Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Explore how carbon offset registries are the backbone of the carbon market, ensuring transparency, trust, and efficiency in carbon trading. Learn how these digital platforms facilitate the issuance, tracking, and retirement of carbon offsets, making it possible for businesses and individuals to invest in a greener, more sustainable future. Dive into the world of carbon market infrastructure and discover why registries are essential for achieving our climate goals.

In a world increasingly concerned with the consequences of climate change, carbon offset registries have emerged as a crucial tool for individuals, businesses and governments alike. These registries play a pivotal role in the fight against global warming by providing a structured framework for tracking, verifying and trading carbon credits.
According to Statista, the global carbon offset/carbon credit market was valued at 331.8 billion U.S. dollars in 2022. It is expected that the global carbon offset/carbon credit market will grow at a CAGR of 31 percent during the forecast period of 2023 to 2028 to reach a value of 1.6 trillion U.S. dollars.
As we delve into the fascinating realm of carbon offset registries, we will explore their significance, the mechanisms they employ, and the impact they have on mitigating green house gas emissions. Join us on this enlightening journey to better understand the key players in the battle for a more sustainable planet.
Carbon market accountability, credibility, and transparency are all ensured through carbon offset registries. They enable effective trade, standardize measurements, confirm emissions reductions, and stop double counting. Registries are essential for fostering compliance, increasing stakeholder trust, and fostering real environmental impact.
Carbon offsets serve as a valuable tool for businesses committed to achieving net-zero emissions or reducing their carbon footprint. These offsets represent one metric tonne of carbon that has been either prevented from entering the atmosphere or captured. To support this, carbon offset registries are established, responsible for issuing credits following specific certification protocols. These registries maintain a record of available offsets in the market.
Carbon offset registries are platforms or databases that keep track of and verify the carbon credits produced by projects that reduce emissions. They play a critical role in maintaining the validity and transparency of these credits, avoiding double counting, and facilitating effective trading in the carbon market. A trustworthy mechanism for tracking and confirming emissions reductions is provided through registries, which are essential in tracking the lifecycle of carbon credits from their creation to retirement.
Carbon Offset registries establish standardized protocols for project registration to issue carbon credits, maintain a comprehensive record of available credits in the market, and most importantly, ensure that the environmental benefits tied to these credits are not double counted. When two different entities lay claim to the same credit, it effectively halves the associated environmental impact, as there’s only one metric tonne of carbon reduction in question.
These registries meticulously monitor credit ownership, assigning each credit a unique serial number. This information is made publicly accessible through a ledger. When a credit is purchased by an entity to offset their emissions, the registry takes swift action by retiring that credit on the ledger, ensuring it cannot be acquired by another party.
By offering a unified platform where comprehensive information on carbon offset projects and credits is made available to the public, carbon offset registries ensure transparency and accountability. This openness enables interested parties to confirm the projects’ credibility and ensures that the projected emissions reductions are true. Additionally, registries avoid duplicate counting by making sure that each credit is only tallied for once.
Carbon offset registries come in three main types:
Government-Operated: Managed by government agencies, these registries ensure compliance with national regulations and emission reduction targets.
Private: Run by private organizations, these cater to voluntary carbon markets, allowing businesses and individuals to offset emissions voluntarily.
International: Operating globally, these registries facilitate cross-border transactions, ensuring consistency in standards and methodologies for projects involving multiple countries.
Government-run databases, like the Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) established by the UN, are essential to the success of global carbon reduction initiatives. These initiatives, which are subject to stringent international regulations, support sustainable development initiatives in numerous nations. Private registers, meanwhile, like The Gold Standard, concentrate on voluntary markets and uphold strict standards for emission reduction programs. They support organizations and people who want to voluntarily reduce their carbon footprints, ensuring the legitimacy and effectiveness of such initiatives.
There are numerous procedures involved in registering and tracking carbon offsets in these registers. The first step is for project developers to submit comprehensive proposals to the relevant registry, along with techniques and anticipated emissions reductions. These suggestions are assessed by the register to make sure they comply with predetermined standards and criteria. The project can produce carbon offset credits based on confirmed emissions reductions once it has been certified.
The reliability of offsets is greatly enhanced by third-party verification. Emission reduction projects are evaluated by independent auditors to ensure their authenticity and conformance to predetermined requirements. Their independent examination guarantees precise emissions reduction measurement, monitoring, and reporting. They increase openness and confidence by offering an outside viewpoint, ensuring purchasers and investors that the offsets are real and significantly aid in carbon reduction efforts.
