Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Discover 4 transformative approaches for food system transformation—sustainable agriculture, circular economy, nature restoration, and plant-based diets—designed to reshape global food sustainability and resilience.

With increasing pressure on our global food systems from climate change, resource depletion, and growing populations, the way we produce, distribute, and consume food needs a radical overhaul. Food system transformation is no longer just an option
Despite the urgent need for change, many businesses and farmers are struggling to adapt to these demands. Outdated practices and fragmented supply chains are still the norm, and without actionable steps, the gap between sustainability goals and reality keeps widening.
Food systems are responsible for approximately one-third of global greenhouse gas emissions, and agriculture is the predominant consumer of land and water, using 70% of freshwater resources.
In a transformative shift, food systems are evolving from mere contributors to climate change to powerful accelerators of climate action. As we stand at the intersection of agriculture, food production, and environmental sustainability, there is a growing recognition of the pivotal role food systems play in shaping the climate narrative. So, what are the transformative approaches that can drive this much-needed shift?
Key Takeaways
Food systems encompass all activities involved in producing and consuming our food daily spanning from farms to tables to waste. These systems include any processes related to the production, aggregation, processing, distribution, consumption, or disposal of food.
It’s imperative to overhaul our food systems. While they have sustained a growing populace, the environmental cost is increasingly untenable. Current food systems frequently encroach on natural ecosystems, contribute to pollution, worsen rural poverty, and are linked to significant health issues. Failures in both the market and government create substantial costs that affect society and the environment.
The hidden environmental, health, and poverty costs associated with these systems are estimated at nearly US$12 trillion annually, surpassing the US$10 trillion generated in market value.
Current food systems significantly contribute to climate change through emissions, deforestation, and resource depletion. Transformation is imperative, shifting food systems from climate change drivers to accelerators of climate action is crucial. Sustainable practices, reduced emissions, and responsible resource management are key to mitigating their environmental impact.
The need for urgent action on the impacts of climate change on agrifood systems has never been more evident, as highlighted in recent reports from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. To withstand the current and future challenges posed by climate change, agrifood systems must enhance resilience, drawing insights from successful practices to foster transformative adaptation policies, plans, and actions. Aligned with the goals of the Paris Agreement, which advocates limiting the global average temperature increase to well below 2 °C and striving for 1.5 °C above pre-industrial levels, there is a crucial demand for swift, profound, and sustained reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, particularly from agrifood systems. Coherent climate action within agrifood systems, tailored to national contexts and capacities, holds significant potential to generate co-benefits for adaptation, mitigation, and the achievement of broader Sustainable Development Goals.
Greenhouse gas emissions from food systems arise primarily from Agricultural practices, including methane from livestock and nitrous oxide from fertilizers. Supply chain and distribution processes also contribute, involving energy-intensive transportation and storage. Addressing emissions requires sustainable farm management, reduced reliance on high-emission fertilizers, and optimizing supply chains for efficiency and lower environmental impact.
Land use change and deforestation in food production contribute to habitat loss and biodiversity decline. These practices lead to ecological imbalances and increased carbon release. Addressing this involves sustainable land management and reforestation efforts.
Additionally, water usage and pollution, often stemming from agricultural runoff and inefficient irrigation, pose significant challenges. Adopting water-efficient farming methods, implementing proper waste management, and promoting eco-friendly agricultural practices are essential to mitigate the negative impacts on water resources and ecosystems.
Contemporary food systems frequently rely on fossil fuels, notably for pesticides, synthetic fertilizers, and plastics, making them energy intensive. In contrast, agro-ecological farming harnesses local and traditional knowledge to adapt sustainably, prioritizing soil health, biodiversity, and the preservation of nature. Embracing sustainable agriculture practices is paramount for mitigating environmental impacts.
Agroecology promotes a holistic approach, integrating ecological principles into farming, fostering biodiversity, and reducing reliance on chemicals. This enhances soil health and resilience.
