Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Learn how integrating agroforestry carbon credits into corporate sustainability strategies can help businesses meet climate goals while supporting local communities and promoting biodiversity. Explore the benefits, challenges, and best practices for maximizing impact.
As climate change and biodiversity loss threaten both ecosystems and global economies, businesses are facing increasing pressure to take meaningful actions that go beyond mere pledges. However, many companies struggle to achieve their carbon neutrality goals due to the limitations of traditional carbon offset mechanisms. Agroforestry-based carbon credits can serve as a powerful tool to drive corporate carbon offset strategies, offering a credible, impactful way to meet emissions targets while supporting regenerative agriculture and sustainable livelihoods.
According to research reports, in 2023, the value of the carbon credit market related to agriculture, forestry, and land use was estimated at $6,283.0 million. It is projected to expand at a CAGR of 31.49%, reaching $97,100.4 million by 2033. This market is experiencing significant growth fueled by improvements in sustainable practices and innovative technologies.
The integration of trees into farming landscapes — Agroforestry is a sustainable practice that offers both environmental and social benefits. By enhancing carbon sequestration, supporting biodiversity, and improving soil health, agroforestry provides a nature-based solution to climate change while fostering community resilience.
Key takeaways
Agroforestry carbon credits are a unique type of carbon offset derived from agroforestry systems, which integrate trees and shrubs into agricultural landscapes. Unlike traditional farming, agroforestry combines crops and trees, creating a mutually beneficial ecosystem that supports biodiversity, improves soil health, and sequesters significant amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Unlike standard carbon credits generated by renewable energy projects or forest preservation, agroforestry credits focus on carbon capture achieved through tree growth within farming systems. This means they offer a dual benefit: reducing atmospheric carbon while enhancing agricultural productivity.
The role of agroforestry carbon credits goes beyond just carbon sequestration; they contribute to broader climate goals by fostering resilient ecosystems, providing habitats for wildlife, and supporting local communities economically. By capturing carbon, these systems help mitigate climate change, making them a valuable tool for companies seeking to meet their carbon neutrality targets and enhance their environmental impact. Agroforestry offers numerous benefits, including enhanced biodiversity, improved soil health, increased carbon sequestration, and greater resilience to climate change.
Integrating agroforestry carbon credits into your sustainability initiatives creates immense environmental value.
Essentially, each credit signifies a tangible step towards reducing greenhouse gases.
Beyond environmental gains, agroforestry carbon credits provide financial benefits to all involved.
For businesses, adopting agroforestry carbon credits helps fulfil Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) targets.
Integrating agroforestry carbon credits into corporate carbon offset strategies offers companies a powerful way to meet sustainability goals while making a positive environmental impact.
Agroforestry credits should be incorporated into a company’s broader Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) strategy to ensure alignment with sustainability objectives. This can include:
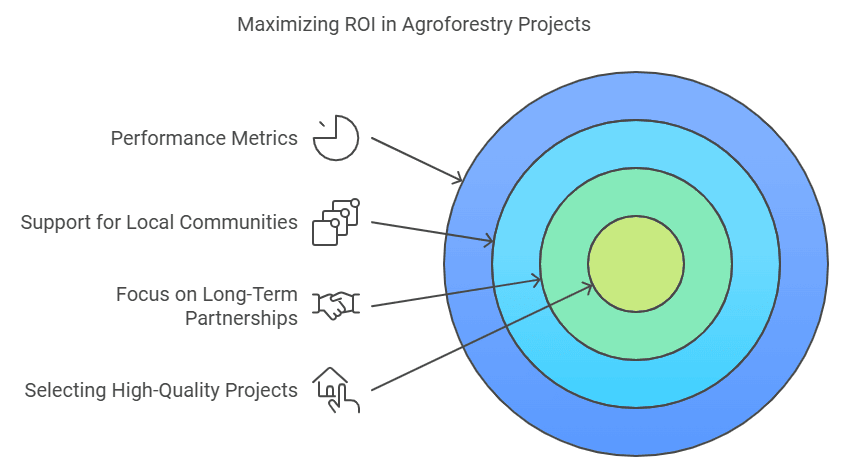
Addressing these challenges requires innovative solutions, multi-stakeholder partnerships, and supportive policy frameworks to create resilient and scalable agroforestry carbon projects.
Technology plays a pivotal role in enhancing the utilization of carbon credits, particularly in sectors like agroforestry, where tracking, verification, and transparency are essential to ensuring the credibility and integrity of carbon offset projects. Here’s a breakdown of key technologies that are revolutionizing the way carbon credits are utilized, helping both project developers and corporations meet compliance and sustainability goals.
Blockchain has emerged as a game-changer for carbon credit projects by providing an immutable and transparent ledger for carbon credit transactions. Each credit is recorded on the blockchain, allowing stakeholders to trace its origin, verify its authenticity, and track its movement throughout the supply chain. This eliminates the risk of double-counting or fraud, which has historically been a challenge in the carbon credit market.
How it works: Each carbon credit is linked to a specific action (like planting trees or reducing emissions). Once the credit is issued, it’s stored on the blockchain, where it cannot be altered or deleted. This ensures that once a credit is bought or sold, its ownership and carbon-saving history are visible to all parties involved, creating trust and reducing fraud.
