Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Unlocking the secrets of spice with Pepper Traceability! Explore the journey from farm to table, ensuring transparency and sustainability. Discover how TraceX revolutionizes pepper traceability for a future of responsible sourcing. Dive into the world of black gold, where every peppercorn tells a story.
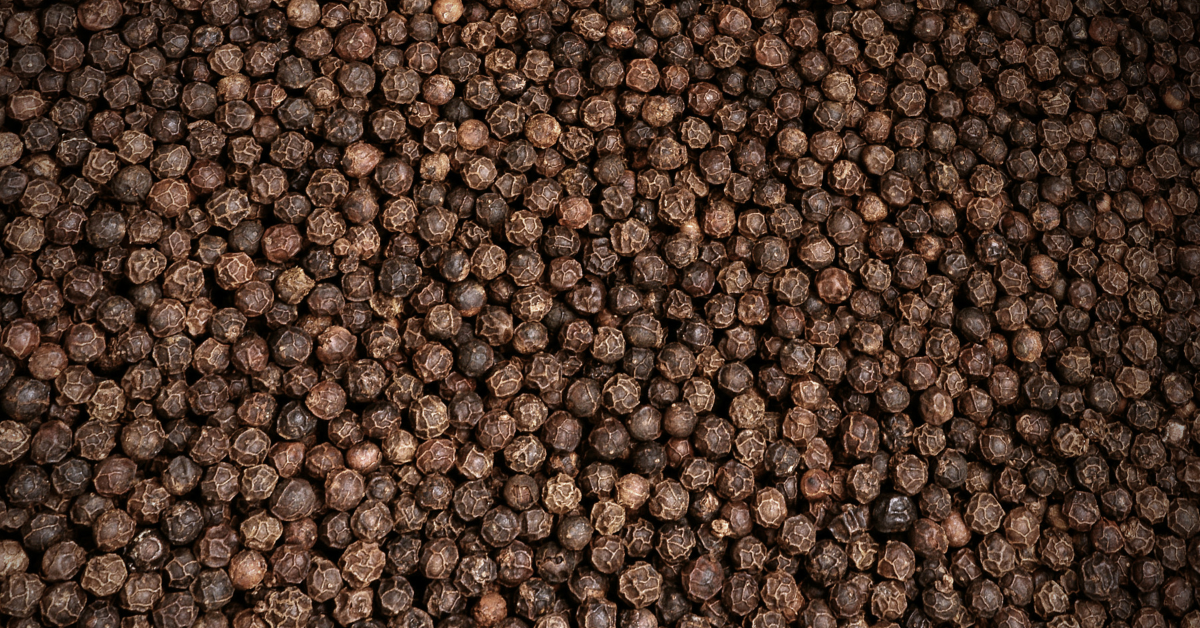

In the global spice market, pepper stands out as one of the most traded and consumed commodities. Yet, beneath its culinary appeal lies a complex and opaque supply chain often marred by issues like fraud, exploitation, and unsustainable farming practices. Enhancing transparency in the pepper supply chain can not only address these challenges but also unlock new opportunities for trust, sustainability, and profitability.
For businesses and consumers alike, the lack of transparency raises pressing concerns about the ethical and environmental footprint of pepper production. Without a clear view of where and how pepper is sourced, companies risk damaging their reputation, losing consumer trust, and facing potential regulatory backlash. Meanwhile, farmers at the source struggle with unfair compensation and market access challenges.
Key Takeaways
Black pepper has woven itself into the fabric of history, an integral and intriguing spice. Wars were waged, alliances formed and shattered, and treaties sealed or betrayed, all in pursuit of this coveted spice. Originating from the lush rainforests along the Malabar coast, pepper earned its title as the ‘king of spices.’ Its scarcity bestowed upon it an air of exoticism and mystique, contributing to its global fame and enduring legacy.
