Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu

Imagine this: your supply chain is flagged for environmental violations, tarnishing your brand image and triggering customer backlash. Suddenly, investors and partners who prioritize ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals start looking elsewhere. Meanwhile, competitors embracing CS3D compliance gain access to new markets, unlock investor trust, and secure loyal customers. The Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CS3D) is the European Union’s groundbreaking framework designed to embed sustainability into the DNA of corporate governance.
To adhere to the CSDDD, businesses are required to recognize, avert, lessen, and report on adverse human rights and environmental effects in their operations, subsidiaries, and value chain.
It mandates businesses to proactively identify, prevent, and address negative environmental and human rights impacts across their entire value chains. By ensuring compliance, CS3D pushes businesses toward a future where profit and responsibility coexist. For companies operating without robust due diligence frameworks, non-compliance isn’t just a regulatory headache; it’s a business risk. Non-compliance penalties—such as exclusion from lucrative European markets, hefty fines, or reputational fallout—can cripple even the most established firms. The time to prepare is now.
Key Takeaways
The Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CS3D) is a transformative regulation introduced by the European Union to ensure that businesses actively identify, prevent, and mitigate negative impacts on human rights and the environment throughout their supply chains. The directive is a response to global sustainability challenges, aiming to hold businesses accountable for the actions and practices within their value chains, extending beyond their direct operations to include suppliers and partners.
The CS3D sets out a clear framework for companies operating in or interacting with the EU market to adopt sustainability-focused practices. It includes the following key features:
The CS3D impacts a broad range of businesses, both within the EU and internationally, based on specific turnover and employee thresholds:
These criteria ensure that the directive targets the largest contributors to global sustainability challenges, balancing the focus on impactful change with business capacity.
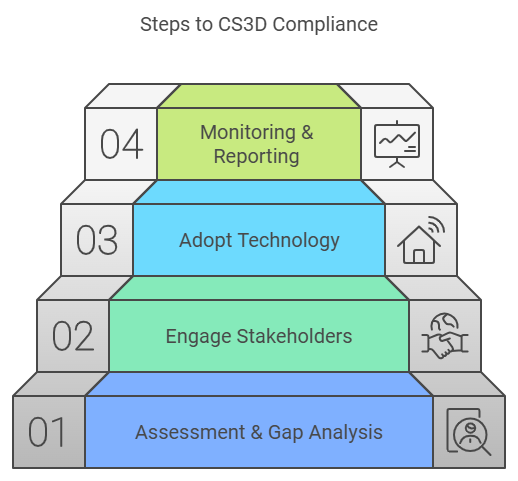
The CS3D is designed to be phased in, allowing businesses time to adapt their operations and build robust compliance frameworks. The key stages are as follows:
Member states are required to establish monitoring mechanisms, ensuring continuous compliance and holding businesses accountable.
By 2027, companies will need to establish comprehensive due diligence processes, engage suppliers transparently, and embrace technologies to manage compliance effectively. For businesses in high-risk sectors, the earlier 2029 deadline necessitates proactive planning and collaboration across their value chains to mitigate risks and ensure compliance.
The Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CS3D) comes with specific requirements that businesses must meet to ensure their practices are sustainable and socially responsible. Let’s break down these requirements in simple terms:
Think of this as creating a rulebook for sustainability. Companies need to develop and maintain policies that guide their operations and supply chains to minimize harm to the environment and human rights. This involves identifying risks, creating strategies to prevent or reduce them, and taking action when issues are discovered. For instance, if a supplier is linked to deforestation or unfair labor practices, the company must step in to resolve these problems.
This isn’t just about writing policies—it’s about actively monitoring and ensuring they’re followed, making sustainability part of the company’s DNA.
Every business under CS3D must create a roadmap showing how they’ll align their operations with global climate goals, like limiting temperature rise to 1.5°C. These are called climate transition plans, and they outline steps like reducing carbon emissions, investing in cleaner technologies, or shifting to renewable energy sources.
If a company operates in a high-emission sector, these plans are even more critical to demonstrate how they’re contributing to a more sustainable future.
Here’s where it gets serious for company leaders. Under CS3D, sustainability isn’t just the responsibility of the sustainability team—it’s also tied to executives. Companies are required to integrate sustainability metrics into their governance structures. This might include linking a portion of executive bonuses or compensation to achieving sustainability targets.
It ensures leaders are accountable and motivated to prioritize sustainability efforts, making it clear that environmental and social performance is as critical as financial success.
Companies will need to continuously monitor their operations and supply chains to ensure compliance with CS3D. This includes regularly assessing risks, auditing supplier practices, and updating policies as needed. Think of it as an ongoing health check for the company’s sustainability practices.
Governments and regulatory bodies will also oversee compliance, with potential penalties for businesses that fail to meet the standards. This makes having robust monitoring systems in place crucial for staying on track.
