes transparent disclosure of resource usage, waste management, greenhouse gas emissions, labor conditions, and supply chain transparency.
In addressing these evolving challenges, Farm Management Software stands out as a robust solution, supporting ESG and CSRD compliance in the agricultural sector.
The landscape of food production is shifting, driven by a rising tide of ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) regulations. From sustainable sourcing and resource usage to fair labor practices and board diversity, food companies must adapt to a new era of transparency and accountability. Understanding these regulations is crucial for ensuring compliance, minimizing operational risks, and seizing the opportunities presented by ethical and sustainable practices. By embracing ESG principles, food companies can build trust with consumers, attract investors, and ultimately contribute to a healthier planet and food system.
The prevalence of data brings about a significant challenge – the fragmentation of data within organizations. Crucial information is scattered across various business functions and systems, making it difficult to integrate and convert into actionable insights. This disjointed data landscape presents multiple business hurdles, especially for organizations striving to enhance business outcomes and harmonize their operations with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) commitments.
Simultaneously, certain companies are proactively collecting specific ESG data, particularly concerning greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. This initiative is driven by the anticipation of upcoming regulations that demand more extensive climate and environmental sustainability disclosures, such as the forthcoming SEC scope 3 emissions disclosure and the EU’s Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD).
However, these regulatory requirements should not be perceived merely as compliance exercises.
Harnessing technology to efficiently extract the necessary information for current and future disclosures empowers organizations to base decision-making on real-time data. Navigating the complex terrain of ESG compliance can be messy, but technology stands as your compass. From automating data collection to streamlining reporting, smart solutions empower you to meet and exceed ESG standards – ensuring sustainability, transparency, and a competitive edge. Embrace tech, chart your course towards responsible practices, and build a future where business thrives alongside our planet and people.
TraceX’s sustainability and carbon management solutions offer agribusinesses the tools and data they need to adopt ESG practices effectively. By addressing environmental impact, promoting social responsibility and ensuring transparency, TraceX empowers companies to build more sustainable and resilient agribusiness sector that aligns with ESG values and contributes to a greener future.
TraceX’s traceability solutions provide end to end visibility in the supply chain, ensuring transparency in sourcing practices and product lifecycle. This transparency is crucial in ESG reporting demonstrating responsible sourcing and providing insights to stakeholders.
Trace Carbon the carbon management solution helps agrobusinesses to monitor and track their GHG emissions at various stages of the supply chain. With accurate emissions data, companies can set emission reduction targets and report their progress towards achieving net-zero goals, aligning with ESG commitments.
TraceX enables companies to engage with farmers and farmer producer organizations in the supply chain, promoting fair practices, ethical labor standards and social responsibility. By fostering responsible labor practices, agribusinesses can positively impact the well-being of workers and local communities.
TraceX’s solutions are designed to align with various sustainability standards and frameworks, including ISO14044 and other ESG reporting guidelines. Agribusinesses can streamline their ESG reporting practices and ensure compliance with industry best practices.
TraceX tools provide insights into resource usage and helps agribusinesses to optimize inputs like water, fertilizers and energy. With this the companies can cut costs and demonstrate responsible resource management.
TraceX also promotes circular economy practices by facilitating efficient waste management and sustainable product design.
In conclusion, developing an ethical and sustainable agricultural industry depends on applying ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) principles to agribusiness. Despite difficulties like complexity and financial repercussions, adopting ESG has several advantages. It increases risk management, develops consumer loyalty, and ensures long-term viability for the business. Agribusinesses can leverage options for ethical fundraising and investment, set themselves apart from competitors, and improve operational effectiveness. The adoption of sustainable practices is accelerated by industry collaboration and knowledge sharing. Agribusinesses may help create a more sustainable future, fulfill stakeholder expectations, and tackle critical environmental and social issues by adopting ESG.
