Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Explore the complexities of the tomato supply chain and discover how challenges in production, post-harvest handling, and infrastructure impact the industry. Learn about innovative solutions like TraceX farm management software, offering insights to streamline processes and enhance sustainability.
From vibrant red salads to tangy sauces, tomatoes are a global culinary staple. But the journey from farm to table isn’t always smooth sailing. The tomato supply chain faces a multitude of challenges, threatening both the quality of this beloved fruit and the livelihoods of those who cultivate it.
The tomato supply chain faces a myriad of challenges that impact its efficiency, sustainability, and resilience. From production to distribution, various factors contribute to these challenges, affecting stakeholders at every stage of the supply chain. Understanding these challenges is crucial for implementing effective strategies to address them and ensure a reliable and sustainable tomato supply chain.
The tomato supply chain encompasses a complex network of activities involved in the production, processing, distribution, and retailing of tomatoes. It typically begins with cultivation on farms, followed by harvesting, sorting, packaging, transportation, and eventually reaches consumers through various retail outlets. This chain involves numerous stakeholders, including farmers, processors, distributors, retailers, and consumers, each playing a crucial role in ensuring a steady flow of tomatoes from farm to table.
The tomato supply chain is essential for meeting the global demand for this versatile and nutritious fruit. However, it faces various challenges that can disrupt its efficiency, sustainability, and profitability. These challenges range from production-related issues such as crop diseases and climate variability to logistical hurdles like transportation delays and market fluctuations. Addressing these challenges is crucial to ensure food security, minimize waste, maintain quality standards, and support the livelihoods of farmers and other stakeholders involved in the supply chain. In this section, we will delve deeper into the specific challenges facing the tomato supply chain and explore potential solutions to overcome them.
Tomato production faces various agronomic challenges, including pest and disease infestations, unpredictable weather patterns, and soil degradation. Pests such as aphids, whiteflies, and tomato hornworms can damage crops, leading to yield losses if not effectively managed. Likewise, diseases like blight, wilt, and viruses pose significant threats to tomato plants, requiring timely intervention through proper sanitation, crop rotation, and the use of disease-resistant varieties.
The indiscriminate use of agri-inputs such as fertilizers and pesticides can have adverse effects on soil health and environmental sustainability. Overuse of chemical fertilizers can lead to nutrient imbalances, soil acidification, and groundwater contamination, while pesticide residues may persist in the soil, water, and food chain, posing risks to human health and biodiversity. Promoting integrated pest management (IPM) practices, organic farming methods, and soil conservation techniques can help mitigate these risks and improve soil health in tomato production systems.
Achieving the desired quality standards for tomatoes is essential for market acceptance and profitability. Factors such as fruit size, shape, color, texture, and taste influence consumer preferences and market prices. However, maintaining consistent quality throughout the production cycle can be challenging due to factors like uneven ripening, fruit deformities, and post-harvest handling practices. Effective grading, sorting, and packaging techniques are critical to ensure that only high-quality tomatoes reach the market, thereby maximizing returns for growers and enhancing consumer satisfaction.
Losses incurred during harvesting, handling, and grading contribute to inefficiencies and waste in the tomato supply chain. Mechanical damage during harvesting, improper storage conditions, and inadequate transportation infrastructure can result in physical losses, reducing overall yields and marketable quantities. Furthermore, human errors in grading and sorting processes may lead to quality downgrade or rejection of produce, further exacerbating losses and lowering farmer incomes. Implementing proper harvesting techniques, investing in post-harvest infrastructure, and training workers on quality control measures can help minimize losses and improve the efficiency of the tomato supply chain.