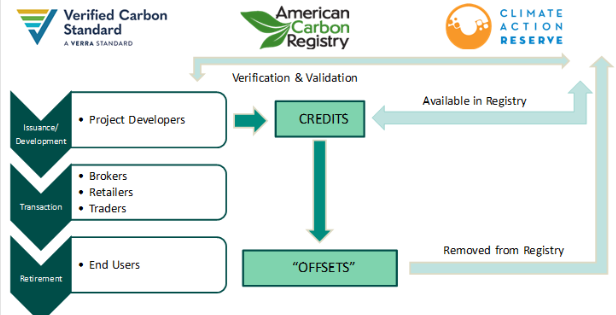
Several renowned carbon offset registries play a vital role in shaping the global carbon market. Verra, with its Verified Carbon Standard (VCS), sets a benchmark for high-quality carbon offsets on a global scale. The American Carbon Registry (ACR) specializes in North American projects, ensuring rigorous standards and third-party verification. The Gold Standard is a globally recognized certification body emphasizing both environmental integrity and sustainable development. Additionally, the Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) operates under the UNFCCC, encouraging emission reduction projects in developing nations. These registries establish credibility, transparency, and consistency in the offset market, fostering environmental sustainability worldwide.
Verra’s Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) is globally respected, emphasizing various project types like renewable energy and forestry, ensuring high-quality carbon offsets. The American Carbon Registry (ACR) focuses on North American projects, maintaining stringent standards and third-party verification for credibility. The Gold Standard stands out for its dual emphasis on environmental integrity and sustainable development, certifying projects with robust environmental and social benefits. The Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) encourages emission reduction projects in developing countries, promoting sustainable development and aiding global climate goals.
Despite being important, carbon offset registries have difficulties like the possibility of double counting. A single offset could be used by several parties if it is not carefully controlled, which would undermine the success of efforts to reduce emissions. Furthermore, it is crucial to guarantee complete transparency during the verification process. Without sufficient transparency, critics contend, there may be questions about the veracity of offset initiatives. Continuous monitoring, stringent protocols, and reliable verification methods are essential to overcome these issues.
To tackle challenges like double-counting and transparency, carbon offset registries implement stringent protocols and rigorous verification processes. They employ unique serial numbers for each credit, preventing double-counting. Independent third-party audits ensure projects meet high standards, enhancing transparency and credibility. Registries also enhance public access to project data, fostering accountability. Ongoing efforts to refine and standardize these practices continue, ensuring the reliability and effectiveness of carbon offset initiatives in the fight against climate change.
TraceX’s DMRV solutions offer a streamlined and comprehensive approach to tracking emission reductions. By providing real-time data, reliable verification and transparent reporting, we empower stakeholders to have confidence in the authenticity of carbon offsets.
The world of carbon offsetting is constantly changing, with an increasing focus on creative, high-impact initiatives and wider international cooperation. As a result, carbon offset registries are quickly altering to satisfy evolving needs. They are broadening their focus to incorporate many project types, such as technical advancements and sustainable agriculture, demonstrating a more comprehensive approach to emission reduction. Additionally, registries are increasing transparency by utilizing blockchain technology for safe, open transactions.
Emerging trends in carbon offset registries reflect a dynamic shift toward innovation and inclusivity. Registries are increasingly embracing blockchain technology, ensuring secure, transparent, and tamper-proof tracking of carbon credits. Moreover, there’s a rising focus on nature-based solutions, emphasizing projects like afforestation and ecosystem restoration to enhance biodiversity and sequester carbon. Social and co-benefit projects, which provide socio-economic advantages to local communities, are gaining traction, aligning environmental goals with social equity.
In conclusion, carbon offset registries are pivotal in the fight against climate change, ensuring credibility, transparency, and accountability in carbon offset initiatives. As the world grapples with the urgent need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, these registries play an increasingly crucial role in promoting sustainable practices and fostering a greener, more environmentally responsible future. With evolving technologies, global collaborations, and a broader array of projects, carbon offset registries continue to adapt and innovate, reflecting a dynamic landscape that aligns with the ever-changing demands of our planet. As businesses, individuals, and governments increasingly rely on these registries, they contribute significantly to the global efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change, marking a positive step towards a more sustainable and resilient world.