Precision farming utilizes technology to optimize resource use, employing data-driven techniques for precise irrigation, fertilization, and pest control. This not only improves efficiency but minimizes environmental footprint. Both agroecology and precision farming play pivotal roles in fostering sustainable agriculture, addressing challenges like soil degradation and resource depletion while enhancing productivity for a more resilient and eco-friendly food production system.
According to the UN, around 13% of food produced globally is lost between harvest and retail and 17% is wasted.
Circular food systems aim to enhance sustainability by addressing key issues. Firstly, by reducing food waste through efficient production, distribution, and consumption practices, we can minimize environmental impact. Secondly, recycling and upcycling food waste into valuable resources contribute to a closed-loop system. These approaches not only mitigate the ecological footprint but also promote a more resilient and resource-efficient food supply chain, fostering a harmonious balance between environmental preservation and human consumption.
Nature could contribute up to a third of emission reductions needed by 2030 to limit warming to 1.5C and help countries adapt to climate change
Nature restoration serves as a catalyst for expediting climate action by actively contributing to carbon sequestration, enhancing biodiversity, and fortifying ecosystems. This process involves the revitalization of natural habitats, afforestation efforts, and sustainable land management practices, collectively aiding in mitigating climate change impacts. Through the restoration of ecosystems, we not only bolster nature’s resilience but also unlock a potent strategy for achieving carbon neutrality and promoting overall environmental sustainability.
According to IPCC, healthier diets are also more climate- and nature-friendly, as they contain fewer animal-based foods and more plant-based foods, particularly pulses and plants.
Plant-based diets and alternative proteins offer a sustainable shift in our approach to nutrition. By emphasizing plant sources and innovative protein substitutes, we reduce reliance on traditional animal agriculture, lowering its associated environmental burdens. This dietary shift not only supports biodiversity and decreases greenhouse gas emissions but also aligns with health-conscious choices. Embracing plant-based diets and alternative proteins is a pivotal step towards a more environmentally friendly and ethical food system.
Technology plays a vital role in fostering climate-resilient food systems. Firstly, digital farming and precision agriculture leverage data-driven insights, sensors, and automation to optimize crop yields, conserve resources, and adapt to changing climates. Secondly, blockchain technology enhances transparency in the supply chain by enabling secure, traceable transactions, ensuring the authenticity of food products. This transparency boosts accountability and facilitates sustainable practices. Thirdly, innovation in food processing and distribution, powered by technology, enables more efficient and eco-friendly methods, reducing waste and energy consumption. Collectively, digital transformation contributes to building resilient food systems capable of withstanding the challenges posed by climate change, while promoting sustainability, transparency, and efficiency across the entire food production and distribution lifecycle.
