Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Learn about carbon neutrality standards, their importance for businesses, and how to achieve compliance. Explore key frameworks, challenges, and the role of technology in meeting climate goals.
As the climate crisis intensifies, businesses around the world are under increasing pressure to reduce their carbon footprints and achieve carbon neutrality. But with a growing number of carbon neutrality standards and frameworks available, how can organizations be sure they are meeting their environmental goals effectively? Many businesses face the challenges of navigating complex, often confusing regulations while trying to meet sustainability targets, all while maintaining operational efficiency and profitability.
This guide aims to cut through the noise, offering businesses a clear roadmap to understanding and implementing carbon neutrality standards, ensuring that their sustainability efforts are aligned with global expectations and deliver real, measurable impact. Let’s dive into what carbon neutrality means, the key standards that businesses need to consider, and how to stay ahead in the race to mitigate climate change.
Key Takeaways
As global temperatures continue to rise, the urgency for organizations to cut down on their carbon emissions is at an all-time high. Consumers, investors, and governments are demanding more from businesses when it comes to sustainability. Those that fail to act risk not only harming the environment but also jeopardizing their reputation and market position. Companies that take proactive steps towards carbon neutrality position themselves as leaders in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
Aligning with global climate goals like the Paris Agreement is more than just a responsible choice—it’s an essential step in mitigating climate change. The Paris Agreement aims to limit global warming to below 2°C, with efforts to cap it at 1.5°C. Achieving carbon neutrality is a key component of this global effort. By reducing emissions to net-zero, businesses contribute to a larger movement aimed at stabilizing the Earth’s climate, helping avoid catastrophic environmental consequences. It’s a win-win for both the planet and a company’s long-term success.
Carbon neutrality standards play a crucial role in this journey. They provide businesses with clear frameworks and measurable goals to track their progress. These standards, such as those set by the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi) or the Greenhouse Gas Protocol, ensure that a company’s efforts are transparent, credible, and in line with international expectations. By following these guidelines, businesses can reduce their carbon emissions effectively, offset the remaining emissions, and demonstrate to stakeholders that they are truly committed to sustainability.
In short, pursuing carbon neutrality isn’t just about meeting regulatory requirements—it’s about taking meaningful action for the planet’s future, improving business resilience, and staying ahead in an evolving market.
Carbon neutrality standards provide a structured approach for businesses, organizations, and governments to measure, reduce, and offset their greenhouse gas emissions in a way that leads to “net-zero” emissions. Simply put, these standards help entities track their carbon footprints and ensure they balance out the emissions they can’t eliminate by compensating for them through offsets or other corrective actions.
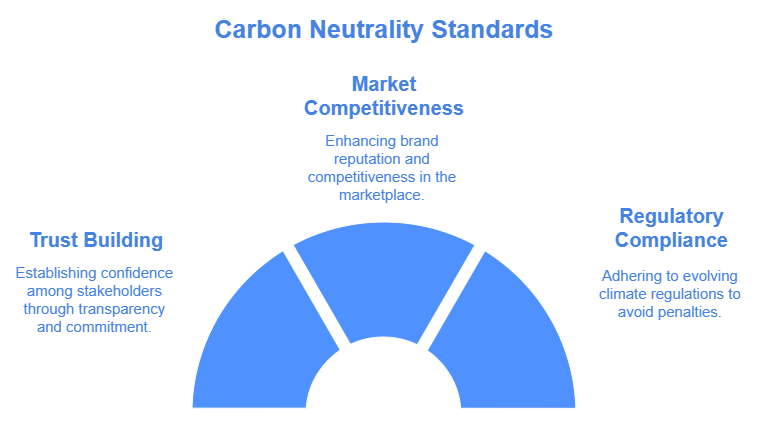
The main objectives of carbon neutrality standards are to set clear guidelines that drive transparency and accountability, enabling businesses to take responsible action towards achieving net zero sustainability goals. By following these standards, companies can demonstrate their commitment to reducing their environmental impact and play a role in mitigating global climate change.
