Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Unlock sustainability with ISO14044! Learn its LCAs & carbon footprint insights. Align practices with global goals for eco-friendly choices.

According to a study by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), 89% of consumers globally expect companies to act on sustainability issues.
ISO14044 provides a robust framework and guidelines for conducting life cycle assessments, enabling organizations to make informed decisions, optimize resource usage and minimize environmental footprints. In this blog post, we will delve into the key principles and applications of ISO14044, throwing light on how this standard plays an important role in promoting sustainability and environmental stewardship across various industries.
Understanding the life cycle of a product is crucial in determining its carbon footprint, encompassing its entire journey from raw materials to delivery. This assessment helps identify areas where excessive carbon emissions occur enabling companies to develop strategies for reducing their environmental impact. LCA is an indispensable tool in the quest for sustainability. LCA is a systematic approach used to evaluate the environmental aspects and potential impacts of a product, process, or service throughout its entire life cycle – from cradle to grave. Unlike traditional environmental assessments that may only consider specific stages, LCA takes a holistic view, accounting for raw material extraction, manufacturing, distribution, use, and end-of-life stages. At the heart of ISO 14044 lies the concept of Life Cycle Assessment (LCA)
By conducting LCA, organizations gain valuable insights into their products’ environmental “hotspots” and can identify areas where improvements can be made to reduce overall environmental burdens. LCA serves as a scientific and data-driven method for assessing environmental performance, fostering informed decision-making that leads to greener, more sustainable practices.
ISO 14044 is designed to provide guidance and standardized procedures for conducting LCA. Its primary purpose is to assist organizations in making informed decisions that contribute to environmental protection and sustainable development. By establishing a consistent and reliable approach to LCA, ISO 14044 ensures that environmental performance assessments are carried out in a robust, transparent, and credible manner.
It also plays a crucial part in promoting sustainable practices across industries and supply chains. By encouraging organizations to evaluate their products and processes comprehensively, ISO 14044 fosters a collective understanding of the environmental impacts associated with various goods and services. This shared knowledge enables industry-wide collaboration and empowers businesses to collectively work towards reducing their ecological footprints. Organizations that implement ISO 14044-compliant LCA gain a competitive advantage as they position themselves as environmentally responsible and committed to sustainability. By identifying opportunities for improvement and optimizing processes, businesses can reduce waste, energy consumption, and emissions, ultimately leading to cost savings and improved operational efficiency.
Moreover, ISO 14044 aligns with broader sustainability frameworks and initiatives, including the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). It provides a foundation for businesses to contribute actively to global environmental objectives, such as climate action, responsible consumption and production, and the preservation of ecosystems.
ISO 14044 is a critical standard within the ISO 14000 series, which focuses on environmental management and sustainability. This series of standards provides organizations with practical tools and guidelines to systematically address environmental challenges and improve their environmental performance.
The ISO 14000 series is a collection of international standards developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Its primary objective is to assist organizations in establishing and implementing effective environmental management systems (EMS). The standards in this series cover a wide range of topics related to environmental management, such as environmental policy, planning, implementation, monitoring, and continuous improvement.
By adopting the ISO 14000 standards, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to environmentally responsible practices, comply with the applicable environmental laws and regulations and enhance their reputation.
ISO 14044 is specifically dedicated to Life Cycle Assessment (LCA), a powerful methodology used to evaluate the environmental impacts of products and services across their entire life cycle. LCA takes a comprehensive and systematic approach, considering all stages of a product’s life, from the extraction of raw materials through production, use, and ultimately, its end-of-life treatment.
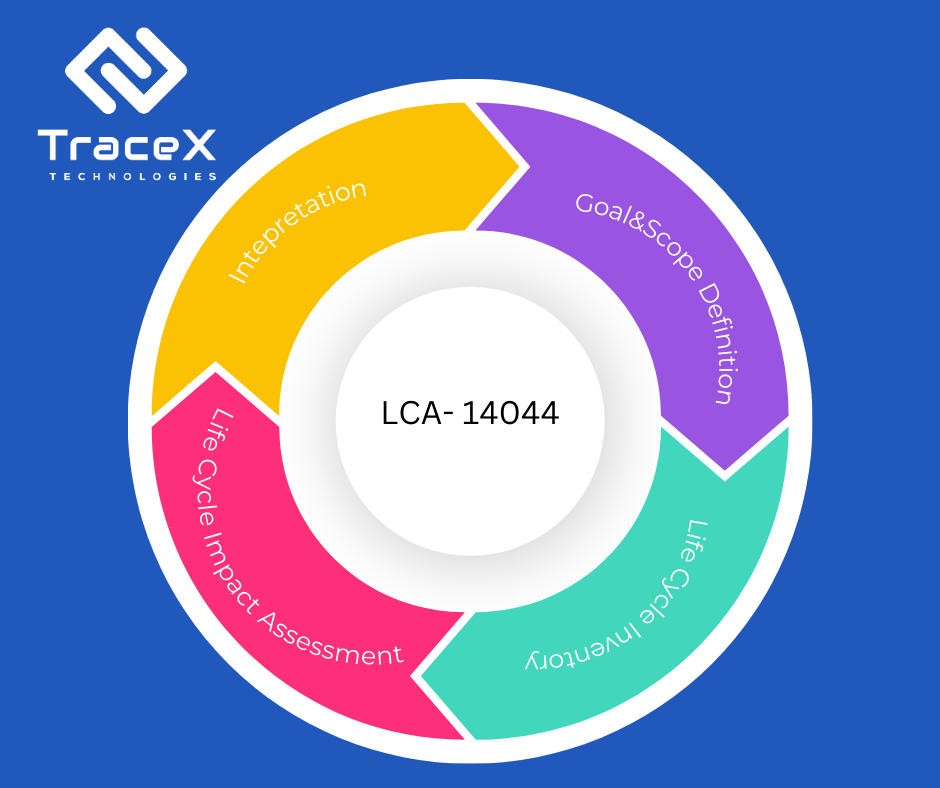
The first step in LCA involves clearly defining the goal and scope of the assessment. This includes specifying the purpose of the study, the system boundaries, the functional unit (e.g., one kilogram of product or one kilometre driven), and any assumptions made during the analysis.