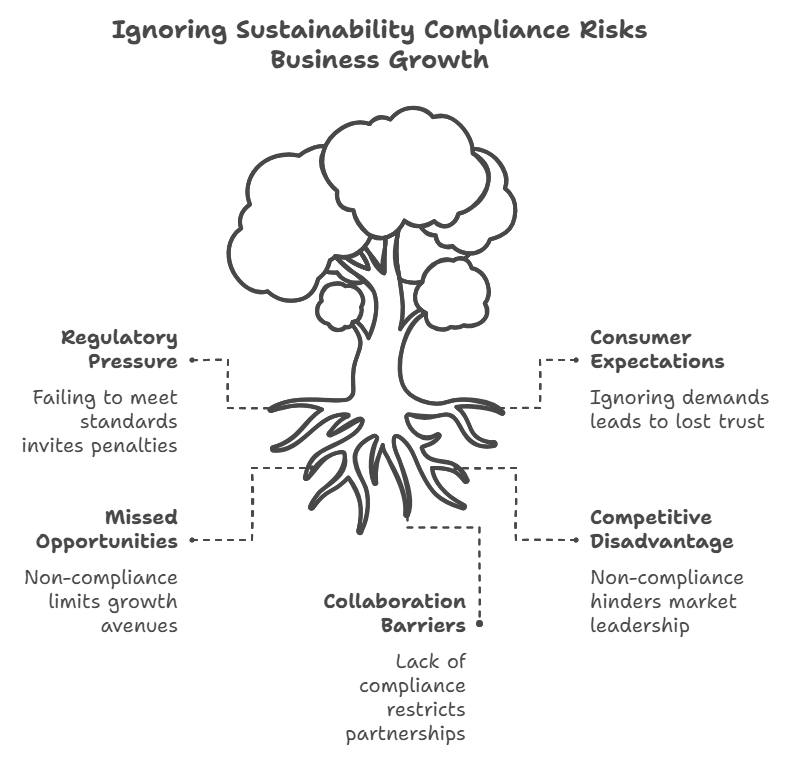
Failing to meet the requirements of the Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CS3D) is not something businesses can afford to take lightly. Here’s what’s at stake if companies fall short:
Non-compliance comes with real financial consequences. Regulatory bodies can impose hefty fines on businesses that fail to meet CS3D standards. For companies reliant on EU markets, this could also mean restricted market access or being excluded from government procurement opportunities.
Imagine losing access to a major customer base because your business wasn’t aligned with sustainability requirements. It’s a risk no company wants to take.
Sustainability is now front and center for customers, investors, and stakeholders. If a business is caught not complying—or worse, being linked to unethical practices like deforestation or labor exploitation—it can take years to rebuild trust.
Consumers are increasingly choosing brands that prioritize sustainability, and non-compliance could tarnish a company’s image, leading to lost sales and investor confidence.
Non-compliance doesn’t just result in external penalties—it can also disrupt operations internally. Businesses that fail to manage risks in their value chains may face production delays, supply shortages, or legal battles with suppliers. For example, an unresolved issue with a supplier linked to illegal logging could halt production for months.
This creates a domino effect, increasing costs and making it harder for companies to deliver on their promises to customers.
The Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CS3D) isn’t working in isolation. It aligns closely with two other key pieces of European Union legislation—the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) and the Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR). Here’s how they all fit together:
The CSRD aims to enhance and standardize the sustainability reporting of businesses. It requires large companies to disclose detailed environmental, social, and governance (ESG) information. This is where CS3D comes into play—by mandating businesses to ensure due diligence along their supply chains, CS3D directly feeds into the CSRD’s call for transparency on sustainability impacts.
For example, when a company must assess and mitigate risks related to human rights or environmental impact within its value chain, it is essentially preparing the groundwork for the kind of reporting required under CSRD. Businesses are being asked to do more than just track their own emissions or corporate policies—they need to ensure that their suppliers and partners follow suit, which is a crucial aspect of CS3D.
On the other hand, SFDR requires financial market participants to disclose how their investments align with sustainability goals. If a company is non-compliant with CS3D—failing to perform adequate due diligence on its supply chains, for example—it can face penalties, which may negatively impact its investment profile. Financial institutions, under SFDR, are keen to know if their portfolio companies have the sustainability credentials needed to align with EU green finance objectives.
In essence, the CS3D complements SFDR by addressing the broader value chain impacts, ensuring that companies not only focus on internal operations but also demonstrate how they mitigate risks across their entire supply chain in their financial disclosures.
In practice, businesses involved in deforestation-linked sectors must comply with both regulations simultaneously. For example, a cocoa exporter needs to ensure that its product is deforestation-free (EUDR), while also proving adherence to ethical labor practices and environmental risk management (CSDDD) within the same supply chain. The two regulations complement each other, with the EUDR providing a more sector-specific lens and the CSDDD offering a broad framework for responsible business conduct, creating a more holistic approach to sustainability.
