Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Discover the Benefits of No-Tillage for Sustainable Agriculture. Explore how this innovative farming practice enhances soil health, reduces erosion, and promotes long-term environmental sustainability. Learn how to implement no-tillage techniques and revolutionize your farming approach for a greener future.

Traditional farming practices, especially tilling, have led to soil erosion, water depletion, and decreased biodiversity. No till farming is a revolutionary practice that promises to address these issues. By eliminating tillage, this method not only reduces soil disturbance but also promotes healthier ecosystems and enhances soil carbon storage.
According to USDA, no-till farming can reduce soil erosion by up to 90% compared to conventional tillage methods.
However, despite its clear environmental benefits, many farmers face challenges in adopting no-till farming due to initial investment costs, knowledge gaps, and resistance to change. This blog explores how no-till farming can transform agriculture for the better and overcome these barriers for a more sustainable future.
Key Takeaways
No-till farming also known as zero tillage or direct seeding is a sustainable agriculture practice where the soil is left undisturbed or minimally disturbed during the planting process.
No-till farming preserves the soil’s natural structure and composition by leaving it undisturbed. Crops are simply sown into the soil without turning it over in place of plowing. The preceding crop’s residues are often kept on the surface as a protective layer because they add organic matter, prevent erosion, and help the soil retain moisture.
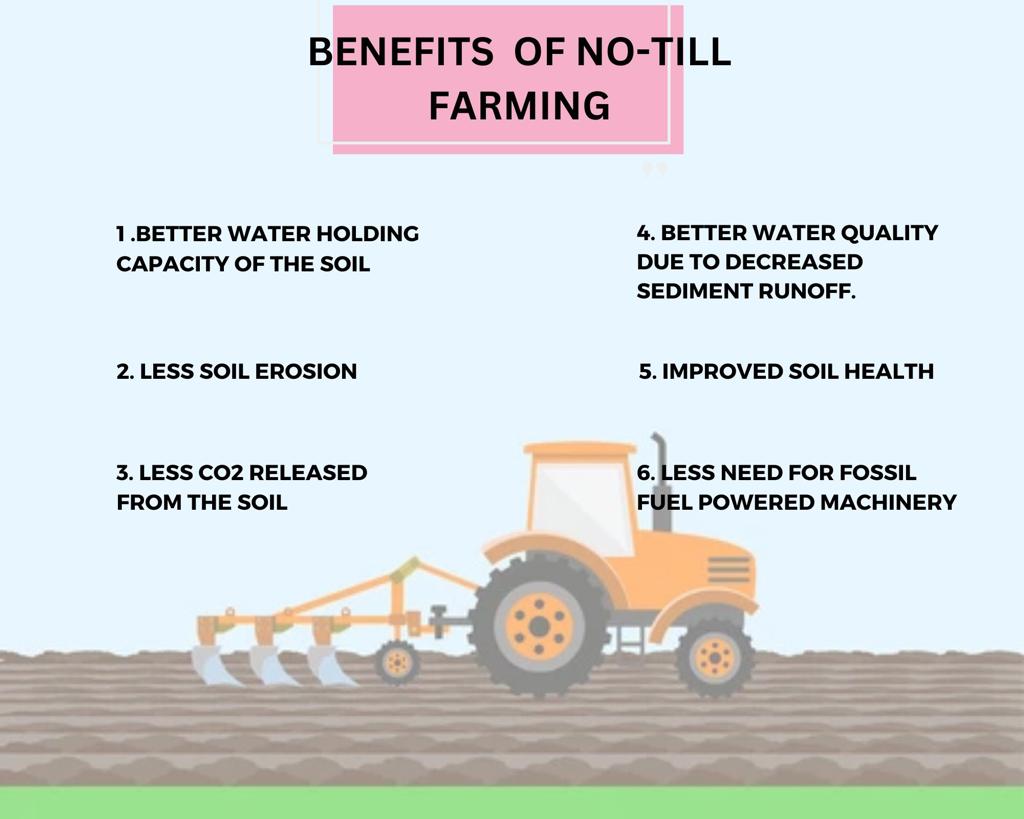
Soil Health and Conservation: No-till farming encourages the improvement of soil health. An unaltered soil structure enables stable aggregates to form, which improves water infiltration and root penetration. The risk of wind and water erosion is decreased by keeping the soil’s natural structure, safeguarding priceless topsoil, and guarding against nutrient loss. No-till farming helps prevent soil erosion by leaving the soil undisturbed. The soil is kept grounded and safeguarded when agricultural wastes are left on the surface. By protecting the soil from the effects of rains and wind, this covering prevents erosion brought on by water runoff and wind. No-till farming helps sustain soil productivity and reduces the loss of fertile topsoil by reducing erosion. By encouraging the production of solid aggregates, increasing water infiltration, and facilitating root penetration, no-till farming enhances soil structure. Crop leftovers used as mulch improve water management by lowering soil evaporation and boosting soil’s ability to store water.