Benefits: Blockchain not only increases transparency but also speeds up the verification process. It automates many of the administrative tasks involved in tracking credits, making compliance easier and more cost-effective.
The Sustainability Foundation utilizes TraceX’s DMRV platform to streamline its operations, enhance transparency with partners, and make informed, data-driven decisions. This technology supports the Foundation in scaling up its tree-planting initiatives while maximizing environmental impact and fostering accountability across projects.
Satellite technology plays a crucial role in monitoring land use, vegetation growth, and carbon sequestration over large areas. For agroforestry projects, it enables real-time data collection on tree health, soil conditions, and land changes, providing an accurate picture of the project’s carbon offset potential.
How it works: Satellites equipped with high-resolution cameras and sensors can capture detailed images of land and vegetation. These images are then processed with advanced software to track growth, map carbon absorption, and assess environmental changes. This data is invaluable for verifying the carbon credits generated by agroforestry projects.
Benefits: Satellite monitoring offers several advantages over traditional ground-based surveys. It’s more cost-effective, covers large and remote areas, and provides more frequent updates, which enhances the reliability of carbon credit reporting and auditing.
AI is being used to analyze large datasets from various sources—satellite images, weather patterns, and soil conditions—to predict carbon sequestration rates and optimize carbon credit generation. AI algorithms can identify trends, forecast outcomes, and suggest improvements for agroforestry projects, helping to maximize their environmental impact and financial viability.
How it works: AI can process vast amounts of environmental data and use machine learning to predict how various factors like weather, soil conditions, and plant growth affect carbon sequestration. This helps developers plan better, ensure higher carbon capture, and enhance project efficiency.
Benefits: AI reduces uncertainty in carbon credit generation by offering insights into the most effective practices and conditions for maximizing carbon sequestration. It also helps automate compliance tasks like data analysis and reporting, making it easier for project developers to stay on track with regulations.
Technology has made it easier to meet the stringent compliance and reporting requirements of carbon markets and standards like the Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) or the Gold Standard. Several tools and platforms are now available to help project developers gather, analyze, and report data in a way that meets regulatory standards.
How it works: These platforms integrate data from various sources—such as satellite monitoring, blockchain, and IoT devices—into a unified dashboard. They can generate automated reports, track the progress of carbon sequestration activities, and ensure that all necessary documentation is up to date.
Benefits: By automating compliance and reporting, these tools save time, reduce human error, and ensure that projects remain in good standing with carbon credit registries. This also simplifies the certification process for projects, making it easier to gain approval from carbon credit registries and buyers.
IoT sensors are increasingly being used in agroforestry projects to monitor soil moisture, temperature, and other environmental factors that affect carbon sequestration. These devices provide real-time data, which is crucial for managing large-scale agroforestry projects.
How it works: IoT sensors are deployed across agroforestry sites to collect data on various factors such as soil health, temperature, and moisture levels. This data is transmitted in real time to central platforms, where it can be analyzed for insights into the carbon sequestration performance of the project.
Benefits: IoT devices allow for precise, continuous monitoring of agroforestry projects. This provides actionable insights that help improve the management of the land and optimize the carbon credits generated, ensuring better long-term outcomes for both the environment and project developers.
TraceX’s Digital MRV Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification) platform provides agroforestry project developers with a comprehensive solution to enhance transparency, accuracy, and efficiency in carbon credit generation. The platform leverages advanced technologies like blockchain and satellite monitoring, to streamline the data collection process, ensuring that carbon sequestration from agroforestry activities is tracked in real-time. This enables developers to meet rigorous verification standards and report on carbon credits more effectively. With automated monitoring tools, the platform simplifies compliance with international carbon standards, helping developers reduce operational complexities and focus on scaling their projects. By offering a reliable and transparent way to measure the environmental impact of agroforestry projects, TraceX supports developers in building trust with investors and regulatory bodies while maximizing the long-term value of their carbon credits.
Integrating agroforestry carbon credits into corporate carbon offset strategies is a powerful step toward achieving sustainability goals while supporting environmental regeneration. By leveraging these credits, businesses can not only contribute to global carbon sequestration efforts but also enhance their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) commitments. As agroforestry offers both environmental benefits, like biodiversity conservation and soil health improvement, and economic advantages for local communities and farmers, it represents an impactful solution for companies seeking ethical and scalable offset opportunities. With technology enabling better monitoring, transparency, and compliance, integrating agroforestry carbon credits can drive long-term, positive change while aligning with global climate goals.
Agroforestry carbon credits are generated by projects that incorporate trees and other vegetation into agricultural practices, helping to sequester carbon from the atmosphere. These credits can be used by companies to offset their carbon emissions, supporting environmental and climate goals.
Companies can integrate agroforestry carbon credits by partnering with credible agroforestry projects, leveraging technology for monitoring, and ensuring that their carbon offset purchases align with their ESG goals. This approach not only supports sustainability but also demonstrates corporate responsibility.
Challenges include the complexity of monitoring and verifying the carbon sequestration process, potential regulatory barriers, and the need for robust data collection tools. However, technology such as blockchain and satellite monitoring can help overcome these obstacles, ensuring transparency and accuracy in the credit generation process.