This synergy underscores the importance of leveraging data-driven solutions for traceability and transparency to meet both environmental and social governance standards. By aligning with both, businesses can build stronger, more resilient supply chains while reducing the risks associated with non-compliance, positioning themselves for a sustainable future
As businesses work towards meeting the requirements set by the Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CS3D), there are a few significant challenges they need to overcome. These hurdles can complicate compliance efforts, but with the right strategies and tools in place, companies can navigate them effectively.
For example, while a company might be committed to sustainability in its operations, its supply chain may involve companies in regions with weaker environmental or labor protections. This can make it tough to guarantee that every tier of the supply chain is adhering to CS3D’s due diligence requirements. Businesses will need systems that allow them to trace and verify sustainability practices across their entire network, from raw material extraction to final product delivery.
Moreover, collecting data at scale requires robust tools and systems to manage, store, and analyze the data. This can be overwhelming for businesses that are used to working with limited data sets or relying on manual processes. Technologies like blockchain and supply chain management software can help bridge this gap by providing real-time data that is secure, accurate, and verifiable.
In addition to the initial outlay for technology and expertise, there are ongoing costs related to monitoring, auditing, and reporting on compliance efforts. Companies may also face penalties if they fail to meet deadlines or produce incomplete or inaccurate reports, adding further financial pressure.
However, it’s essential to view compliance as an investment rather than just a cost. Being ahead of regulations can offer significant long-term benefits, including access to green finance, improved brand reputation, and better risk management.
To successfully comply with the Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CS3D), businesses need to leverage technology that enhances transparency, traceability, and decision-making. The directive’s requirements push companies to not only monitor their own sustainability practices but also ensure that their suppliers, sometimes across complex global networks, meet these same standards. Let’s look at the role of key technologies that can help businesses meet these challenges.
Platforms for traceability and transparency allow businesses to monitor the flow of goods, resources, and services throughout the entire supply chain. These tools provide visibility into supplier operations and help businesses verify whether their suppliers are adhering to ethical and environmental standards.
For example, platforms like TraceX enable companies to track the origin and movement of products, helping ensure that all parts of the supply chain comply with sustainability criteria. With such platforms, businesses can easily access real-time data on their suppliers’ sustainability practices, from raw materials to the final product. This helps reduce the risk of non-compliance, fosters accountability, and supports a seamless data collection process, ensuring that businesses can confidently meet CS3D’s due diligence an
Blockchain technology is another powerful tool for CS3D compliance. Blockchain provides a secure and immutable ledger that records transactions across the supply chain, ensuring data integrity and supplier accountability. Each transaction, whether it’s the sourcing of materials or the confirmation of sustainable practices, is recorded in a way that cannot be altered, providing transparency and trust to all stakeholders.
For businesses, blockchain solutions ensure that data about suppliers’ environmental and social practices is accurate, verifiable, and resistant to tampering. This level of transparency makes it easier for companies to demonstrate compliance with the CS3D’s due diligence requirements and build trust with consumers and investors. Additionally, blockchain helps track the full lifecycle of products, ensuring that sustainability measures are implemented at every stage, from sourcing to manufacturing.
The integration of AI and predictive analytics into supply chain management can also be instrumental in meeting CS3D goals. AI-powered platforms help businesses identify patterns, assess risks, and make data-driven decisions related to sustainability. These tools can analyze large datasets from suppliers, helping businesses anticipate potential disruptions, track progress towards climate goals, and evaluate the environmental impact of their operations.
For example, predictive analytics can help companies forecast which suppliers may pose a risk due to non-compliance with sustainability standards. AI algorithms can also support companies in evaluating the effectiveness of their sustainability programs, optimizing energy use, and reducing carbon emissions across their operations. Platforms like SAP Ariba and EcoReal leverage AI to support decision-making by providing real-time insights and suggesting alternative sourcing strategies that meet both regulatory standards and company goals.

The TraceX Sustainability platform offers several features that can help companies in their compliance with the Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CS3D).
In conclusion, the Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CS3D) represents a significant shift in how companies approach sustainability, particularly in their supply chains. As businesses face increasing pressure to meet rigorous environmental and social standards, the CS3D provides a framework for ensuring responsible sourcing, reducing environmental impact, and fostering ethical practices throughout the supply chain. By embracing technology, particularly blockchain and traceability solutions like TraceX, businesses can streamline their compliance processes, mitigate risks, and enhance transparency. Ultimately, early adoption and proactive strategies will position companies for long-term success, ensuring they are not only meeting regulatory demands but also leading the way in sustainability.



WhatsApp us