Pepper, also known as black pepper, is derived from the dried berries of the Piper nigrum vine and is renowned for its pungent flavour. Major pepper-producing countries include India, Vietnam, Indonesia, Brazil, and Malaysia. The industry encompasses cultivation, harvesting, processing, and export of pepper. The demand for pepper is driven by its extensive use in culinary applications worldwide. Pepper is not only a staple spice but also valued for its medicinal properties. The industry faces challenges such as price volatility, weather conditions affecting crop yield, and international trade dynamics. Continuous efforts are being made to enhance cultivation techniques, ensure sustainable practices, and meet quality standards. The pepper industry plays a crucial role in global spice markets, contributing to diverse culinary traditions and economies.
Indonesia ranks as the second-largest producer of black pepper (Piper Nigrum L) globally, following Vietnam and trailed by India, Brazil, and Malaysia. Although Vietnam leads in black pepper production, Indonesia holds the distinction as the largest producer of white pepper.
With a global production averaging 3,50,000 to 4,00,000 tonnes annually, India contributes significantly by producing approximately 2,60,000 tonnes per year, accounting for approximately 75% of the total world pepper production.
Pepper’s journey from the farm to your table involves multiple intricate steps, each adding its unique challenges.
1. Farming
Pepper cultivation is largely driven by smallholder farmers, particularly in tropical regions like India, Vietnam, and Brazil. These farmers often work on fragmented plots of land and rely on traditional practices. The challenges here include inconsistent yields due to climate conditions, pest infestations, and lack of access to modern farming tools.
2. Processing
Once harvested, peppercorns are dried, sorted, and processed. This step is crucial to ensure quality and consistency. However, inadequate infrastructure and outdated methods in many regions can lead to contamination or inconsistent product quality.
3. Packaging
The processed pepper needs to be packaged for distribution. This stage requires adherence to strict standards to prevent contamination and maintain freshness. Inconsistent packaging practices or poor storage facilities can degrade the quality of pepper, impacting its market value.
4. Distribution
Pepper is then transported globally, often passing through several intermediaries. This stage is where the lack of visibility becomes evident—tracking the product back to its source can be a logistical nightmare. Additionally, supply chain inefficiencies like delays and spoilage are common challenges.
The pepper supply chain involves numerous stakeholders—farmers, processors, middlemen, exporters, and retailers. Each has its processes, and without a unified system, ensuring transparency and quality becomes a monumental task.
The pepper industry may not always come to mind when thinking about environmental challenges, but its farming practices can significantly impact ecosystems. Unsustainable pepper farming, often driven by the demand for higher yields, contributes to deforestation as forests are cleared to create farmland. This leads to the loss of biodiversity, soil erosion, and disruptions to water cycles. Additionally, overuse of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides can degrade the soil and contaminate nearby water sources, further harming the environment.
A spice processing company successfully leveraged TraceX solutions to enhance its sustainability monitoring efforts, incorporating comprehensive assessments to ensure adherence to sustainable agricultural practices. By integrating TraceX’s blockchain-based platform, the company gained robust traceability capabilities, enabling them to track sustainability metrics across their entire supply chain.
There’s a growing realization that sustainable farming isn’t just beneficial—it’s necessary. Agroforestry, where pepper crops are grown alongside trees and other plants, is one such solution. This method not only reduces the need to clear forests but also enhances biodiversity, improves soil health, and creates a more resilient farming ecosystem.
Regenerative practices, like using organic fertilizers, cover cropping, and crop rotation, go a step further. These techniques replenish the soil, minimize water usage, and cut down on chemical inputs. By adopting these methods, farmers can grow pepper sustainably without compromising the environment.
Sustainability isn’t just about preserving the planet—it makes good business sense too. For farmers, sustainable practices mean healthier crops, reduced dependency on expensive chemical inputs, and access to premium markets willing to pay more for ethically sourced pepper.
For businesses, sustainability translates into stronger supply chains and compliance with international standards like the EU Deforestation Regulation (EUDR). Additionally, it builds consumer trust and loyalty, as today’s buyers are increasingly looking for ethically produced goods.
For the environment, sustainable practices ensure that ecosystems thrive, forests remain intact, and carbon emissions are reduced. It’s a holistic approach that benefits everyone involved in the pepper value chain, from farm to fork.
