Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Unlock the power of supply chain visibility across tiers with our comprehensive guide. Discover strategies, tools, and best practices to enhance collaboration, mitigate risks, and optimize operations for greater efficiency and resilience.
As companies grow and globalize, the complexity of these supply chains increases, making it more challenging to ensure everything operates smoothly. A multi-tier supply chain is one where goods and services pass through several levels of suppliers, often across different countries and regions, before reaching the final consumer. With this complexity comes a pressing need for supply chain transparency. Simply put, businesses can no longer afford to be in the dark about what’s happening at every level of their supply chain
According to a survey conducted by Deloitte on Chief Procurement Officers (CPOs), just 15% of them reported having visibility beyond their tier-one suppliers. Gaining visibility into tier-one suppliers alone is already a significant challenge.
From raw materials to finished products, it’s vital for companies to have clear visibility into how their goods are sourced, processed, and transported. This visibility, or traceability in supply chains, ensures that companies can track the journey of products and make informed decisions that promote sustainability, compliance, and overall supply chain efficiency.
Laws around sustainability and ethical sourcing, such as the EU Deforestation Regulation (EUDR), are making it mandatory for businesses to show exactly where and how their materials are sourced. In this article, we’ll dive deeper into how improving transparency and traceability can strengthen your multi-tier supply chain, helping your business stay competitive, compliant, and responsible.
Key Takeaways
At its core, a multi-tier supply chain is a supply chain that includes several levels of suppliers or vendors, each providing goods or services that contribute to the final product. In food and agriculture supply chains, the journey might begin with sourcing raw materials such as grains, fruits, or livestock. Then, it moves to suppliers who provide ingredients or processed materials, like flour, oils, or packaged produce. Finally, the supply chain leads to processing facilities or distribution centers where the final food products are packaged and prepared for retail. Supply chain Traceability allows each step to be tracked and managed to ensure food safety, quality, and compliance with regulations. Each of these suppliers is part of the multi-tier supply chain, which means the company has to track and manage relationships with multiple vendors at different levels.
In short, multi-tier supply chain management involves understanding and overseeing each level of the chain— from the first-tier suppliers who provide direct materials to the second-tier suppliers who might supply raw materials for the components, and beyond. The more complex the product, the more tiers exist in the supply chain. The goal is to ensure that every part of the supply chain works efficiently, and that products reach the consumer in the best condition, on time, and in a sustainable way.
Supply chain visibility refers to the ability of organizations to track and monitor the movement of goods, information, and resources across various stages of the supply chain in real-time or near real-time. It involves gaining insights into inventory levels, production processes, transportation activities, and other relevant data points to facilitate informed decision-making and enhance operational efficiency.
Visibility in supply chain management is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it enables organizations to identify potential bottlenecks, delays, and inefficiencies within their supply chains, allowing them to proactively address issues and minimize disruptions. Additionally, enhanced visibility enables better demand forecasting, inventory management, and resource allocation, leading to cost savings and improved customer satisfaction. Moreover, in an increasingly complex regulatory environment, visibility helps organizations ensure compliance with various industry standards and regulations.
Supply chains are typically divided into multiple tiers, each representing different stages of production, distribution, and procurement. Understanding and managing these supply chain tiers is critical for organizations to gain comprehensive visibility into their operations. Tier-one suppliers directly supply goods or services to the focal organization, while tier-two and subsequent tiers consist of suppliers further upstream in the supply chain. Each tier plays a vital role in the overall supply chain network, and visibility across these tiers enables organizations to identify dependencies, assess risks, and optimize performance effectively.