Water Management and Conservation: By lowering water runoff, enhancing water infiltration, and boosting water holding capacity, no-till farming improves water management and conservation By reducing soil moisture loss owing to evaporation and maximizing the amount of water available for plant growth, crop wastes can be used as mulch to promote sustainable agriculture. By enhancing soil structure and lowering soil erosion, no-till farming helps to reduce water runoff. Crop residues operate as a shield, shielding the soil surface from direct contact with rainwater, which would otherwise cause runoff. Instead, water seeps into the soil, where it is accessible to plants, and less water is lost to evaporation. Water infiltration rates are increased by the unaltered soil structure in no-till systems. Water can permeate the soil more effectively when there are stable soil aggregates present from no-tillage. This promotes plant growth and lowers the possibility of drought stress by increasing the quantity of water that can be stored in the root zone. Improved soil water retention capacity results from no-till farming.
Biodiversity and Habitat Preservation: By giving beneficent insects a place to live and food to eat, encouraging microbial variety, supporting wildlife, preserving soil fauna, and fostering the establishment of native plants, no-till farming practices protect biodiversity and habitats. This encourages a healthy, sustainable agricultural ecosystem. By limiting soil disturbance, using fewer chemicals, and encouraging biodiversity, no-till farming helps to preserve natural ecosystems. No-till farming supports the long-term health and sustainability of the environment by conserving the integrity of soil structure, nutrient cycles, and habitat diversity. This contributes to the maintenance of natural ecosystem equilibrium. By minimizing soil disturbance, lowering chemical inputs, and fostering biodiversity, no-till farming helps to preserve natural ecosystems
Carbon Sequestration and Climate Change Mitigation: By increasing soil organic carbon, no-till farming reduces climate change by sequestering carbon in the soil The amount of soil disturbance is kept to a minimum, and crop residue retention is encouraged, which lowers carbon emissions and makes agricultural systems more resilient to climate-related problems. Increased soil organic carbon (SOC) levels are a result of no-till farming’s contribution to the accumulation of organic matter in the soil. Carbon inputs to the soil are increased by preserving crop residues and causing as little soil disturbance as possible. As a result, the amount of greenhouse gases is decreased since the carbon is sequestered from the atmosphere and stored in the soil. Compared to regular tillage, no-till farming techniques help cut down on carbon emissions.
No-till farming plays a vital role in achieving carbon-neutral agriculture. By eliminating traditional tillage, this practice reduces soil disturbance, which helps to retain organic carbon in the soil. It also minimizes greenhouse gas emissions from machinery and enhances soil’s natural ability to sequester carbon. Coupled with cover cropping and crop rotation, no-till farming supports healthy ecosystems, reduces erosion, and promotes biodiversity, making it an integral part of sustainable, carbon-neutral farming systems.
Technology plays a pivotal role in capturing, monitoring, and optimizing no-till farming practices. It helps farmers navigate the complexities of no-till methods by providing tools that streamline operations, improve soil management, and ensure better crop yields.
The TraceX Farm Management Platform plays a significant role in supporting no-till farming practices by leveraging advanced technologies to enhance soil health, monitor field conditions, and provide precise data for decision-making.
TraceX integrates soil health monitoring into its platform, offering real-time data on key soil parameters, such as moisture levels, temperature, and compaction. This is crucial for no-till farming, where the soil structure is preserved, and any changes need to be carefully monitored. By using this data, farmers can track soil health over time, identifying areas that may need additional attention, such as compaction or nutrient imbalances. This proactive approach ensures that the soil remains fertile without the need for disruptive tilling.
A leading agribusiness partnered with TraceX’s sustainability platform to pioneer sustainable agricultural practices and land restoration through regenerative techniques.
Key Highlights:
By integrating data-driven insights and sustainable methodologies, the initiative demonstrated measurable improvements in soil health and showcased the potential of technology to support environmental and agricultural sustainability goals.
TraceX’s traceability solutions enable farmers to track the journey of their products throughout the supply chain, from farm to market. This feature is particularly valuable for no-till farmers who want to ensure the sustainability of their practices. By verifying that their crops are grown using sustainable methods, farmers can access premium markets and certifications for environmentally friendly practices, enhancing their competitiveness in the market.
No-till farming is an innovative and environmentally friendly approach to agriculture that can significantly reduce soil erosion, conserve water, and enhance soil health. By minimizing soil disturbance, it helps maintain biodiversity, reduces the carbon footprint of farming, and can lead to more sustainable food production in the long term. While the adoption of no-till farming may pose challenges like high initial costs and the need for specialized equipment, the long-term benefits of improved soil health, water conservation, and reduced input costs make it an attractive choice for farmers committed to sustainable practices. With advancements in technology and farm management solutions like TraceX, farmers can effectively monitor and optimize no-till farming practices, paving the way for a greener, more sustainable agricultural future.
No-till farming is an agricultural practice where soil disturbance is minimized, helping to preserve soil structure, enhance water retention, and reduce erosion. It contributes to sustainability by promoting healthier soils, reducing the need for chemical inputs, and conserving water.
The main challenges include the high initial costs of specialized equipment, the need for farmers to adapt to new farming techniques, and potential resistance due to cultural and behavioral factors. Additionally, there are knowledge gaps regarding soil management in no-till systems.
Technology like TraceX helps farmers track and optimize their no-till practices by providing real-time soil health data, precision agriculture tools, and enhanced traceability from farm to market. This ensures better decision-making, increased efficiency, and long-term sustainability.