The pathway to carbon neutrality is built on three fundamental principles:
Several carbon neutrality standards are globally recognized and provide frameworks that businesses can adopt. Here are a few key examples:
By adhering to these standards, businesses can not only track and reduce their carbon emissions but also gain credibility by aligning with widely accepted global benchmarks.
Achieving carbon neutrality isn’t just about measuring emissions; it’s a comprehensive process that involves measurement, reduction, offsetting, and verification. Here’s a breakdown of the key components of carbon neutrality standards:
Accurately measuring your carbon emissions is the first crucial step toward neutrality. You need to know the scope and scale of your emissions before you can manage them effectively.
Once you know your carbon footprint, the next step is reducing emissions wherever possible.
Even with rigorous reduction strategies, there will always be some emissions that can’t be eliminated immediately. This is where carbon offsetting comes in.
For carbon neutrality claims to be credible, transparency and third-party validation are essential.
Technology plays a crucial role in helping businesses meet carbon neutrality standards, offering tools that make tracking, managing, and reducing carbon emissions easier and more efficient.
One of the most exciting technologies in carbon neutrality is blockchain. It offers a transparent, immutable way to track emissions and verify sustainability claims across complex supply chains. Blockchain ensures that every step of a product’s lifecycle—from raw material sourcing to final delivery—can be traced for its carbon footprint.
TraceX’s DMRV Platform uses blockchain to create tamper-proof records of carbon emissions, providing businesses with a reliable way to demonstrate their sustainability efforts. Blockchain ensures that data cannot be altered, giving both businesses and consumers confidence that claims about carbon neutrality are genuine. This technology is particularly useful for tracking carbon credits and ensuring that offsetting projects are legitimate.
Another breakthrough in emissions management comes from Internet of Things (IoT) devices and satellite monitoring. These tools allow businesses to track emissions in real time, providing valuable insights into their environmental impact. IoT devices can be placed on factory equipment, vehicles, and other machinery to monitor energy usage and emissions. Satellite technology, on the other hand, helps track carbon emissions from entire regions, such as deforestation or large-scale industrial activities.
For instance, satellites can monitor emissions from power plants or agricultural operations, providing real-time data on CO2 levels. Companies can then use this data to identify problem areas, adjust operations, and improve their carbon footprint. The use of these technologies significantly reduces the time needed for emissions tracking, allowing businesses to react quickly and make more informed decisions.
Managing carbon emissions can be overwhelming, especially for large organizations with multiple operations and supply chains. Carbon management platforms help automate the process of tracking and reporting emissions, making compliance with carbon neutrality standards much more manageable.
These platforms allow businesses to collect, analyze, and report on their emissions automatically. They also generate reports that can be submitted to regulatory bodies, ensuring transparency and helping businesses stay compliant with carbon neutrality standards.
As global pressures to reduce carbon emissions rise, aligning with recognized carbon neutrality standards becomes an essential step toward meeting climate goals. The process involves measuring emissions, reducing them through strategic changes, and offsetting what cannot be eliminated.
While challenges such as high costs and complex global supply chains exist, the role of technology in making this journey smoother cannot be overstated. From blockchain for traceability to real-time emissions tracking using IoT and satellite monitoring, technology offers businesses powerful tools to make accurate, transparent decisions.
By understanding and implementing carbon neutrality standards, businesses not only reduce their environmental impact but also build trust with consumers, investors, and regulators. Ultimately, committing to these standards is a strategic decision that benefits both the planet and the bottom line.
Carbon neutrality standards provide guidelines for measuring, reducing, and offsetting greenhouse gas emissions to achieve net-zero impact.
Adopting these standards builds credibility, enhances competitiveness, and ensures regulatory compliance while contributing to climate goals.
Businesses can use carbon management platforms, blockchain for transparency, and IoT for real-time emissions tracking to meet standards efficiently.