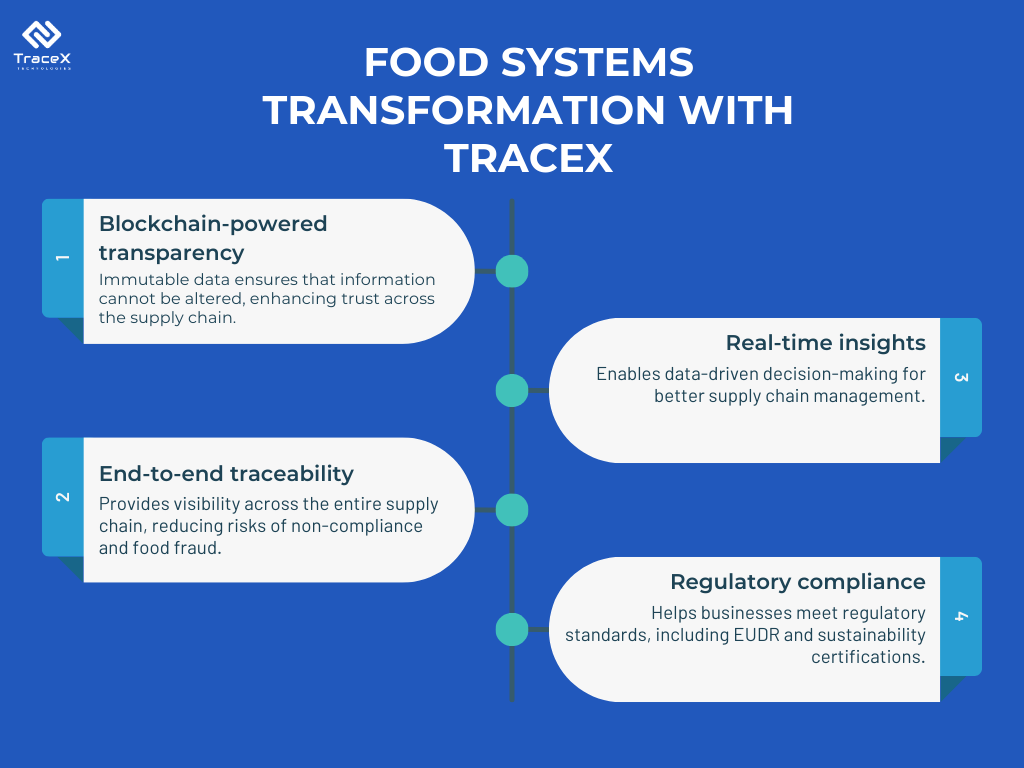
TraceX is an innovative sustainability platform that addresses the evolving challenges in food systems, agriculture, and supply chains, helping businesses meet stringent regulations and sustainability goals through its robust technology solutions. Here’s an overview of the platform’s key offerings:
TraceX supports businesses aiming to implement sustainability practices by providing tools to monitor and report on environmental impacts across the supply chain. This includes tracking carbon emissions, land use, water consumption, and biodiversity conservation. By leveraging real-time data and blockchain, the platform helps agribusinesses, food brands, and carbon project developers achieve their sustainability targets, aligning their practices with global environmental standards.
Explore our Sustainability Platform
The platform includes comprehensive DMRV capabilities that streamline the process of monitoring and verifying sustainability metrics, such as carbon sequestration or emissions reductions. This solution provides transparency and accuracy, which are critical for carbon credits, emissions reporting, and climate finance. TraceX’s DMRV tools enable stakeholders to verify their environmental claims with credibility and ensure compliance with evolving sustainability regulations.
Explore our DMRV Platform
TraceX plays a key role in helping businesses comply with the **EU Deforestation Regulation** (EUDR). The regulation mandates that commodities like soy, palm oil, coffee, cocoa, and wood entering the EU must not contribute to deforestation. TraceX provides tools to trace the origin of these products, ensuring transparency from farm to fork. The platform’s blockchain-based traceability ensures that businesses can meet EUDR requirements by monitoring land use and forest management practices along the supply chain.
Explore our EUDR Compliance Platform
With its farm management solution, TraceX empowers farmers and agribusinesses to optimize their operations. The platform offers features to monitor crop health, soil conditions, weather patterns, and resource usage. This data-driven approach enables more efficient farming practices, leading to higher productivity, reduced environmental impact, and enhanced sustainability.
Explore our Farm Management Platform
At its core, TraceX is a food traceability platform designed to ensure transparency across the food supply chain. Utilizing blockchain technology, TraceX offers end-to-end traceability, from the farm to the consumer, ensuring that every step of the supply chain is recorded and tamper-proof. This enhances food safety, builds trust with consumers, and helps businesses comply with food safety regulations.
Explore our Food Traceability Platform
Incorporating these 4 transformative approaches—sustainable agriculture practices, circular economy models, nature restoration, and plant-based diets or alternative innovations—offers a powerful pathway to reshape the global food system. Each of these strategies addresses critical aspects of environmental impact, resource efficiency, and food security. By adopting these approaches, we can create a more resilient, sustainable, and equitable food system that benefits not just the planet but also future generations.
