Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Discover how the circular economy can drive sustainable business success. Learn how adopting circular practices can reduce costs, enhance resilience, and contribute to a greener future.

Imagine a world where waste isn’t just minimized, but virtually eliminated—where every product is designed to be reused, repurposed, or regenerated. This is the promise of the circular economy, a revolutionary approach to business that challenges the traditional “take, make, dispose” model. But for many businesses, the transition feels daunting, as they grapple with the inefficiencies and environmental damage of their current operations. The pain is real: escalating costs, resource scarcity, and growing consumer demand for sustainability are pushing companies to rethink their strategies.
According to IBEF, by 2030, India’s approach to developing a circular economy could create an annual worth of US$ 218 billion (Rs 14 lakh crores) and rise to US$ 624 billion (Rs 40 lakh crores) by 2050
In today’s world, where environmental concerns are at the forefront of global discourse, businesses are increasingly recognizing the need to shift from traditional linear models of production and consumption to more sustainable practices. One of the most promising and impactful approaches to achieving this is the circular economy.
Key Takeaways
At its core, the circular economy is a system designed to minimize waste and make the most of resources. It represents a fundamental shift in how we think about production and consumption, moving away from the traditional ‘take-make-dispose’ model towards one that is regenerative by design.
“The greatest threat to our planet is the belief that someone else will save it.”
– Robert Swan, Author
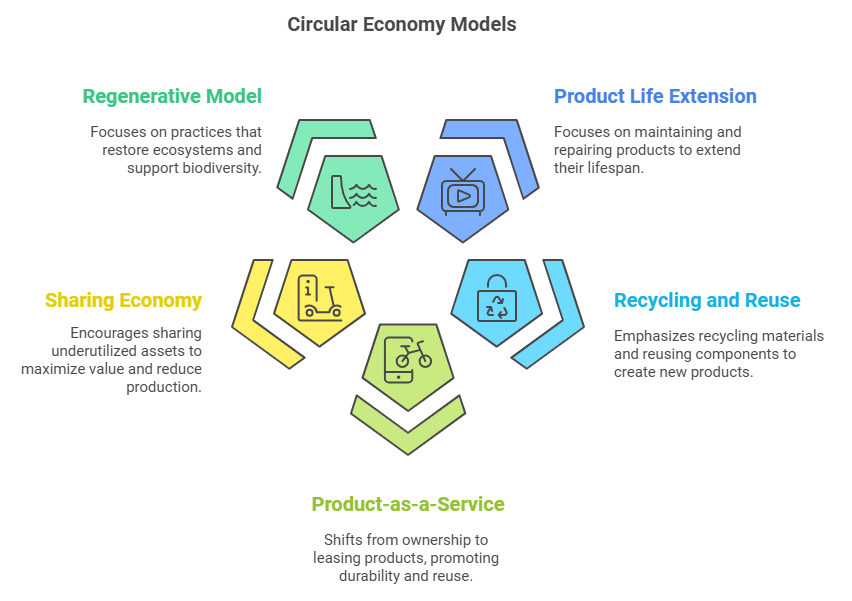
1. Designing out waste and pollution: Products and processes are designed with the intention of eliminating waste from the very beginning. This might involve using materials that are easily recyclable or biodegradable, or designing products that can be easily disassembled and reused.
2. Keeping products and materials in use: Instead of discarding products after use, the circular economy encourages businesses to find ways to keep materials in circulation. This could mean repairing or refurbishing products, recycling materials, or creating products that can be easily repurposed.
3. Regenerating natural systems: The circular economy goes beyond just reducing harm—it aims to have a positive impact on the environment. This involves using renewable resources, restoring ecosystems, and designing processes that contribute to the health of the planet.
Adopting a circular economy requires a fundamental revaluation of business strategy. Instead of a linear model focused on consumption and waste, a circular approach prioritizes resource efficiency, product longevity, and waste minimization. This necessitates a systemic shift in business operations, from product design to supply chain management.
The circular economy offers a wide range of benefits for businesses, society, and the environment.
