Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Learn how upcycling food waste helps reduce landfill emissions, promotes circular economies, and creates new food products. Discover the environmental and social benefits of upcycling in this comprehensive guide.

How would it be where food waste isn’t discarded but transformed into delicious, sustainable products that nourish people and the planet. Sounds revolutionary, right? Every year, over one-third of all food produced globally ends up as waste. This doesn’t just represent wasted resources; it also contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, with rotting food in landfills accounting for up to 10% of global emissions. Food waste upcycling is an innovative approach that not only reduces waste but creates value by transforming leftovers, by-products, and surplus food into high-quality, market-ready products
According to the FAO, roughly one-third of food produced for human consumption is lost or wasted globally, which amounts to about 1.3 billion tons per year
Businesses and consumers alike struggle to find practical, scalable ways to address this growing crisis. From repurposing fruit pulp into flour to crafting snacks from spent grains, upcycling offers a circular solution to a linear problem, redefining how we manage food waste. Stay with us as we explore the power of upcycling and how it’s shaping the future of sustainable food systems.
Key Takeaways
Upcycling in food waste refers to the process of transforming food by-products, leftovers, or surplus into new, high-value products that are safe and beneficial for consumption. Unlike recycling, which often breaks materials down into their raw form, upcycling focuses on creatively repurposing items to extend their lifecycle and utility. For example, turning spent coffee grounds into body scrubs or converting fruit peels into animal feed are practical ways upcycling is applied.
The world is facing a mounting food waste crisis. This waste doesn’t just mean lost resources—it also intensifies environmental issues such as greenhouse gas emissions and deforestation. At the same time, millions of people face food insecurity, creating a stark contrast in resource distribution.
Upcycling offers a win-win solution. By reducing food waste, it helps save precious natural resources like water, land, and energy. On top of that, it fosters innovation, empowering businesses to create unique, sustainable products while meeting the growing consumer demand for eco-friendly practices. In a world increasingly focused on environmental sustainability, upcycling has the potential to revolutionize how we think about food waste.
By adopting upcycling, we can transform what was once considered trash into valuable treasures, paving the way for a more circular and sustainable food system.
Food waste is a global challenge that has far-reaching consequences, affecting the environment, economies, and society
Globally, approximately 1.3 billion tons of food go to waste every year, accounting for nearly one-third of all food produced. This waste occurs at every stage of the supply chain:
The environmental toll of food waste is massive:
The financial cost of wasted food is staggering. Globally, it amounts to nearly $1 trillion annually. For businesses, wasted food means sunk costs in production, logistics, and disposal. For households, it’s money spent on food that is never consumed.
While millions of tons of food are wasted, 828 million people worldwide go hungry. This stark imbalance makes addressing food waste not just an environmental necessity but also a moral imperative. By reducing waste, we can mitigate climate change, conserve resources, and create a more equitable food system.
Addressing the food waste crisis requires innovative solutions like upcycling, which can turn this challenge into an opportunity for sustainability and economic growth and circularity in agriculture.
Upcycling is the process of taking food by-products, surplus, or ingredients that would otherwise go to waste and transforming them into new, usable products. This process not only helps in reducing food waste but also creates innovative products that are both nutritious and valuable.
Upcycling involves repurposing food waste or by-products like peels, stems, and pulp. For example, fruit pulp left over after juicing can be dried and processed into flour or snacks. This flour can then be used to make baked goods, offering a healthier and more sustainable alternative to traditional flours.
By upcycling food waste, companies not only contribute to a reduction in landfill waste but also help conserve resources and reduce carbon footprints. This approach aligns with sustainable practices by keeping valuable nutrients within the food system and offering affordable, eco-friendly alternatives to conventional food products.
Upcycling in the food industry is growing rapidly, with more and more companies finding creative ways to repurpose food waste into new, delicious, and sustainable products. Whether it’s through upcycled flours or spent grain snacks, the possibilities are endless!
