Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Discover how food waste recycling and composting can help reduce environmental impact, improve soil health, and contribute to a more sustainable food system. Learn the benefits and actions businesses and consumers can take.

Did you know that nearly 1/3 of all food produced globally is wasted every year? That’s about 1.3 billion tons of food that ends up in landfills, where it contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. This massive waste problem doesn’t just impact the environment but also exacerbates resource depletion. Food waste recycling and composting are emerging as vital strategies to combat this issue
In fact, food waste accounts for approximately 8% of global carbon emissions, making it one of the largest contributors to climate change (FAO, 2019).
As food continues to be wasted at such alarming rates, the environmental toll grows, placing even more pressure on our already strained resources. Food waste recycling and composting practices not only divert food waste from landfills, reducing harmful emissions, but they also contribute to building a circular economy by turning organic waste into valuable resources. Whether it’s creating nutrient-rich compost to enrich soils or converting food scraps into biogas, recycling and composting offer effective, sustainable solutions to a growing global problem. Let’s explore how these practices are transforming the food system for the better.
Key Takeaways
Food waste is a significant environmental issue that contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, particularly methane, which has a much greater warming potential than carbon dioxide.
When food waste ends up in landfills, it decomposes anaerobically, meaning it breaks down without oxygen. This process produces methane, a potent greenhouse gas that is about 28 times more effective at trapping heat in the atmosphere than carbon dioxide over a 100-year period.
According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), food waste accounts for roughly 24% of methane emissions from landfills.
In 2020 alone, food waste generated approximately 55 million metric tons of CO2 equivalent emissions from U.S. landfills. This alarming statistic highlights the urgent need to divert food waste from landfills to mitigate its environmental impact.
The problem of food waste extends beyond just what we see in landfills. Consider the vast resources that go into producing food that ultimately gets thrown away:
The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) emphasizes that reducing food waste is critical not only for the environment but also for conserving these valuable resources.
The environmental cost of food waste is intricately linked to the larger climate crisis. As we face increasing temperatures and extreme weather events, the inefficiencies in our food systems become even more pronounced.
The United Nations estimates that around 1.3 billion tons of food are wasted globally each year, contributing to 8-10% of global greenhouse gas emissions—equivalent to emissions from the entire aviation industry.
To combat climate change effectively, we must prioritize solutions that reduce food waste at every stage of the supply chain—from production to consumption. This includes better planning, improved storage techniques, consumer education, and innovative recycling methods like composting.
Definition and Process: Food waste recycling and composting are processes that help divert organic waste from landfills and turn it into useful, eco-friendly products. Composting is the process of breaking down food scraps, yard waste, and other organic materials into rich, dark, nutrient-filled humus. This humus, also known as compost, can be used to enrich soil, promoting healthier plant growth. On the other hand, food waste recycling often refers to the conversion of food scraps into bioenergy, like biogas, through anaerobic digestion. This process not only reduces waste but also generates energy from organic matter. Food waste recycling and composting are pivotal components in driving the circular economy, where resources are kept in use for as long as possible, and waste is minimized
Types of Food Waste: Food waste can be broadly categorized into two types: organic and non-organic.
Source: According to the Food Recovery Hierarchy by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), composting ranks high as one of the most effective ways to handle food waste, as it prevents organic material from ending up in landfills where it would release harmful methane.
Composting plays a vital role in circular agriculture by closing nutrient loops and reducing reliance on external chemical inputs. Circular agriculture emphasizes resource efficiency and sustainability, where waste from one part of the system is used to regenerate or enhance another.
Benefits of Composting: Composting has numerous environmental benefits, including:
Composting and recycling food waste not only cut down on greenhouse gas emissions but also contribute to healthier ecosystems and more sustainable agricultural practices. As the EPA highlights, incorporating these practices into daily life is a critical step towards reducing environmental impacts and creating more sustainable food systems.
1. Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions: One of the most significant benefits of food waste recycling and composting is the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, particularly methane. When food waste ends up in landfills, it decomposes anaerobically (without oxygen), producing methane, a potent greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change. By diverting food scraps from landfills and composting them instead, this harmful gas is significantly reduced. A study by the University of California found that composting food waste can reduce carbon emissions, making it an important strategy for mitigating climate change.
2. Soil Enrichment: Composting is an excellent way to improve soil health and fertility. The nutrient-rich compost created from food scraps adds organic matter to the soil, which enhances its structure and supports plant growth. The Soil Association reports that compost can not only improve soil structure but also increase its ability to retain water and provide essential nutrients to plants, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers. This leads to healthier crops and supports sustainable farm management
3. Water and Resource Conservation: Composting also helps conserve water, a precious resource. The organic material in compost retains moisture, reducing the need for frequent irrigation. Additionally, by replacing chemical fertilizers with compost, the soil becomes more efficient in its use of water. This is especially crucial in areas facing water scarcity. According to studies, composting also reduces the dependency on pesticides and chemical fertilizers, which can be harmful to the environment and the health of agricultural workers.