By focusing on sustainability, the pepper industry can secure its future while contributing to a healthier planet. It’s time for all stakeholders—farmers, businesses, and consumers—to work together for a greener, more sustainable pepper supply chain.
For businesses, these challenges translate into higher risks, inefficiencies, and potential financial losses. For farmers, it means missing out on fair compensation and access to premium markets. Addressing these issues is key to creating a resilient, transparent, and equitable pepper supply chain.
In today’s complex supply chains, technology is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity. With consumers and regulators demanding higher levels of accountability, traceability tools have emerged as game-changers for industries like pepper production. These tools provide the much-needed visibility to track products across every stage, from the farm to the retailer’s shelf.
Blockchain technology, often associated with cryptocurrency, is transforming supply chain management. Imagine a digital ledger that records every transaction in the pepper supply chain—when and where the pepper was harvested, processed, and packaged. What makes blockchain unique is that these records cannot be altered, ensuring transparency and trust.
For example, if a shipment of pepper faces a quality issue, blockchain can instantly trace the problem back to its source. Was the pepper harvested too early? Did it come from a farm using non-compliant practices? This level of detail not only improves accountability but also helps businesses make informed decisions quickly.
Digital platforms are another powerful tool for traceability. These platforms aggregate data from multiple sources—like farms, processors, and logistics partners—into a single, easy-to-navigate interface. They use technologies like GPS tracking, IoT devices, and cloud computing to offer real-time updates about the pepper’s journey through the supply chain.
The Spice Tech Company leveraged TraceX’s blockchain-powered traceability solutions to transform its online platform. This shift provided enhanced transparency and security, empowering farmers with verified data and fostering trust across the spice supply chain. The result was a more ethical and sustainable industry ecosystem, ensuring better collaboration and compliance for all stakeholders.
These platforms can also integrate compliance checks, ensuring that every stakeholder adheres to regulations like the EU Deforestation Regulation (EUDR). Additionally, they allow consumers to scan QR codes on pepper packaging to learn its origin story, building trust and transparency with the end customer.
By adopting traceability tools, companies in the pepper industry can address common challenges like quality inconsistencies, adulteration risks, and non-compliance. It’s about turning complex supply chains into transparent, efficient, and reliable systems. Technology is no longer just a tool—it’s the backbone of a sustainable and ethical pepper industry.

The TraceX Food Traceability Platform is an advanced blockchain-powered solution designed to enhance visibility, accountability, and trust across food supply chains. It ensures end-to-end traceability by recording every transaction and movement of food products, from farming and production to processing, packaging, and retail.
1. Blockchain Technology: Immutable records ensure transparency and prevent data tampering.
2. End-to-End Visibility: Tracks products across all supply chain stages, offering insights into origin, quality, and handling.
3. Compliance and Standards: Facilitates adherence to global food safety and sustainability regulations, such as EUDR and ESG frameworks.
4. Consumer Trust: QR codes enable consumers to trace the journey of their food, enhancing trust and brand loyalty.
5. Data-Driven Decisions: Provides actionable insights for optimizing operations and improving sustainability practices.
The platform is highly adaptable and used in diverse sectors, including agriculture, seafood, dairy, and beverages, to combat fraud, reduce waste, and ensure sustainability in food systems.
This technology empowers agribusinesses to transform their supply chains into transparent, efficient, and reliable ecosystems while meeting regulatory and consumer expectations.
Transparency in the pepper supply chain is no longer optional—it is a necessity. By addressing challenges like fragmented production, quality inconsistencies, and traceability gaps, businesses can build trust, ensure compliance, and promote sustainability. Leveraging technology such as blockchain traceability platforms, companies can revolutionize their operations, foster collaboration across stakeholders, and contribute to a resilient, sustainable pepper industry. The journey toward a transparent supply chain begins with the commitment to innovate and act responsibly.
Transparency ensures product authenticity, reduces risks of adulteration, and builds trust among stakeholders, from farmers to consumers.
Blockchain creates an immutable record of every transaction, providing end-to-end visibility and accountability for each stage of the supply chain.
Sustainable practices protect the environment, ensure long-term productivity, and help businesses meet global compliance standards while enhancing brand reputation.