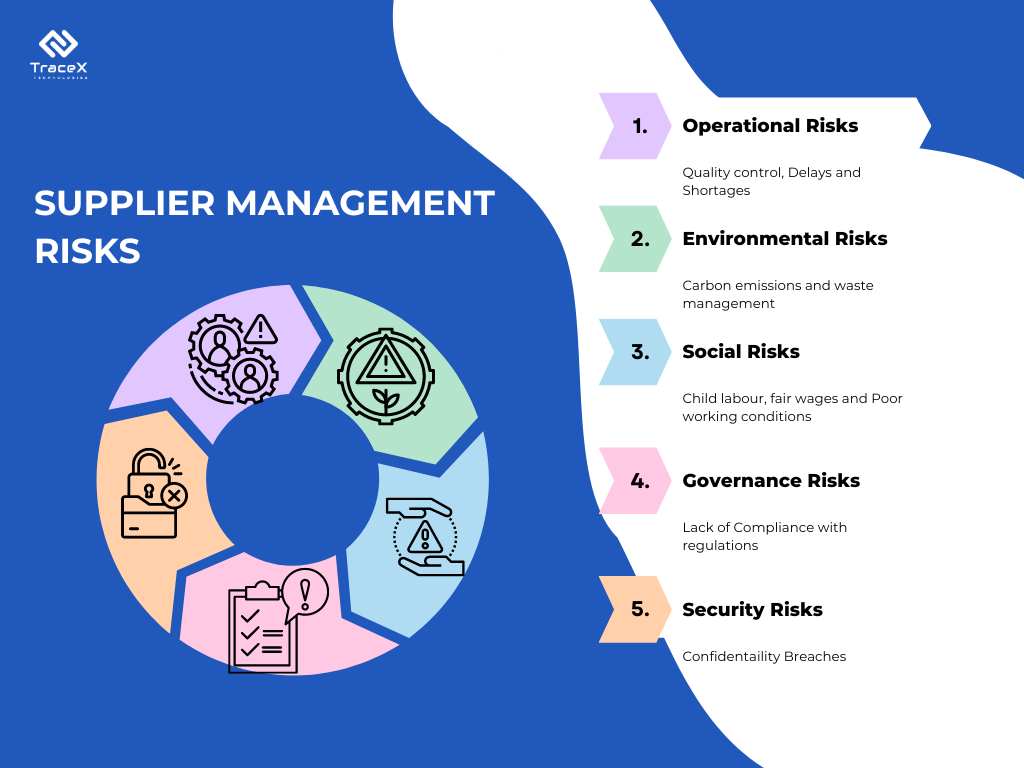
1. Enhanced Flexibility and Scalability: Multi-tier supply chains allow businesses to scale operations quickly by leveraging various suppliers. This flexibility helps companies respond to market demands more effectively.
2. Cost Efficiency: By diversifying their supplier base, organizations can reduce costs associated with sourcing materials. This can lead to competitive pricing and improved profit margins.
3. Innovation Opportunities: Collaborating with multiple tiers of suppliers can foster innovation. Companies can access new materials, technologies, and production techniques that enhance product offerings.
4. Risk Mitigation: Understanding the entire supply chain helps businesses identify potential risks associated with specific suppliers or regions. This knowledge enables proactive risk management strategies.
5. Sustainability Compliance: As consumers increasingly demand sustainable practices, companies must ensure that their entire supply chain adheres to environmental and social governance (ESG) standards. Multi-tier visibility allows organizations to track compliance throughout the supply chain.