4. Economic Benefits: Food waste recycling and composting can provide significant economic advantages for businesses. For food production companies, agriculture operations, and waste management sectors, these practices can reduce waste disposal costs and even create new revenue streams. By selling the compost produced, businesses can generate income while simultaneously reducing waste. As more industries and communities embrace composting, the demand for high-quality, organic compost will likely grow, creating a sustainable market for these products.
Overall, food waste recycling and composting not only benefit the environment by reducing waste and greenhouse gas emissions but also offer financial advantages to businesses, enhance agricultural practices, and promote resource conservation.
In the context of food waste recycling and composting, blockchain traceability can play a critical role in ensuring transparency, accountability, and efficiency across the entire process. By leveraging blockchain technology, stakeholders—from businesses to consumers—can track and verify the journey of food waste and compost, ensuring that recycling and composting efforts are being handled properly, sustainably, and responsibly.
Blockchain allows for real-time tracking of food waste as it moves through the recycling process. Every step—from food collection in commercial kitchens to sorting and processing in recycling facilities—can be logged on a blockchain. This transparency helps businesses verify that food scraps are indeed being diverted from landfills and processed for composting or other sustainable uses. It also ensures that food waste isn’t “lost” or mismanaged during the transfer to recycling facilities, as each transaction or movement is recorded securely on the blockchain.
For businesses engaged in food waste recycling, ensuring compliance with regulations and quality standards is crucial. Blockchain systems can provide a secure and immutable record of compliance, verifying that all food waste is handled according to regulatory standards for composting or bioenergy production. For instance, companies can document that their food waste is sent to certified composting facilities, where it is processed according to sustainable standards. This can help businesses demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and reduce the risk of environmental violations or inefficiencies.
Consumers can also play a role in food waste recycling. By using blockchain-powered apps or platforms, they can track their own food waste and composting efforts. These platforms can allow consumers to register food waste disposal actions, monitor how much waste they are generating, and check if their waste is being processed sustainably. For example, blockchain-based platforms could let users track the amount of food waste sent for composting and even reward them with eco-points or incentives for their contributions to sustainability.
Blockchain enables the creation of circular food systems by tracking not just waste but the reuse of recycled materials. Once food waste is composted and turned into valuable organic matter, blockchain can track how that compost is used in agriculture or landscaping. This provides a fully traceable supply chain, ensuring that the compost is applied to improve soil health and reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers. Such transparency supports businesses and consumers by proving the benefits of food waste recycling and composting to the environment.
By recording all food waste transactions and composting processes on a blockchain, businesses and consumers can analyze trends, measure the efficiency of their recycling programs, and identify areas for improvement. Blockchain’s ability to store vast amounts of data securely and immutably allows for long-term tracking of sustainability efforts, ensuring that progress is being made in reducing food waste and enhancing recycling programs.
TraceX Food Traceability Platform is a robust, blockchain-based solution designed to provide complete transparency and accountability in the food supply chain. By enabling real-time tracking of food products from origin to consumer, TraceX ensures that every step of the food’s journey is recorded securely and immutably. This helps businesses, regulators, and consumers verify the authenticity and sustainability of food products. With TraceX, companies can ensure compliance with global regulations like the EU Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) and demonstrate their commitment to sustainability through verified data on sourcing practices, food waste recycling, and more. The platform enhances trust across the supply chain, mitigates risks related to fraud or contamination, and supports a circular food economy by tracking the reuse and recycling of materials.
Incorporating food waste recycling and composting into everyday practices is crucial for combating climate change, reducing landfill waste, and conserving valuable resources. By adopting these methods, businesses and consumers can play an active role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions, enhancing soil fertility, and supporting a circular economy. The environmental and economic benefits of these practices make them essential components of a sustainable food system, where waste is minimized, resources are optimized, and the planet thrives.
Food waste recycling helps divert waste from landfills, reducing methane emissions, a potent greenhouse gas. Composting also enriches soil health, supports sustainable farming, and reduces the need for chemical fertilizers.
Composting improves soil structure, enhances water retention, and boosts nutrient content, which supports healthy plant growth and reduces dependency on synthetic fertilizers.
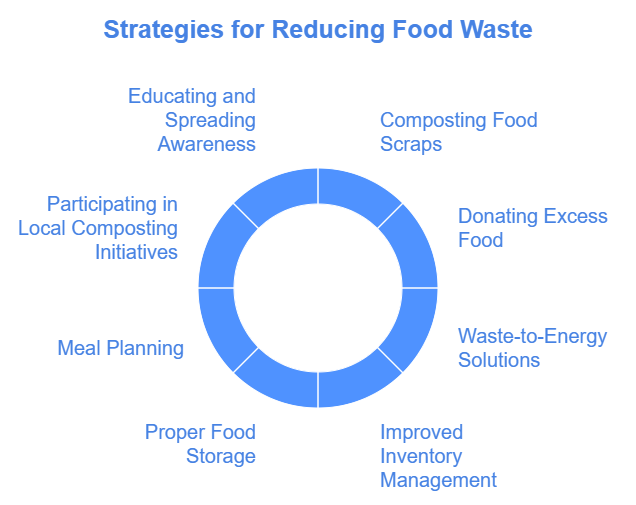
Businesses can adopt practices like composting food scraps, donating excess food, and utilizing waste-to-energy solutions to reduce their environmental footprint and improve sustainability.