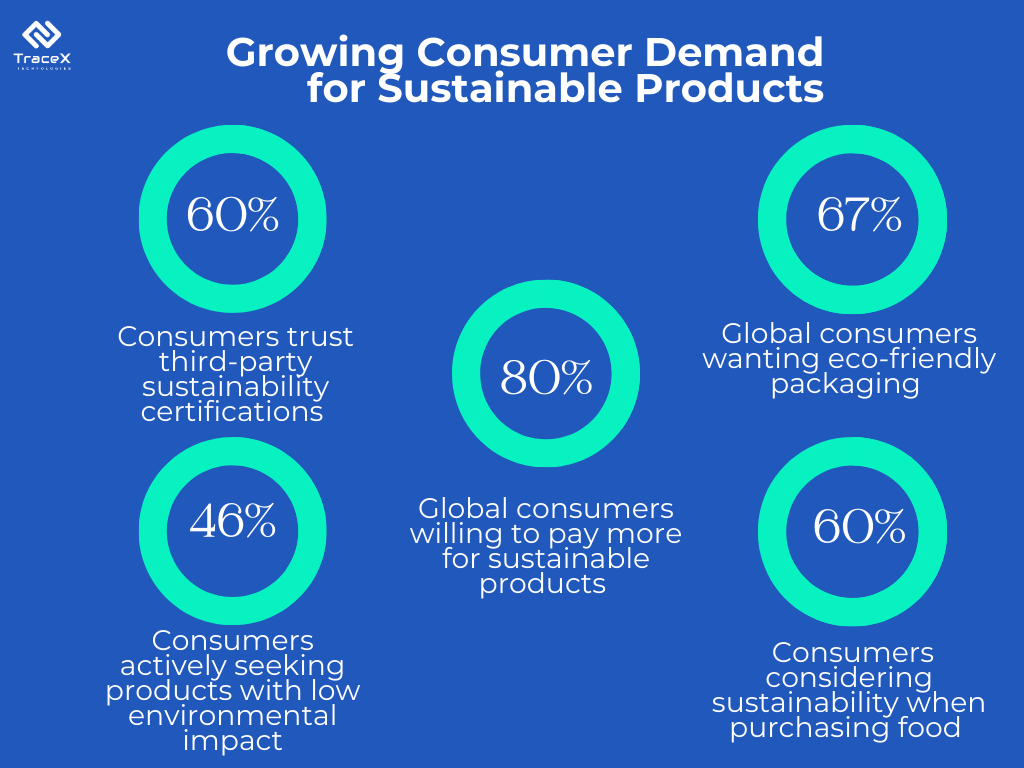
Upcycling food waste is not just a way to create new products – it’s also an impactful solution to some of the world’s pressing environmental and social challenges.
Food waste is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, especially when it ends up in landfills. As food decomposes in landfills, it produces methane, a potent greenhouse gas that significantly contributes to climate change. By upcycling food waste into valuable products, we can reduce the amount of food sent to landfills, effectively lowering methane emissions. This process promotes a circular economy, where waste is viewed as a resource rather than a problem. Instead of discarding food by-products, we use them to create new products, creating a more sustainable and closed-loop system.
In fact, studies show that reducing food waste by upcycling can significantly lower carbon footprints across industries (National Geographic, 2021). By keeping waste out of landfills, we help conserve resources and lessen the overall environmental burden.
Upcycling food waste can also have positive social impacts. When surplus or discarded food is repurposed, it creates opportunities for local communities, especially those that may be facing economic challenges. For example, surplus grains from breweries or fruit pulp from juice production can be turned into new products that provide jobs in processing, sustainable packaging, and marketing. This is especially beneficial in rural areas, where agriculture is a key industry.
Moreover, upcycled products can offer affordable food options, helping to address food insecurity. By transforming food waste into nutritious, high-quality products, businesses can provide healthier food choices at lower prices while simultaneously reducing waste. In some cases, upcycled food products are even distributed to underserved communities, ensuring that valuable nutrients don’t go to waste while helping to feed people in need.
In essence, upcycling food waste creates an ecosystem where environmental benefits and social good go hand in hand. It’s a win-win for both the planet and local communities, turning something that would have been discarded into something of value.
The world of food upcycling is evolving rapidly, and technology is playing a significant role in making this process more efficient and impactful. From Artificial Intelligence (AI) to the Internet of Things (IoT) and blockchain, innovative technologies are making it easier for businesses to identify and capitalize on upcycling opportunities
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning are becoming critical tools in the food upcycling process. AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of data to identify underutilized by-products from food processing or agriculture. For example, AI can analyze supply chains to find patterns and help companies figure out where excess food or waste could be repurposed into new products. It can also optimize production processes to minimize food waste, ensuring that every part of the raw material is used efficiently.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing the way food waste is tracked, monitored, and managed. With IoT sensors, food manufacturers can keep real-time tabs on the quality and quantity of surplus food or by-products generated during production. These sensors can track temperature, humidity, and other environmental factors to ensure that food waste is handled properly and ready for upcycling.