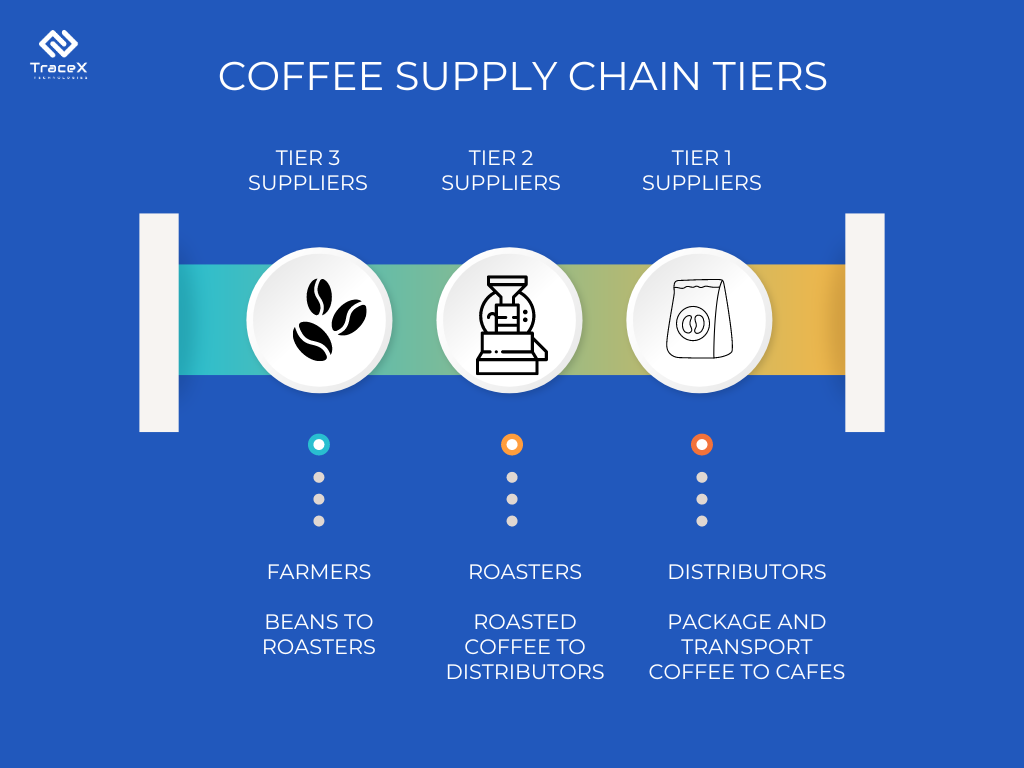
Each supply chain tier fulfills specific roles and functions that contribute to the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the supply chain. Tier 1 suppliers typically have direct relationships with the focal organization, supplying critical components or finished products. Tier 2 and subsequent tiers provide the necessary inputs and resources for Tier 1 suppliers, enabling the production process to proceed smoothly. Additionally, each tier may have its own set of suppliers, subcontractors, and logistics partners
Start by gaining visibility into the first-tier suppliers and work your way down the chain. Ensuring transparency from the beginning helps build a strong foundation for traceability.
Platforms like TraceX provide comprehensive end-to-end visibility, allowing businesses to track products across all supply chain tiers, from raw materials to the final product.
Regularly review and audit supply chain data to ensure compliance and identify potential risks, helping maintain up-to-date visibility and avoid issues down the line and facilitates due diligence.
Using third-party auditors and certifications ensures independent verification of supply chain practices, enhancing transparency and providing credibility to your traceability efforts.
The TraceX traceability platform addresses challenges in multi-tier supply chains by offering end-to-end visibility, ensuring transparency across all tiers. It integrates data from various sources, eliminating data gaps, and improves interoperability with existing systems. TraceX uses advanced blockchain technology to maintain secure, immutable records, allowing businesses to track products in real-time. With its audit trail, the platform enhances compliance and reduces risks related to supply chain transparency, ensuring better management of each tier’s data.
Improving transparency and traceability in multi-tier supply chains is crucial for risk management, compliance, and sustainability. By adopting advanced technologies like blockchain ,IoT, and satellite monitoring, businesses can gain real-time visibility and ensure data accuracy across all supply chain levels. Regular audits, the use of certified suppliers, and integrated traceability software can further streamline the process, enhancing trust and ensuring better management of goods.
Common challenges include data gaps, lack of standardization, and interoperability issues between systems.
Traceability software offers end-to-end visibility, tracks goods in real-time, and ensures compliance, reducing risks and improving efficiency.
Collaboration ensures that all stakeholders follow standardized practices, which are essential for achieving accurate data and ensuring consistent traceability across the supply chain.