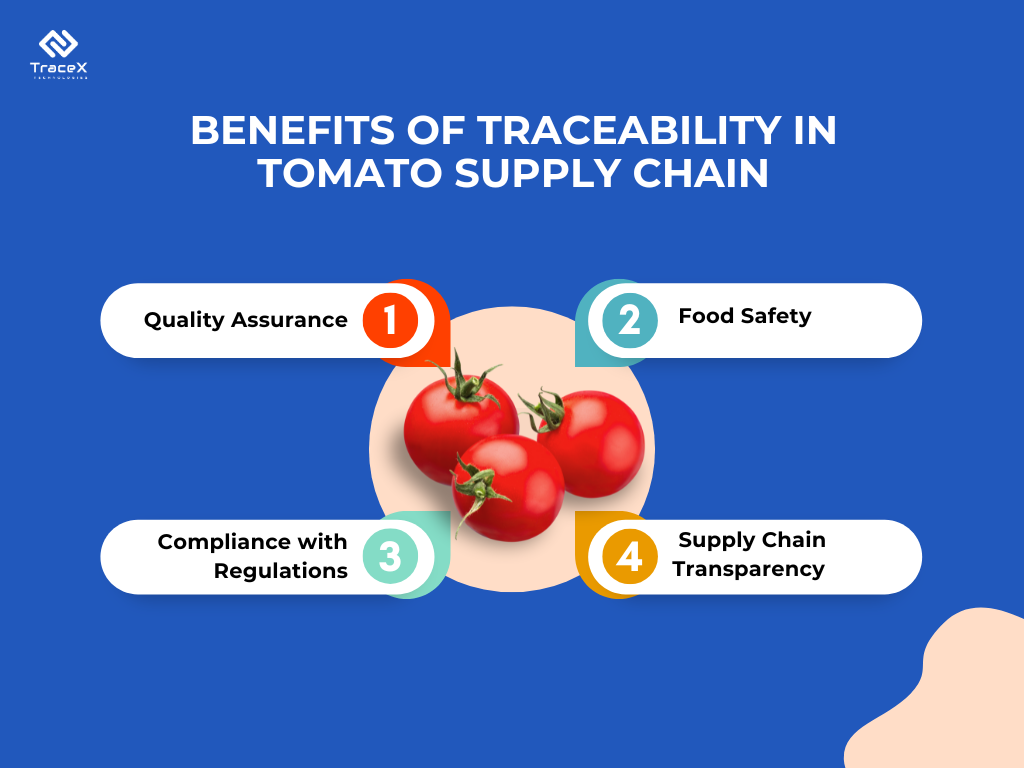
Innovative technological solutions are revolutionizing the tomato supply chain, offering promising avenues for addressing long-standing challenges. These advancements play a crucial role in enhancing efficiency, transparency, and traceability throughout the supply chain. By introducing cutting-edge traceability and digital solutions, such as blockchain-powered platforms and farm management software like TraceX, stakeholders can effectively track the journey of tomatoes from farm to fork. These technologies enable real-time monitoring of production practices, post-harvest handling, and transportation, facilitating better decision-making and quality control. With technology at the forefront, the tomato supply chain is poised for a transformative shift towards greater sustainability and resilience.
With TraceX Blockchain platform, farmers can now easily:
Here’s how TraceX Blockchain platform empowered CSAFE farmers:
By providing targeted information and guidance, TraceX empowered CSAFE farmers to move from overreliance on intuition to a more data-driven and sustainable approach to resource management. This shift has the potential to improve crop yields, boost profitability, and protect the environment.
Here’s how farm digitization with TraceX helped CSAFE farmers navigate post-harvest complexities:
By embracing farm digitization through TraceX, CSAFE farmers can now focus on delivering high-quality tomatoes to consumers. This not only benefits their own livelihoods but also contributes to a more efficient and sustainable food supply chain.
The future of tomato supply chain management holds exciting possibilities as emerging trends and innovations reshape the industry landscape. Stakeholders are increasingly leveraging technology to address existing challenges and unlock new opportunities for improvement. From blockchain-powered traceability solutions to AI-driven predictive analytics, the adoption of innovative tools promises to enhance efficiency, transparency, and sustainability across the supply chain. Additionally, there is growing recognition of the need for collaboration and partnerships to drive collective action and address systemic issues. As the industry continues to evolve, there are vast opportunities for innovation and improvement, paving the way for a more resilient and sustainable tomato supply chain.
In conclusion, the tomato supply chain faces multifaceted challenges across production, post-harvest handling, and infrastructure. These challenges, ranging from agronomy issues to insufficient cold chain infrastructure, contribute to inefficiencies and losses throughout the supply chain. However, with the advent of technology solutions like TraceX farm management software, there’s hope for overcoming these hurdles. By embracing digital solutions and innovation, stakeholders in the tomato supply chain can work towards a more resilient, efficient, and sustainable future.
