Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Discover how the role of SDGs in agriculture drives sustainability by addressing hunger, climate change, and biodiversity challenges while promoting innovative solutions.

Agriculture is at the heart of global sustainability challenges, feeding billions while balancing the planet’s health. Yet, this vital sector faces mounting pressure from climate change, soil degradation, and a growing population demanding food security. The Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) in agriculture offer a transformative framework to tackle these challenges. By aligning farming practices with SDG principles, we can address issues such as zero hunger (SDG 2), climate action (SDG 13), and life on land (SDG 15), paving the way for a resilient and sustainable agricultural future.
Among all sectors, agriculture is the unifying link that connects the 17 Sustainable Development Goals
How can we ensure that agriculture not only feeds the world but also supports environmental sustainability and economic growth? This question becomes even more pressing as unsustainable practices threaten ecosystems and livelihoods.
Key Takeaways
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a global call to action, and agriculture is at the heart of many of them. The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), adopted by the United Nations in 2015, encompass 17 global objectives aimed at addressing pressing challenges such as poverty, hunger, and environmental degradation. Agriculture plays a pivotal role in achieving these goals, particularly due to its direct impact on food security, economic growth, and environmental sustainability.
1. No Poverty (SDG 1): Agriculture is essential for poverty alleviation, especially in developing countries where a significant portion of the population relies on farming for their livelihoods. Sustainable agricultural practices can enhance productivity and income for smallholder farmers, breaking the cycle of poverty.
2. Zero Hunger (SDG 2): This goal emphasizes the need to end hunger and achieve food security. Sustainable agriculture promotes practices that increase crop yields and improve nutrition, ensuring that all individuals have access to sufficient and nutritious food.
3. Good Health and Well-being (SDG 3): By minimizing the use of harmful chemicals and promoting organic farming, sustainable agriculture contributes to healthier diets and reduces health risks associated with food production.
4. Gender Equality (SDG 5): Women play a crucial role in agriculture; empowering them through equal access to resources and opportunities can significantly enhance productivity and community well-being.
5. Clean Water and Sanitation (SDG 6): Sustainable agricultural practices promote responsible water management, ensuring clean water availability for both agricultural use and local communities.
6. Climate Action (SDG 13): Agriculture is both a contributor to and a victim of climate change. Implementing sustainable practices helps mitigate greenhouse gas emissions while enhancing resilience against climate impacts.
7. Life on Land (SDG 15):Healthy ecosystems are essential for agriculture. However, unsustainable farming practices can degrade land, destroy forests, and threaten biodiversity. SDG 15 emphasizes halting deforestation and restoring degraded land, promoting sustainable farming methods that enhance soil health and protect biodiversity and ensuring that agriculture coexists with wildlife conservation.
Collaboration among governments, businesses, NGOs, and local communities is essential for advancing sustainable agriculture practices that align with the SDGs. Partnerships can provide the necessary resources, knowledge, and technology to empower farmers and enhance agricultural productivity sustainably.
Agriculture isn’t just about food—it’s deeply intertwined with social, environmental, and economic systems. It influences the livelihoods of billions, determines the health of ecosystems, and plays a critical role in fighting climate change. By addressing these SDGs through sustainable practices, agriculture can:
The path to achieving SDGs lies in transforming agriculture to become more sustainable, innovative, and resilient—because the future of our planet depends on what we sow today.
Sustainable agriculture holds the promise of balancing food production with environmental and social well-being, but the journey is far from simple.
Unpredictable weather patterns, extreme temperatures, droughts, and floods are becoming more frequent due to climate change. These conditions:
For instance, a region once suitable for rice cultivation may now face water shortages, making it unsustainable. Farmers need innovative solutions to build resilience against these climate shifts.
Smallholder farmers, who produce a significant portion of the world’s food, often face poverty, limited education, and lack of access to modern tools and technology. These barriers:
Empowering these farmers through affordable technology, training, and better market access is critical for achieving sustainability on a global scale.
Consumers increasingly want to know where their food comes from and if it meets sustainability standards. This demand creates pressure on farmers and supply chain managers to:
Aligning agricultural practices with the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) can help tackle global challenges like climate change, poverty, and food security.
Climate-smart agriculture focuses on building resilience to climate change while improving productivity. These practices include:
By mitigating climate impacts, these strategies ensure farms can produce more sustainably over the long term.
Biodiversity is essential for resilient ecosystems. Regenerative farming builds on this by focusing on soil health, water management, and ecosystem restoration. Key approaches include:
These practices restore ecosystems and ensure long-term agricultural sustainability while protecting natural resources.
SDGs prioritize improving the socio-economic conditions of smallholder farmers, who are often the backbone of agriculture. Solutions include:
These efforts not only enhance livelihoods but also promote equitable and inclusive growth.
Technology is a game-changer for aligning agriculture with SDGs. Innovations include:
These technologies help farmers boost productivity while ensuring sustainability and compliance with global standards.
