Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Explore Malaysia's journey towards sustainable agriculture and food security. Discover how the country is leveraging innovative practices and policies to ensure a resilient and secure food system for the future.

Sustainable agriculture in Malaysia is marked by a concerted effort to address the intricate challenges facing its agricultural landscape. As a nation rich in biodiversity and agricultural heritage, Malaysia recognizes the imperative of transitioning towards sustainable practices to safeguard its food security and ecological integrity.
According to the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO), approximately 9% of the world’s population is malnourished, and climate change’s unexpected effects on food production exacerbate this issue even further.
Malaysia is charting a course towards a more resilient and equitable agricultural future. By prioritizing sustainability and embracing cutting-edge technologies, Malaysia is poised to lead the region in forging a path towards food security while preserving its natural resources for future generations. In this blog post, we’ll look at Malaysia’s efforts to cultivate resilience in its agriculture sector, as well as the actions taken to attain sustainable food production.
Key Takeaways
Malaysia’s agricultural sector has long been a pillar of the country’s economy, providing major employment, rural development, and food supply. However, the industry faces a number of issues, including deforestation, soil degradation, water scarcity, and biodiversity loss. In response, the Malaysian government, in collaboration with industry stakeholders and civil society, has begun on a sustainable agriculture journey to solve these pressing concerns.
With over 170,000 species of flora and fauna, Malaysia contributes significantly to global biodiversity, encompassing approximately 16% of the world’s classified species.
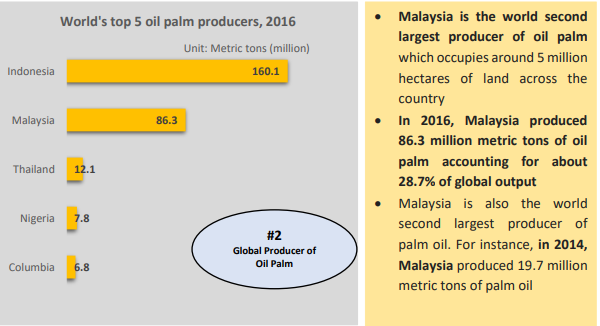
Malaysia boasts a rich array of crops including palm oil, rubber, rice, fruits, and vegetables. While the palm oil industry remains a cornerstone of Malaysia’s agricultural exports, the sector faces scrutiny over environmental sustainability and ethical concerns. Additionally, the nation grapples with issues such as land scarcity, labor shortages, climate change impacts, and the need for technological advancements to enhance productivity and resilience. Despite these challenges, Malaysia continues to strive towards achieving a balance between economic growth, environmental conservation, and social equity in its agricultural sector. Malaysia boasts an exceptionally abundant and highly varied array of biological resources, earning its status as one of the world’s twelve mega-diverse nations.
One of the primary techniques used is to promote sustainable farming practices
that prioritise environmental conservation and social fairness. This includes measures to limit chemical inputs, promote organic farming, and implement agroecological practices that improve soil health and biodiversity. Malaysian farmers are not only protecting the environment, but also increasing resistance to climate change and lowering reliance on external inputs.
A steady and abundant food supply is critical to national security and the well-being of the people. A strong agricultural industry is critical for mitigating potential interruptions in global food trade, particularly during times of crisis. Agriculture has a substantial contribution to Malaysia’s economy. Strengthening the industry can boost economic growth, provide new job opportunities, and alleviate rural poverty, all of which contribute to overall economic stability. Improving the agricultural sector’s resistance to climate change can help Malaysia adjust to changing weather patterns. Malaysia may reduce the negative effects of extreme weather events and temperature changes by adopting sustainable farming practices and diversifying its crop base. Malaysia’s distinct biodiversity and ecosystems are inextricably related to agriculture.
Sustainable agriculture addresses both economic and social issues by promoting resilient farming systems that prioritise environmental stewardship, economic viability, and social justice. Economically, it encourages effective resource use, lowers input costs, and increases market access, hence boosting agricultural profitability and rural livelihoods. Socially, sustainable agriculture promotes fair salaries, safe working conditions, and community engagement, which benefits farmers and rural communities. Sustainable agriculture
helps to provide long-term food security, preserve the environment, and promote inclusive rural development by combining economic prosperity and social responsibility.
Addressing climate change and developing climate resilience entails implementing methods to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, adapt to changing climatic circumstances, and increase communities’ ability to tolerate and recover from climate-related impacts. This involves switching to renewable energy, improving infrastructural resilience, encouraging sustainable land management techniques, and assisting disadvantaged communities. Societies may lower the risk of climate-related disasters, safeguard ecosystems and biodiversity, and promote sustainable development paths for future generations by implementing proactive measures to address climate change and build resilience.
However, addressing Malaysia’s long-term food security is a far more difficult task. Climate change is a big threat. Changes in weather patterns and extremes, increased frequency of droughts and floods, and rising temperatures will all have a negative impact on the productivity of food crops grown in Malaysia, potentially increasing our reliance on food imports and threatening our farmers’ livelihoods.
