Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Explore the latest agriculture technologies for efficient and sustainable crop management. Discover how innovative solutions like TraceX can streamline processes, enhance traceability, and optimize decision-making in the agricultural sector. Uncover the future of crop management and elevate your farming practices to new levels of productivity and sustainability.

Agriculture today faces a crucial challenge: balancing the need for increased food production with the pressures of climate change and resource scarcity. Farmers grapple with unpredictable weather patterns, soil degradation, and rising input costs—all while trying to meet the demand for sustainable practices. These issues can make traditional farming methods feel like an uphill battle. But there’s a way forward with crop management technologies.
By leveraging advanced tools like precision agriculture, digital monitoring, and data-driven solutions, farmers can optimize their operations, reduce waste, and improve yields. It’s a shift that promises not only more efficient farming but a more sustainable future for agriculture.
Key Takeaways
The need for sustainable agriculture has never been more urgent. As the global population grows, so does the demand for food, putting immense pressure on agricultural systems. At the same time, climate change, soil degradation, and dwindling water resources threaten the long-term viability of traditional farming methods. To address these challenges, a shift towards sustainable practices is essential practices that can produce more with fewer resources, protect the environment, and ensure food security for future generations. This is where crop management becomes crucial. By adopting advanced crop management technologies, farmers can make more informed decisions about planting, watering, and nutrient application. This not only increases productivity but also reduces waste, conserves resources, and helps in maintaining soil health, making agriculture more resilient to climate challenges.
Crop management is like giving your plants the best care possible so they can grow healthy and produce a good harvest. It involves a variety of practices farmers use to ensure their crops thrive from planting to harvest.
Crop management plays a crucial role in sustainable agriculture, which aims to meet current food needs while preserving resources for future generations. Here are some key points highlighting its importance:
1. Resource Efficiency: Effective crop management optimizes the use of water, nutrients, and land. By implementing practices like crop rotation and cover cropping, farmers can reduce waste and maximize resource use, leading to more sustainable farming.
2. Soil Health: Healthy soil is vital for productive crops. Crop management practices, such as reduced tillage and organic fertilization, help maintain soil structure, enhance nutrient content, and promote beneficial microorganisms. This leads to healthier plants and less dependence on chemical inputs.
3. Biodiversity: Sustainable crop management encourages the use of diverse cropping systems. This not only helps improve soil health but also supports a variety of pests and beneficial organisms, which can reduce the need for pesticides and promote a balanced ecosystem.
4. Climate Resilience: By adapting crop management techniques to local climates and conditions, farmers can build resilience against extreme weather events, such as droughts or floods. Practices like selecting drought-resistant crops or implementing efficient irrigation systems help maintain productivity despite climate challenges.
5. Pest and Disease Management: Sustainable crop management promotes integrated pest management (IPM) strategies, which use biological control methods and minimize chemical pesticide use. This reduces environmental impact and supports healthier ecosystems.
6. Economic Viability: Sustainable practices in crop management can lead to cost savings and higher yields over time. By investing in methods that improve soil health and resource efficiency, farmers can enhance their long-term profitability while contributing to environmental sustainability.
7. Food Security: By promoting sustainable crop management, we can ensure a consistent and reliable food supply. Healthy, well-managed crops contribute to local and global food security, which is essential as the population continues to grow. Plant nutrient management involves optimizing the supply of essential nutrients to crops, ensuring balanced soil fertility and maximizing crop growth for sustainable agriculture.
Crop management technologies are transforming sustainable agriculture by enhancing decision-making, optimizing resource use, and improving productivity while minimizing environmental impact.
GIS involves using spatial data to analyze and visualize information about agricultural land. It helps farmers understand their fields better by:
Remote sensing uses satellite or aerial imagery to gather information about crops and land use without direct contact. This technology provides valuable insights such as:
Satellite imagery plays a crucial role in modern crop management by providing detailed views of agricultural areas. Key benefits include:
NDVI is a remote sensing measurement that assesses plant health and vigor. It calculates the difference between the near-infrared (which vegetation strongly reflects) and visible light (which vegetation absorbs) to provide insights such as:
Smart farming refers to the integration of technology into farming practices to enhance productivity and sustainability. Key components include:
Data-driven agriculture involves leveraging data analytics and machine learning to make informed decisions. This approach includes:
Effective crop monitoring is essential for ensuring healthy growth and maximizing yields. Technologies involved include:
Challenge 1: Farmers often struggle with managing and analyzing vast amounts of data from various sources, such as weather reports, soil conditions, and crop health assessments.
Solution: Digital technologies like data analytics platforms can process and analyze this data efficiently. Machine learning algorithms can identify patterns and provide actionable insights, enabling farmers to make informed decisions based on real-time data.
Challenge 2: Efficiently managing resources such as water, fertilizers, and pesticides can be difficult, leading to overuse or underuse, which can harm both crops and the environment.
Solution: Precision agriculture technologies, including IoT sensors and drone monitoring, allow for real-time tracking of resource levels. This enables farmers to apply inputs more accurately, optimizing usage and reducing waste.
Challenge 3: Early detection of pests and diseases is critical, but traditional methods can be slow and reactive.
Solution: Digital platforms using remote sensing and machine learning can analyze data from fields to detect early signs of pest infestations or disease outbreaks. This allows for timely interventions, minimizing crop loss.
Challenge 4: Climate change poses significant risks to agriculture, including unpredictable weather patterns, droughts, and flooding.
Solution: Digital technologies can provide weather forecasting tools and climate modeling, helping farmers anticipate adverse conditions and adjust their practices accordingly. This includes planning for crop varieties that are more resilient to climate impacts.