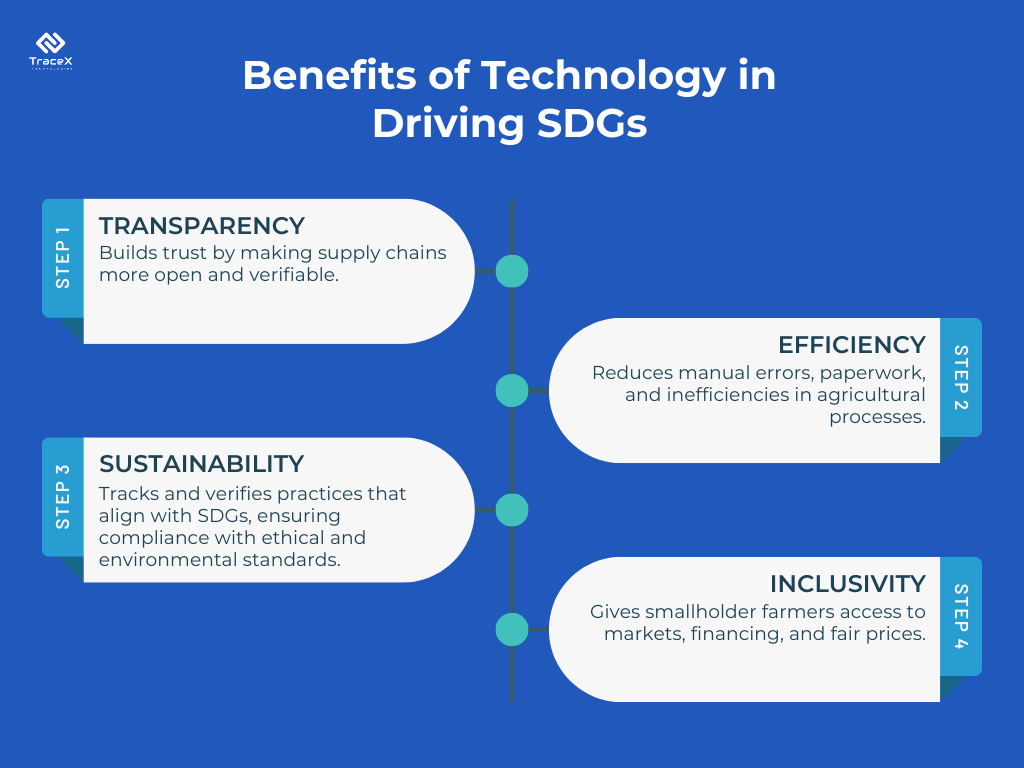
Technology is a powerful enabler in achieving the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), especially in agriculture and supply chain management. By fostering transparency, sustainability, and efficiency, digital innovations bring us closer to a future where agriculture and food systems align with global sustainability targets.
Digital platforms have revolutionized the way agricultural supply chains operate. These tools ensure end-to-end traceability, helping stakeholders track products from farm to fork.
By documenting processes and creating a transparent supply chain, digital platforms build trust among consumers, suppliers, and regulators alike.
A prominent agribusiness adopted TraceX’s sustainability platform to transform its approach to land restoration through regenerative agriculture. By leveraging TraceX’s advanced tools for traceability and sustainability tracking, the company implemented regenerative techniques to restore soil health, enhance biodiversity, and ensure sustainable farming practices. This not only improved operational efficiency but also aligned the business with global sustainability goals, demonstrating a strong commitment to environmental stewardship and sustainable growth.
Blockchain technology adds an immutable layer of trust and accountability to agricultural practices, making it a game-changer for sustainable farming.
For example, farmers using blockchain can document their adherence to climate-smart techniques, such as low-emission fertilizers or water-efficient irrigation, strengthening their contribution to SDG 13 (Climate Action).
The TraceX Sustainability Platform is an innovative solution designed to enhance transparency, traceability, and sustainability across agricultural and food supply chains. Powered by blockchain technology, the platform provides an immutable ledger that enables stakeholders to track every stage of a product’s journey, from farm to fork. It supports sustainable practices by monitoring resource usage, verifying certifications like organic or fair trade, and ensuring compliance with global regulations . With features for carbon management, digital traceability, and robust reporting, TraceX empowers agribusinesses, foundations, and carbon project developers to align with sustainability goals, reduce inefficiencies, and build consumer trust.
Agribusinesses play a critical role in transforming the agriculture sector to align with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Companies can adopt sustainable farming practices such as regenerative agriculture, which improves soil health and biodiversity. Investing in digital tools for traceability ensures transparency in supply chains, helping to meet consumer demands for ethical and sustainable products. Agribusinesses can also engage smallholder farmers by providing training, fair pricing, and access to technology, enabling them to adopt climate-smart practices while improving their livelihoods. By embedding sustainability into their core operations, businesses not only contribute to global goals but also build trust with consumers and partners.
Policymakers can support sustainable farming by implementing favorable policies and incentives. Subsidies for adopting eco-friendly practices, such as organic farming or water-saving irrigation methods, can motivate farmers to shift toward sustainability. Governments should also prioritize investments in rural infrastructure, such as better roads and storage facilities, to reduce post-harvest losses and improve market access for farmers. Promoting research and development in sustainable technologies and providing grants for their adoption are essential for scaling solutions.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) hold the key to transforming agriculture into a driver of positive change for people, the planet, and prosperity. By adopting sustainable practices, leveraging technology, and fostering collaboration, agriculture can combat hunger, mitigate climate change, and preserve biodiversity. Businesses, governments, and communities must work together to unlock the sector’s full potential and align efforts with SDG objectives, paving the way for a more resilient and sustainable future.
The most relevant SDGs for agriculture are SDG 2 (Zero Hunger), SDG 13 (Climate Action), and SDG 15 (Life on Land). They focus on ensuring food security, combating climate change, and protecting ecosystems.
Technology can drive SDG goals by improving traceability, enabling sustainable farming practices through data-driven insights, and enhancing supply chain transparency with solutions like blockchain.
Businesses can promote sustainability by adopting eco-friendly practices, supporting smallholder farmers, ensuring fair trade, and leveraging digital tools to align operations with SDGs.