One of the most significant benefits of the circular economy is its emphasis on resource efficiency. By reusing materials and designing products for longer life cycles, businesses can reduce their reliance on raw materials. This not only lowers costs but also helps to mitigate the risks associated with resource scarcity, which is becoming an increasingly pressing issue as the global population grows and demand for resources rises.
The circular economy plays a critical role in reducing environmental impact. By designing out waste and pollution, businesses can significantly decrease their carbon footprint and reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills. Additionally, by regenerating natural systems, the circular economy helps to restore ecosystems, promote biodiversity nurturing sustainable business practices and contributing to a healthier planet. This approach aligns with net-zero sustainability goals, enabling businesses to minimize greenhouse gas emissions and transition toward climate-neutral operations.
The transition to a circular economy opens up new economic opportunities for businesses. By developing innovative products and services that align with circular principles, companies can tap into new markets and meet the growing demand for sustainable goods. The circular economy also encourages the creation of new business models, such as product-as-a-service, where customers pay for the use of a product rather than owning it outright.
In an era where consumers are increasingly concerned about sustainability, businesses that embrace the circular economy can enhance their brand reputation. By demonstrating a commitment to sustainability, companies can build trust with customers, attract new audiences, and differentiate themselves from competitors.
The circular economy promotes resilience by reducing dependence on volatile raw material markets and supply chains. By keeping resources in use for longer and reducing the need for new materials, businesses can better weather market fluctuations and maintain stability in the face of economic uncertainty.
The world loses one-third of the food produced for human use. This equates to roughly 1.3 billion tonnes each year, or US$1 trillion.
In terms of the effect caused to the environment, the total food waste amounts rank as 3rd largest producer of carbon dioxide. Around 40% of such losses occur post-harvest and in processing. Today’s food system has an enormous social and environmental footprint starting from climate change to food waste, water availability to inequality and healthy living to biodiversity loss. USD 5.7 trillion costs are due to the linear nature of food production which utilizes finite resources, pollutes them and harms the natural systems.
Circular economy offers a vision for a fit future for all with a healthy food system. Circularity in agriculture is a system of regeneration that aims to minimize waste by making the most out of resources available. It aims to keep the supply chain in a closed loop of maximizing product life and reducing waste. It is performed through sustainable and natural modes of regeneration, in a way that by-products are reused in a different cycle to minimize inputs and reduce waste.
The circular economy promotes elimination of waste and use of natural resources that can yield up to $4.5 trillion in economic benefits to 2030.
Food waste can occur at every stage of the supply chain—from production and storage to distribution and consumption—due to factors like overproduction, improper storage, transportation losses, or unsold stock. This not only leads to resource waste but also contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. Efficient supply chain management can make a huge difference in cutting down waste. For example, improving logistics and cold storage can reduce spoilage, while accurate demand forecasting helps ensure the right amount of food is produced and distributed. Additionally, technologies like waste tracking and data analytics provide visibility, enabling businesses to identify waste hotspots and take corrective action.
Sustainable packaging is key to building a circular economy, as it helps reduce waste and resource use. Traditional packaging often ends up as landfill waste or pollutes the environment, but sustainable alternatives can change that. Biodegradable, compostable, and reusable packaging materials break down naturally or can be reused, minimizing their environmental impact. Many companies are already embracing these innovations. For instance, some food brands have switched to compostable packaging for their products, while others offer reusable packaging that customers can return. These changes not only help the planet but also resonate with eco-conscious consumers.
Upcycling takes food by-products or waste that would otherwise be discarded and transforms them into new, higher-value products. It’s a great way to reduce food waste while creating something useful. For example, some companies turn spent grains from brewing beer into nutritious snacks, or make chips from leftover fruit pulp. Upcycling helps the environment by cutting down on landfill waste and conserving resources. Plus, businesses can unlock new revenue streams and appeal to eco-friendly consumers by upcycling. It’s a win-win for the planet and the economy!
Recycling and composting food waste are important parts of a circular economy. Instead of letting food scraps end up in landfills, these practices transform them into valuable resources. Composting, for example, turns food waste into nutrient-rich soil, which can improve soil health and support plant growth. This reduces waste and greenhouse gas emissions while helping agriculture. Many governments and businesses are also stepping up, offering incentives and policies to promote composting and food waste recycling, like tax breaks or grants, making it easier and more appealing to adopt these eco-friendly practices.