Blockchain technology is playing a key role in upcycling by offering transparency and traceability in the supply chain. By using blockchain, companies can track and verify the source of upcycled food products. This is crucial for consumers who are increasingly concerned with the sustainability of the products they purchase.
For instance, a company producing snacks from upcycled fruit pulp can use blockchain to provide customers with detailed information about where the fruit pulp came from, how it was processed, and the environmental benefits of choosing upcycled products. Blockchain ensures that every step of the process is transparent and verifiable, building trust with consumers and supporting sustainability claims.
Innovation in food processing technologies is also key to turning food waste into high-value products. Techniques like dehydration, fermentation, and enzymatic processes allow manufacturers to convert food waste into nutritious and desirable products. For instance, food waste such as spent grains or fruit skins can be processed into powders, bars, or beverages with added nutritional benefits.
TraceX offers a comprehensive traceability and sustainability platform that leverages blockchain to ensure transparency, traceability, and accountability across the entire food supply chain. This platform provides significant value in the context of upcycling by allowing companies to track and verify the origin of upcycled food products, ensuring that sustainability claims are credible and verifiable.
TraceX’s food traceability platform captures every key piece of information throughout the food journey, from farm to fork. With blockchain integration, each step in the supply chain is recorded in an immutable ledger. This ensures that the journey of upcycled products—whether it’s fruit pulp turned into snacks or surplus grains transformed into animal feed—is clearly documented, traceable, and accessible to all stakeholders, including consumers. By verifying the source of raw materials and their transformation into final products, consumers can make informed choices based on solid proof of sustainability.
With the increasing consumer demand for sustainable and eco-friendly products, TraceX addresses a key pain point for businesses: ensuring that sustainability claims are not only authentic but also backed by data. Through the TraceX sustainability platform, companies can demonstrate their commitment to reducing waste, conserving resources, and promoting circular economies. Blockchain’s role in providing secure, auditable records of sustainability practices ensures that every step of the upcycling process—from sourcing by-products to the final product—aligns with environmental goals, such as reducing carbon emissions and supporting biodiversity.
By using IoT sensors and other data collection tools integrated with the TraceX platform, businesses can gather real-time insights on how food waste is managed, upcycled, and transformed into value-added products. This allows for continuous monitoring of sustainability practices, with the added benefit of ensuring that all data is traceable. Whether it’s tracking emissions reductions or measuring the environmental impact of upcycling efforts, TraceX’s platform ensures that sustainability efforts are both transparent and actionable.
Today’s eco-conscious consumers are increasingly demanding more information about the products they purchase. They want to know where their food comes from, how it is produced, and whether it is sustainable. TraceX provides companies with the tools they need to meet these expectations. Through blockchain’s secure and transparent structure, TraceX enables businesses to provide consumers with verifiable data about the origins, processing methods, and sustainability credentials of upcycled food products.
Upcycling food waste is not only an innovative solution to a growing environmental crisis but also a powerful driver of sustainability. By transforming by-products and surplus food into valuable, new products, we can reduce waste, conserve resources, and improve the overall environmental footprint of food production. As the demand for sustainable practices grows, upcycling offers businesses the opportunity to contribute to circular economies, enhance brand value, and address global challenges like food insecurity and climate change. Leveraging technologies like blockchain and IoT can further boost transparency and traceability in the upcycling process, ensuring that products meet sustainability goals while building consumer trust. As a result, upcycling is set to play a key role in the future of sustainable food systems, benefiting both the environment and the economy.
Upcycling food waste involves turning by-products and surplus food into new, edible products. This process reduces food waste, conserves resources, and creates high-value, sustainable products.
Upcycling helps reduce landfill waste, cutting down on harmful methane emissions. It also contributes to resource conservation by reusing raw materials that would otherwise go to waste, supporting a circular economy.
Yes, upcycled food products can retain much of the nutritional value of the original food, especially when processed with minimal alteration. Many upcycled foods, such as flour made from fruit pulp or snacks made from spent grains, are both nutritious and sustainable alternatives.