The LCI phase involves collecting and quantifying data on all inputs (e.g., materials, energy) and outputs (e.g., emissions, waste) associated with each life cycle stage. This information is crucial for understanding the environmental burdens of the product or service.
In the LCIA phase, the inventory data is evaluated to assess the potential environmental impacts. This assessment considers various impact categories, such as climate change, resource depletion, human health, and ecosystem quality.
The results of the LCIA are interpreted to understand the significant environmental impacts of the product or service. This interpretation helps identify areas where improvements can be made to reduce the overall environmental footprint.
This stage involves the extraction and processing of raw materials required to manufacture the product. It includes activities such as sourcing, harvesting, and transportation of resources.
The production phase encompasses all processes involved in transforming the raw materials into the final product. This may include manufacturing, assembly and packaging.
The use stage involves energy consumption and emissions associated with product during its operational life.
This refers to the disposal or the treatment of the product after its useful life. It includes recycling, landfilling, incineration and the associated environmental impacts.
Data Collection – Collecting extensive data on inputs, outputs and environmental impacts across all life cycle stages, from raw material extraction to disposal.
Data Quality – Ensuring data relevancy, accuracy and consistency, while acknowledging and addressing uncertainties and limitations.
Defining Functional Unit– Establishing a functional unit that represents the quantified performance of the product or service that enables comparisons between alternatives.
Impact assessment– Conducting Impact assessments to quantify and evaluate environmental impacts using selected impact categories and characterization factors.
Interpretation and Reporting– Analysing LCA results, identifying impacts and drawing conclusions.
Complexity in data collection
Gathering data throughout the product’s life cycle can be time-consuming and challenging requiring cooperation from stakeholders and reliable data sources.
Need for Data Accuracy
Validating data quality is a daunting task if reliable LCA results have to be achieved.
Impact assessment is a complex exercise.
Selecting impact categories and applying characterization factors is complex and difficult to quantify environmental impacts.
Resource constraints
Time and budget are constraints making it challenging.
Need for transparent Sustainable Reporting
Analyzing and communicating LCA findings should be transparent.
Need for collaborative engagement.
Engaging and aligning stakeholders requires effective communication and collaboration.
Evolving Standards
Staying up to date with the evolving standards can be truly challenging.
Implementing an ISO14044 into your company’s business operations can help to maximize the effects of conducting a life cycle assessment.
The first step is to study the main principles, requirements and guidelines of ISO14044 for conducting an LCA.
The next step is to identify which products, services and systems are going to be assessed and which life cycle stages will be included in the LCA.
Conducting a LCA means a lot of numerical data and interpretation of this data is important and a lot needs to be collected.
It is crucial that conducting a good LCA entails aligning with the standards presented in an ISO14044.
And finally, reporting on the key findings helps not only to create strategies for reducing emissions but also demonstrate sustainability commitments to stakeholders and potential investors.
Trace Carbon the carbon management solution from TraceX streamlines the implementation of ISO14044 for LCA empowering businesses to track, analyse and manage their environmental impact more efficiently. The platform helps in comprehensive data collection, data accuracy and transparency, impact assessment and interpretation and reporting. The DMRV platform adds granularity and credibility to the processes thereby ensuring companies of effective results.
Understanding ISO14044 is essential for any organization committed to achieving sustainability and reducing its environmental impact. This internationally recognized standard provides a systematic and comprehensive framework for conducting LCAs, enabling businesses to gain valuable insights into their product’s environmental performance. By following the ISO14044’s guidelines, companies can identify hotspots, measure their carbon footprint and make informed decisions to minimize their ecological footprint. It empowers organizations to align their practices with global sustainability goals and demonstrate their commitment to responsible environmental stewardship.