Achieving food security through sustainable agriculture in Malaysia is not just a goal but a necessity in the face of growing population pressures and environmental challenges. With its rich biodiversity and agricultural potential, Malaysia holds the key to ensuring a stable food supply for its citizens while preserving its natural resources for future generations. By embracing sustainable farming practices such as agroforestry, organic farming and precision agriculture, Malaysia can enhance crop resilience, improve soil health, and minimize environmental impact. Through concerted efforts from policymakers, farmers, and stakeholders, Malaysia can pave the way towards a more food-secure and sustainable future.
Malaysian agribusinesses face challenges such as climate change, resource management, labor shortages, and the need for technology adoption to ensure sustainable growth and compliance with evolving global standards.
Explore how agribusinesses can use technology
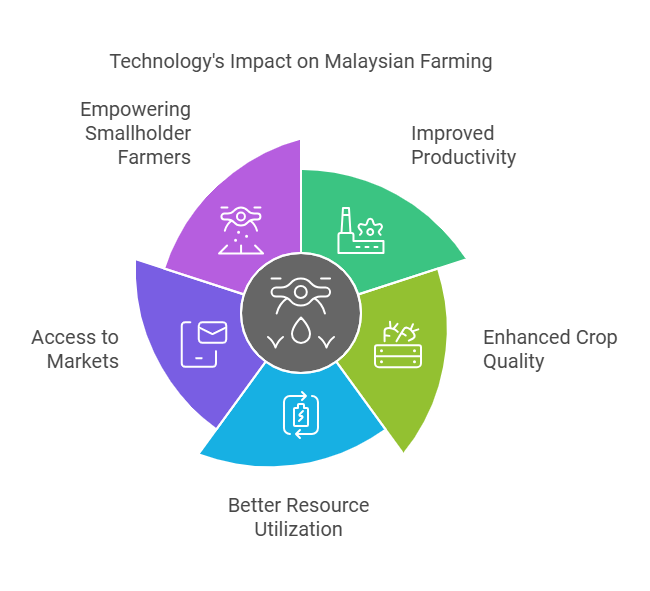
Malaysia is embracing technology and innovation to increase agricultural output and efficiency while reducing environmental effect. Digital solutions, precision farming techniques, and data-driven approaches are being used to optimise resource utilisation, monitor crop health, and reduce the hazards associated with climatic variability. These technology improvements enable farmers to make more informed decisions and react to changing environmental conditions, increasing resilience in the face of unpredictability.
In addition to on-farm methods, Malaysia is working to strengthen the supply chain and improve smallholder farmers’ market access. Initiatives to improve infrastructure, connect markets, and encourage fair trade practices all help to establish a more resilient and inclusive agricultural economy. Malaysia is working to create a more sustainable and socially just food system by empowering smallholder farmers and guaranteeing equitable benefit sharing.
TraceX’s Farm Management Platform addresses several key challenges in sustainable agriculture by integrating cutting-edge technology with practical solutions for farmers. Here’s how:
1. Real-Time Data for Informed Decision-Making
The platform provides farmers with real-time data on soil health, weather conditions, crop performance, and resource usage. This helps in making informed decisions that optimize yields while minimizing environmental impact.
2. Resource Efficiency
TraceX helps farmers monitor and manage inputs like water, fertilizers, and pesticides more efficiently. By using data-driven insights, the platform promotes the precise application of resources, reducing waste and improving sustainability.
3. Traceability and Transparency
With blockchain technology, TraceX ensures full traceability of crops from farm to market. This transparency helps to verify sustainable farming practices, ensuring compliance with sustainability standards, and building consumer trust in ethically produced goods.
4. Compliance with Sustainability Regulations
The platform simplifies compliance with environmental regulations and certifications by offering tools that track sustainability metrics, carbon footprints, and other relevant data, making it easier for farmers to meet legal and market requirements.
5. Improved Soil and Crop Health
By using data to optimize crop rotation and soil management practices, TraceX helps farmers adopt regenerative agriculture practices, which restore soil health, enhance biodiversity, and increase resilience to climate change.
6. Enhanced Market Access
TraceX connects farmers with buyers who prioritize sustainability, creating opportunities for farmers to access premium markets. This supports the growth of sustainable agriculture and provides financial incentives for adopting eco-friendly practices.
7. Supporting Smallholder Farmers
For smallholder farmers, TraceX provides easy-to-use tools and insights that were previously accessible only to large-scale operations. This democratization of technology helps elevate smallholder farmers’ sustainability efforts, ensuring they benefit from advanced farm management practices.
Sustainable agriculture plays a pivotal role in ensuring food security in Malaysia, balancing environmental health with the growing demand for food. By adopting sustainable practices, such as precision farming, agroforestry, and efficient resource management, Malaysia can achieve long-term food security while safeguarding its natural resources. Collaborative efforts from the government, farmers, and private sectors are essential to drive innovation and scale these practices for the benefit of future generations.
Sustainable agriculture helps to increase food production while minimizing environmental impact, ensuring that future generations have access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food.
Precision farming, agroforestry, integrated pest management, and water-efficient irrigation systems are some key sustainable agriculture practices helping to make Malaysian agriculture more sustainable.
Farmers can adopt sustainable practices through government programs, training initiatives, and by integrating advanced technologies like smart farming and precision agriculture tools.