Technology plays a vital role in simplifying circular economy practices by enhancing transparency, efficiency, and accountability across supply chains, especially when it comes to traceability. Digital tools such as blockchain, IoT devices, and data analytics enable businesses to track the journey of products from raw materials to end-of-life recycling. This ensures that every stage of the product’s lifecycle is visible, promoting responsible sourcing, reducing waste, and maximizing resource reuse.
For example, traceability platforms using blockchain can verify if a product is sustainably produced or if materials are being recycled as promised. Real-time data and automated systems also allow companies to identify and address inefficiencies, reduce losses, and ensure compliance with circular economy regulations. By making the entire process more transparent and manageable, technology empowers businesses to adopt sustainable practices with greater ease and impact.
A leading spice processor based in Karnataka, India, with operations in Vietnam and Turkey, used TraceX’s Sustainability platform to enhance product authenticity and safety. Renowned for its commitment to quality and sustainability, the company leveraged TraceX’s solutions to ensure traceability across its supply chain, verifying the origin and quality of its spices. This helped the company maintain high standards, comply with regulatory requirements, and build trust with consumers, reinforcing its dedication to sustainable practices.
Technology also enhances traceability in waste management by enabling the tracking of waste from its generation to disposal or recycling. Digital tools provide real-time data on waste streams, ensuring that materials are properly handled, recycled, or disposed of according to environmental regulations
Many businesses around the world are already embracing the circular economy and demonstrating its potential to drive sustainability and innovation.
Patagonia, the outdoor clothing company, has long been a leader in sustainable business practices. The company has embraced the circular economy by designing durable products that are built to last and offering repair services to extend the life of its products.
IKEA, the global furniture retailer, has committed to becoming a fully circular business by 2030. The company is redesigning its products to be more sustainable, using renewable and recycled materials, and offering services such as furniture leasing and buy-back programs.
The TraceX Sustainability platform is at the forefront of enabling the circular economy by harnessing the power of technology to create more transparent and efficient supply chains. With its blockchain-powered traceability solutions, TraceX allows businesses to verify the origin of materials, ensuring they are sustainably sourced and aligned with circular economy principles. This immutable ledger system enhances trust and accountability across the supply chain, from raw material extraction to end-of-life management. Additionally, TraceX’s advanced data analytics tools help companies identify key opportunities for waste reduction and resource efficiency, allowing them to optimize processes and minimize their environmental impact. By providing a comprehensive and integrated platform, TraceX empowers businesses to embrace the circular economy, drive sustainability, and build a more resilient and responsible future.
In conclusion, adopting a circular economy approach is not just a trend—it’s a strategic necessity for businesses aiming to thrive in a resource-constrained world. By embracing principles that prioritize reuse, regeneration, and sustainable resource management, companies can reduce costs, mitigate risks, and unlock new opportunities for innovation. The transition may be challenging, but the rewards are substantial: a more resilient business model, enhanced brand reputation, and a significant contribution to a more sustainable future. Now is the time for businesses to lead the way in the circular economy, turning challenges into opportunities and paving the path to long-term success.
A circular economy focuses on minimizing waste and making the most of available resources. In a sustainable business, it involves designing products and processes that extend product life, encourage reuse, and ensure materials are recycled or regenerated. This approach reduces environmental impact, conserves resources, and promotes long-term economic viability by closing the loop on product lifecycles.
Businesses can transition to a circular economy model by adopting strategies such as redesigning products for longevity, implementing recycling programs, and shifting from ownership to access (e.g., leasing or sharing). Companies should also track their materials and waste flows, engage with stakeholders, and invest in technologies like blockchain and IoT to ensure efficient resource management and traceability.
Adopting a circular economy can lead to significant cost savings through resource optimization, waste reduction, and improved operational efficiency. It can also open new revenue streams, such as selling refurbished products, offering repair services, or providing products-as-a-service. Additionally, businesses that embrace circular principles are better positioned to meet regulatory requirements and appeal to consumers who prioritize sustainability, enhancing brand reputation and market share.