Challenge 5: Maintaining healthy soil is vital for crop productivity, but monitoring soil health can be complex and time-consuming.
Solution: Soil sensors and data analytics can provide real-time information on soil moisture, pH, and nutrient levels. This information helps farmers make informed decisions about fertilization and irrigation practices, promoting better soil health.
Challenge 6: Many farmers face difficulties in accessing markets and ensuring their products meet regulatory requirements, leading to issues with traceability.
Solution: Digital platforms can enhance supply chain transparency by providing traceability features. Blockchain technology, for example, can track the journey of crops from farm to market, ensuring compliance and building consumer trust.
Challenge 7: Farmers may struggle to access markets and receive fair prices for their products due to lack of information and transparency.
Solution: Digital marketplaces can connect farmers directly with consumers and suppliers, providing better pricing information and reducing reliance on intermediaries. This can enhance market access and ensure farmers receive fair compensation for their produce.
Challenge 8: Navigating regulations related to sustainability and environmental standards can be complex and burdensome for farmers.
Solution: Digital tools can simplify compliance by automating record-keeping, monitoring practices, and generating reports required by regulatory bodies. This reduces the administrative burden and helps ensure adherence to standards.
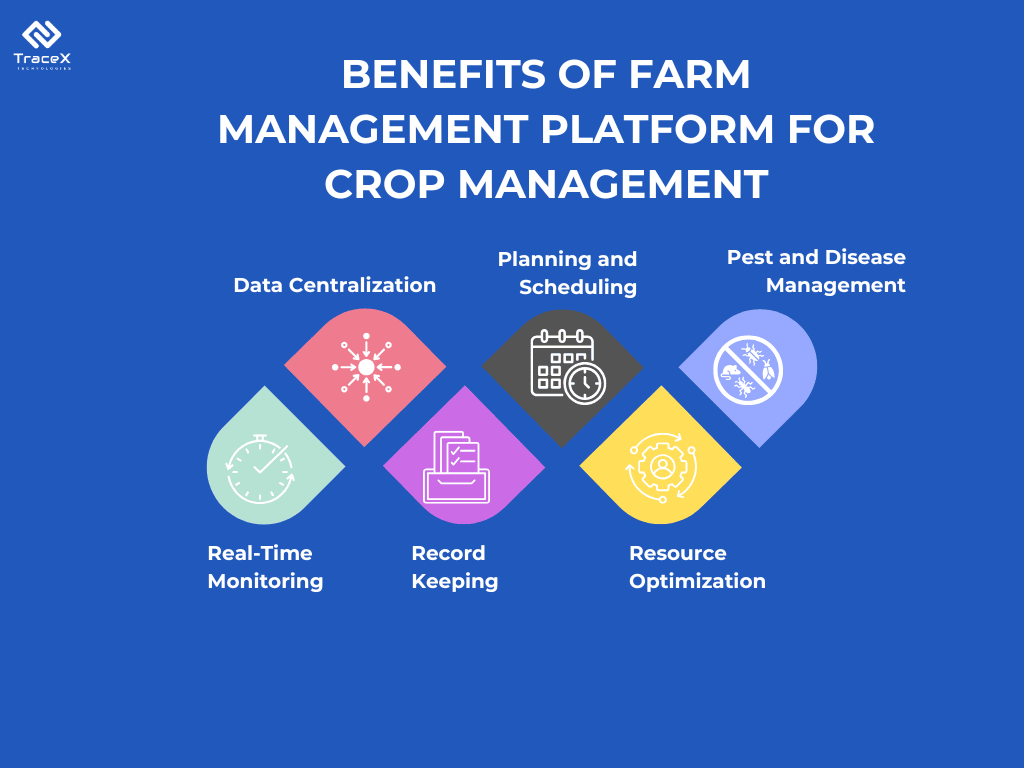
TraceX’s Farm management platform that leverages technology to address various challenges in agricultural production and sustainability.
Traceability: One of the standout features of TraceX is its focus on traceability throughout the supply chain. It enables farmers to track their products from seed to sale, ensuring transparency and accountability.
Sustainable Practices: TraceX promotes sustainable agricultural practices by providing insights and recommendations based on data analysis. Farmers can adopt climate-smart techniques, improve soil health, and enhance biodiversity through informed decision-making.
Real-Time Monitoring and Reporting: The platform offers real-time monitoring of crop health, soil conditions, and environmental factors. It also generates reports that help farmers understand their performance and identify areas for improvement.
Data Integration: TraceX integrates data from various sources, including satellite imagery, remote sensing, and IoT devices. This holistic approach provides a comprehensive view of farm operations, enabling better management decisions.
User-Friendly Interface: TraceX is designed with user experience in mind, making it accessible for farmers with varying levels of technological expertise. This encourages more widespread adoption of digital tools in agriculture.
Collaboration Tools: The platform facilitates collaboration among different stakeholders, such as farmers, agronomists, and supply chain partners. This enhances knowledge sharing and helps in developing best practices.
In conclusion, the integration of crop management technologies is crucial for advancing sustainable agriculture. By harnessing tools such as precision agriculture, data analytics, remote sensing, and smart farming practices, farmers can optimize resource usage, enhance crop yields, and mitigate environmental impacts. These technologies not only empower farmers to make data-driven decisions but also contribute to the overall sustainability of the agricultural sector. As we continue to face challenges such as climate change, resource scarcity, and food security, adopting innovative crop management solutions will be essential for ensuring a resilient and sustainable future for agriculture.
